动态树之(雾)树链剖分
这货是不是动态树里的我就不清楚了,fhq的blog好像有提到orz
一些不需要link-cut操作的树上路径的题可以用树链剖分做,常数比lct小多了。 //upd:所以这已经不是动态树了囧。。。。。标题我就不改了。。。。。。还好原来机智打了个“雾”
学习了下hld(树链剖分),嗯,挺简单的。hld可以在树中的操作有很多,hld可以说只是一种概念结构,它可以套很多其它的数据结构来进行操作,比如我现在只要求路径最值和求和,那么套线段树就行了;如果我要求第k大,可以套splay和主席树(这个不知道),也可以套分块(不会,分块以后学,必须学。。)但是我觉得,树剖比lct还要难写。。我lct一下就能写出来了。。可是lct的常数,不忍直视。。概念:
重儿子:num[u]为v的子节点中num值最大的,那么u就是v的重儿子。
轻儿子:v的其它子节点。
重边:点v与其重儿子的连边。
轻边:点v与其轻儿子的连边。
重链:由重边连成的路径。
轻链:轻边。
剖分后的树有如下性质:
性质1:如果(v,u)为轻边,则siz[u] * 2 < siz[v];
性质2:从根到某一点的路径上轻链、重链的个数都不大于logn。
我们来说他怎么在路径操作吧:
下边是一个例图:黑边为重边,带红点的为重边组成的链的最顶点(没有重边的点最顶点就是它自己),蓝字为重边的序号
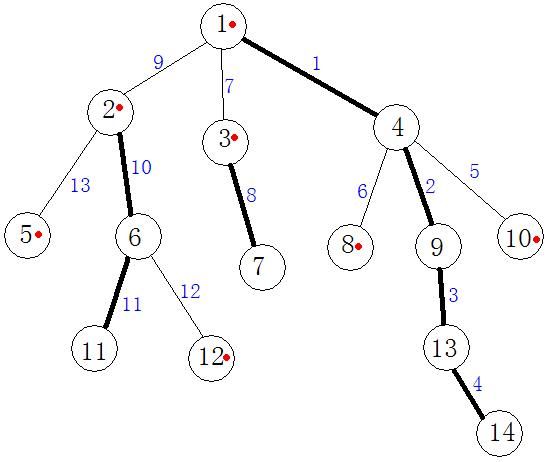
哈哈,发现了什么吗?
重链的序号是连续的。 不会有两条重链相交~~
哈哈?套各种树维护啦~~~。
我们在这个连续的区间操作就行了,然后不断向根走,直到走到最顶点相交(这里不是重链相交,是最顶点相交,即一条轻边和重边的交点)
向上走的时候,不是一个个走,那么效率大大提高啦~。。这就是树链剖分的主体思想。
我们在这些链(或点)重新标号后,用各种数据结构维护信息。
求树剖需要维护的域很简单,两个深搜搞定,大家自己想吧,我不说了(要是想不通,,点这:http://blog.csdn.net/jiangshibiao/article/details/24669751)
例题:
基于点分类:【BZOJ】1036: [ZJOI2008]树的统计Count(lct/树链剖分)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << "=" << x << endl
#define read(x) x=getint()
#define print(x) printf("%d", x)
#define lc x<<1
#define rc x<<1|1
#define lson l, m, lc
#define rson m+1, r, rc
#define MID (l+r)>>1
const int oo=~0u>>1;
inline int getint() { char c; int ret=0, k=1; for(c=getchar(); c<'0' || c>'9'; c=getchar()) if(c=='-') k=-1; for(; c>='0'&&c<='9'; c=getchar()) ret=ret*10+c-'0'; return k*ret; }
const int N=30010, M=100005;
int ihead[N], inext[M], to[M], cnt, n, m;
int top[N], son[N], fa[N], dep[N], sz[N], id[N], a[N], b[N], tot;
int L, R, key;
struct node { int mx, sum; }t[N*50];
inline const int max(const int& a, const int& b) { return a>b?a:b; }
inline void pushup(const int &x) { t[x].mx=max(t[lc].mx, t[rc].mx); t[x].sum=t[lc].sum+t[rc].sum; }
void dfs1(const int &u) {
sz[u]=1; int v;
for(int i=ihead[u]; i; i=inext[i]) if(fa[u]!=(v=to[i])) {
fa[v]=u;
dep[v]=dep[u]+1;
dfs1(v);
sz[u]+=sz[v];
if(sz[v]>sz[son[u]]) son[u]=v;
}
}
void dfs2(const int &u, const int &tp) {
id[u]=++tot; top[u]=tp; b[tot]=a[u];
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u], tp);
for(int i=ihead[u]; i; i=inext[i]) if(to[i]!=fa[u] && to[i]!=son[u]) dfs2(to[i], to[i]);
}
void build(const int &l, const int &r, const int &x) {
if(l==r) { t[x].mx=t[x].sum=b[l]; return; }
int m=MID;
build(lson); build(rson);
pushup(x);
}
void update(const int &l, const int &r, const int &x) {
if(l==r) { t[x].mx=t[x].sum=key; return; }
int m=MID;
if(L<=m) update(lson);
if(m<R) update(rson);
pushup(x);
}
int getmax(const int &l, const int &r, const int &x) {
if(L<=l && r<=R) return t[x].mx;
int m=MID, mx=oo+1;
if(L<=m) mx=max(mx, getmax(lson));
if(m<R) mx=max(mx, getmax(rson));
return mx;
}
int query(const int &l, const int &r, const int &x) {
if(L<=l && r<=R) return t[x].sum;
int m=MID, ret=0;
if(L<=m) ret+=query(lson);
if(m<R) ret+=query(rson);
return ret;
}
inline int getmax(int x, int y) {
int fx=top[x], fy=top[y], ret=oo+1;
while(fx!=fy) {
if(dep[fx]<dep[fy]) { swap(x, y); swap(fx, fy); }
L=id[fx], R=id[x];
ret=max(ret, getmax(1, n, 1));
x=fa[fx]; fx=top[x];
}
if(dep[x]>dep[y]) swap(x, y);
L=id[x], R=id[y];
return max(ret, getmax(1, n, 1));
}
inline int query(int x, int y) {
int fx=top[x], fy=top[y], ret=0;
while(fx!=fy) {
if(dep[fx]<dep[fy]) { swap(x, y); swap(fx, fy); }
L=id[fx], R=id[x];
ret+=query(1, n, 1);
x=fa[fx]; fx=top[x];
}
if(dep[x]>dep[y]) swap(x, y);
L=id[x], R=id[y];
return ret+query(1, n, 1);
}
inline void add(const int &u, const int &v) {
inext[++cnt]=ihead[u]; ihead[u]=cnt; to[cnt]=v;
inext[++cnt]=ihead[v]; ihead[v]=cnt; to[cnt]=u;
}
int main() {
read(n);
int u, v, ans;
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i) {
read(u); read(v);
add(u, v);
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) read(a[i]);
dfs1(1);
dfs2(1, 1);
build(1, n, 1);
char c[10];
read(m);
for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) {
scanf("%s", c);
if(c[0]=='C') {
read(u); read(key); L=R=id[u];
update(1, n, 1);
}
else if(c[0]=='Q') {
read(u); read(v);
if(c[1]=='M') ans=getmax(u, v);
else ans=query(u, v);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
基于边分类:【SPOJ】375. Query on a tree(树链剖分)
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define lc x<<1
#define rc x<<1|1
#define lson l, m, lc
#define rson m+1, r, rc
#define MID (l+r)>>1
#define read(x) x=getint()
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << "=" << x << endl
inline const int max(const int& a, const int& b) { return a>b?a:b; }
inline int getint() { char c; int ret=0, k=1; for(c=getchar(); c<'0' || c>'9'; c=getchar()) if(c=='-') k=-1; for(; c>='0' && c<='9'; c=getchar()) ret=ret*10+c-'0'; return k*ret; }
const int N=50010, oo=~0u>>1;
struct Ed { int u, v, w; }e[N];
int ihead[N], inext[N<<1], to[N<<1], cnt;
int fa[N], sz[N], son[N], top[N], dep[N], id[N], mx[N*5], num[N], tot, L, R, key, n;
inline void pushup(const int &x) { mx[x]=max(mx[lc], mx[rc]); }
void build(const int &l, const int &r, const int &x) {
if(l==r) { mx[x]=num[l]; return; }
int m=MID;
build(lson); build(rson);
pushup(x);
}
void update(const int &l, const int &r, const int &x) {
if(l==r) { mx[x]=key; return; }
int m=MID;
if(L<=m) update(lson); if(m<R) update(rson); pushup(x);
}
int getmax(const int &l, const int &r, const int &x) {
if(L<=l && r<=R) return mx[x];
int m=MID, ret=oo+1;
if(L<=m) ret=max(ret, getmax(lson)); if(m<R) ret=max(ret, getmax(rson)); return ret;
}
void dfs1(const int &u) {
sz[u]=1; int v;
for(int i=ihead[u]; i; i=inext[i]) if(fa[u]!=(v=to[i])) {
fa[v]=u; dep[v]=dep[u]+1;
dfs1(v);
sz[u]+=sz[v];
if(sz[v]>sz[son[u]]) son[u]=v;
}
}
void dfs2(const int &u, const int &tp) {
id[u]=++tot; top[u]=tp;
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u], tp);
for(int i=ihead[u]; i; i=inext[i]) if(fa[u]!=to[i] && to[i]!=son[u]) dfs2(to[i], to[i]);
}
inline int getmax(int x, int y) {
int fx=top[x], fy=top[y], ret=oo+1;
while(fx!=fy) {
if(dep[fx]<dep[fy]) { swap(x, y); swap(fx, fy); }
L=id[fx]; R=id[x];
ret=max(ret, getmax(2, n, 1));
x=fa[fx]; fx=top[x];
}
if(dep[x]>dep[y]) swap(x, y);
if(x!=y) L=id[x]+1; R=id[y]; //这里,如果不特判的话,L会>R,然后线段树那里果断死循环
return max(ret, getmax(2, n, 1));
}
inline void add(const int &u, const int &v) {
inext[++cnt]=ihead[u]; ihead[u]=cnt; to[cnt]=v;
inext[++cnt]=ihead[v]; ihead[v]=cnt; to[cnt]=u;
}
int main() {
int c=getint(), a, b; char ch;
while(c--) {
read(n);
tot=cnt=0;
memset(ihead, 0, sizeof(int)*(n+10));
memset(fa, 0, sizeof(int)*(n+10));
memset(son, 0, sizeof(int)*(n+10));
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i) {
read(e[i].u); read(e[i].v); read(e[i].w);
add(e[i].u, e[i].v);
}
dfs1(1); dfs2(1, 1);
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i) {
if(dep[e[i].u]>dep[e[i].v]) swap(e[i].u, e[i].v);
num[id[e[i].v]]=e[i].w;
}
build(2, n, 1);
for(ch=getchar(); ch<'A' || ch>'Z'; ch=getchar());
while(ch!='D') {
read(a); read(b);
if(ch=='C') { key=b; L=R=id[e[a].v]; update(2, n, 1); }
else printf("%d\n", getmax(a, b));
for(ch=getchar(); ch<'A' || ch>'Z'; ch=getchar());
}
}
return 0;
}