iOS 使用UIBezierPath类实现随手画画板
在上一篇文章中我介绍了 UIBezierPath类 介绍 ,下面这篇文章介绍一下如何通过这个类实现一个简单的随手画画板的简单程序demo,功能包括:划线(可以调整线条粗细,颜色),撤销笔画,回撤笔画,清除画布,橡皮擦。当然也可以扩展其他的功能。

一、首先看看实现划线部分的关键代码吧!
- (void) drawRect: (CGRect) rect
{
//绘制图片
int width = self.pickedImage.size.width;
int height = self.pickedImage.size.height;
CGRect rectForImage = CGRectMake(0,0, width, height);
[self.pickedImage drawInRect:rectForImage];
if (self.arrayStrokes)
{
int arraynum = 0;
// each iteration draw a stroke
// line segments within a single stroke (path) has the same color and line width
for (NSDictionary *dictStroke in self.arrayStrokes)
{
NSArray *arrayPointsInstroke = [dictStroke objectForKey:@"points"];
UIColor *color = [dictStroke objectForKey:@"color"];
float size = [[dictStroke objectForKey:@"size"] floatValue];
[color set]; // Sets the color of subsequent stroke and fill operations to the color that the receiver represents.
// draw the stroke, line by line, with rounded joints
UIBezierPath* pathLines = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
CGPoint pointStart = CGPointFromString([arrayPointsInstroke objectAtIndex:0]);
[pathLines moveToPoint:pointStart];
for (int i = 0; i < (arrayPointsInstroke.count - 1); i++)
{
CGPoint pointNext = CGPointFromString([arrayPointsInstroke objectAtIndex:i+1]);
[pathLines addLineToPoint:pointNext];
}
pathLines.lineWidth = size;
pathLines.lineJoinStyle = kCGLineJoinRound; //拐角的处理
pathLines.lineCapStyle = kCGLineCapRound; //最后点的处理
[pathLines stroke];
arraynum++;//统计笔画数量
}
}
}
// Start new dictionary for each touch, with points and color
- (void) touchesBegan:(NSSet *) touches withEvent:(UIEvent *) event
{
NSMutableArray *arrayPointsInStroke = [NSMutableArray array]; //点数组,相当于一个笔画
NSMutableDictionary *dictStroke = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
[dictStroke setObject:arrayPointsInStroke forKey:@"points"];
[dictStroke setObject:self.currentColor forKey:@"color"];
[dictStroke setObject:[NSNumber numberWithFloat:self.currentSize] forKey:@"size"];
CGPoint point = [[touches anyObject] locationInView:self];
[arrayPointsInStroke addObject:NSStringFromCGPoint(point)];
[self.arrayStrokes addObject:dictStroke];//添加的是一个字典:点数组,颜色,粗细
}
// Add each point to points array
- (void) touchesMoved:(NSSet *) touches withEvent:(UIEvent *) event
{
CGPoint point = [[touches anyObject] locationInView:self];
CGPoint prevPoint = [[touches anyObject] previousLocationInView:self];
NSMutableArray *arrayPointsInStroke = [[self.arrayStrokes lastObject] objectForKey:@"points"];
[arrayPointsInStroke addObject:NSStringFromCGPoint(point)];
CGRect rectToRedraw = CGRectMake(\
((prevPoint.x>point.x)?point.x:prevPoint.x)-currentSize,\
((prevPoint.y>point.y)?point.y:prevPoint.y)-currentSize,\
fabs(point.x-prevPoint.x)+2*currentSize,\
fabs(point.y-prevPoint.y)+2*currentSize\
);
//Marks the specified rectangle of the receiver as needing to be redrawn.
//在指定的rect范围进行重绘
[self setNeedsDisplayInRect:rectToRedraw];
// [self setNeedsDisplay];
}
这里简单的说明介绍吧!
1、使用一个数组 arrayStrokes(称之为笔画数组) 来记录整一幅画,这个数组中保存的是一个个的字典,而这些字典就是这幅画中的每一笔画(而且是有顺序的),字典中有三项内容:包括笔画的size,color还有一个数组arrayPointsInStroke,注意:这个数组保存的touch begin和move过程中经过的点的坐标(这些点统统用直线连接起来,就可以形成一个笔画了。当然,这个数组中是保存了好多个点的!所以连接起来笔画还是很逼真的!)。
2、那么在绘制的时候,就要用到 arrayStrokes 这个关键的数组了,从里面拿出每一个字典(一个字典就是代表一个笔画),根据字典中笔画的size,color和笔画所经过的点坐标,那么让UIBezierPath这个类来完成笔画的绘制就很简单了。
这样应该可以理解吧!
二、笔画的撤销和回撤的实现
我们知道每一个笔画都是通过一个字典来保存的,那么我们在画线的过程中对笔画的撤销和回撤那也就很简单了吧!
我们可以使用另一个数组 arrayAbandonedStrokes (称之为废弃数组)来保存我们所撤销的笔画,而撤销,肯定是我们所有笔画中的最后一划,所以我们在arrayAbandonedStrokes 废弃数组保存 arrayStrokes 笔画数组中的最后一个元素,同时将 arrayStrokes 笔画数组中的最后一个元素删除。这样就可以实现笔画的撤销。
反之,就是实现回撤了。即将废弃数组中的最后一个元素添加到笔画数组中,同时将废弃数组中的最后一个元素删除。
实现的代码如下:
//撤销
-(IBAction) undo {
if ([arrayStrokes count]>0) {
NSMutableDictionary* dictAbandonedStroke = [arrayStrokes lastObject];
[self.arrayAbandonedStrokes addObject:dictAbandonedStroke];
[self.arrayStrokes removeLastObject];
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
}
//回撤
-(IBAction) redo {
if ([arrayAbandonedStrokes count]>0) {
NSMutableDictionary* dictReusedStroke = [arrayAbandonedStrokes lastObject];
[self.arrayStrokes addObject:dictReusedStroke];
[self.arrayAbandonedStrokes removeLastObject];
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
}
三、清楚画布的功能实现
//清除画布
-(IBAction) clearCanvas {
self.pickedImage = nil;
[self.arrayStrokes removeAllObjects];
[self.arrayAbandonedStrokes removeAllObjects];
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
四、笔画颜色的选择
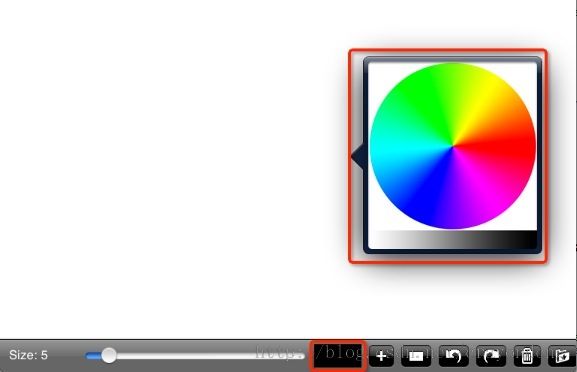
这里的处理是用到一个弹出框,点击可以选择颜色。
下面讲一下如何实现这个颜色选择器。其中参考自:点击打开链接
实现原理:弹出框中显示的是一张图片,我们通过一个函数处理,获取到这个图片的所有像素点的透明度和RGB(每一个值占1Byte)数据(是一个数组),然后通过点击获取到点的坐标,就可以获取到这个像素点的透明度和RGB值了。
实现的有关代码如下:
- (void) touchesEnded:(NSSet*)touches withEvent:(UIEvent*)event {
UITouch* touch = [touches anyObject];
CGPoint point = [touch locationInView:self.imgView]; //where image was tapped
lastColor = [self getPixelColorAtLocation:point];
[pickedColorDelegate pickedColor:(UIColor*)lastColor];
}
// Please refer to iOS Developer Library for more details regarding the following two methods
- (UIColor*) getPixelColorAtLocation:(CGPoint)point {
UIColor* color = nil;
CGImageRef inImage = self.imgView.image.CGImage;
// Create off screen bitmap context to draw the image into. Format ARGB is 4 bytes for each pixel: Alpa, Red, Green, Blue
CGContextRef contexRef = [self createARGBBitmapContext:inImage];
if (contexRef == NULL) { return nil; /* error */ }
size_t w = CGImageGetWidth(inImage); // problem!
size_t h = CGImageGetHeight(inImage);
CGRect rect = {{0,0},{w,h}};
// Draw the image to the bitmap context. Once we draw, the memory
// allocated for the context for rendering will then contain the
// raw image data in the specified color space.
CGContextDrawImage(contexRef, rect, inImage);
// Now we can get a pointer to the image data associated with the bitmap
// context.
unsigned char* data = CGBitmapContextGetData (contexRef);
if (data != NULL) {
//offset locates the pixel in the data from x,y.
//4 for 4 bytes of data per pixel, w is width of one row of data.
int offset = 4*((w*round(point.y))+round(point.x)); //这是一个二维数组,offset是确定数组下标
int alpha = data[offset];
int red = data[offset+1];
int green = data[offset+2];
int blue = data[offset+3];
NSLog(@"offset: %i colors: RGB A %i %i %i %i",offset,red,green,blue,alpha);
color = [UIColor colorWithRed:(red/255.0f) green:(green/255.0f) blue:(blue/255.0f) alpha:(alpha/255.0f)];
}
// When finished, release the context
CGContextRelease(contexRef);
// Free image data memory for the context
if (data) { free(data); }
return color;
}
- (CGContextRef) createARGBBitmapContext:(CGImageRef) inImage {
CGContextRef context = NULL;
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace;
void * bitmapData;
int bitmapByteCount;
int bitmapBytesPerRow;
// Get image width, height. We'll use the entire image.
size_t pixelsWide = CGImageGetWidth(inImage);
size_t pixelsHigh = CGImageGetHeight(inImage);
// Declare the number of bytes per row. Each pixel in the bitmap in this
// example is represented by 4 bytes; 8 bits each of red, green, blue, and
// alpha.
bitmapBytesPerRow = (pixelsWide * 4);
bitmapByteCount = (bitmapBytesPerRow * pixelsHigh);
// Use the generic RGB color space.
//colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateWithName(kCGColorSpaceGenericRGB); //deprecated
colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
if (colorSpace == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error allocating color space\n");
return NULL;
}
// Allocate memory for image data. This is the destination in memory
// where any drawing to the bitmap context will be rendered.
bitmapData = malloc( bitmapByteCount );
if (bitmapData == NULL)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Memory not allocated!");
CGColorSpaceRelease( colorSpace );
return NULL;
}
// Create the bitmap context. We want pre-multiplied ARGB, 8-bits
// per component. Regardless of what the source image format is
// (CMYK, Grayscale, and so on) it will be converted over to the format
// specified here by CGBitmapContextCreate.
context = CGBitmapContextCreate (bitmapData,
pixelsWide,
pixelsHigh,
8, // bits per component
bitmapBytesPerRow,
colorSpace,
kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst);
if (context == NULL)
{
free (bitmapData);
fprintf (stderr, "Context not created!");
}
// Make sure and release colorspace before returning
CGColorSpaceRelease( colorSpace );
return context;
}