Leetcode | Wildcard Matching
Implement wildcard pattern matching with support for '?' and '*'.
'?' Matches any single character.
'*' Matches any sequence of characters (including the empty sequence).
The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
The function prototype should be:
bool isMatch(const char *s, const char *p)
Some examples:
isMatch("aa","a") → false
isMatch("aa","aa") → true
isMatch("aaa","aa") → false
isMatch("aa", "*") → true
isMatch("aa", "a*") → true
isMatch("ab", "?*") → true
isMatch("aab", "c*a*b") → false
递归的话会超时。
Method I
然后想用二维的DP。
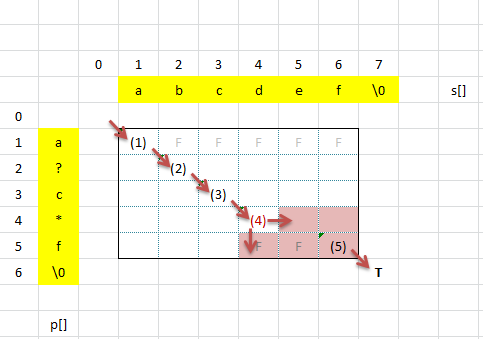
借用了discussion上面的图。m[i+1][j+1]就是p[0...i]与s[0...j]的匹配结果。
1. 如果p[i] = '?' 或者 p[i] = s[j] (暗含p[i] != '*'的意思),那么m[i+1][j+1]就是等于它的对角线左上方的位置, m[i][j]。也就是都移动了一个字符。
2. 如果p[i] = '*'。从图里面就可以看出来,从(3)走到(4),其实p[0...3]="a?c*"应该是能够匹配到s[0...j],2<=j<6。也就是说,m[4][3...6]=true;
就是从上一行找到第一个为true的位置,那么从当前行中从该位置到最后都应该设为true。
1 bool isMatch(const char *s, const char *p) { 2 if (p == '\0') return (s == '\0'); 3 int n1 = strlen(s); 4 int n2 = strlen(p); 5 6 vector<vector<bool> > m(n2 + 1, vector<bool>(n1 + 1, false)); 7 m[0][0] = true; 8 9 for (int i = 0; i < n2; ++i) { 10 if (p[i] == '*') { 11 int j = 0; 12 for (j = 0; j <= n1; ++j) { 13 if (m[i][j]) break; 14 } 15 if (j > n1) return false; 16 for (int k = j; k <= n1; ++k) { 17 m[i + 1][k] = true; 18 } 19 } else { 20 for (int j = 0; j < n1; ++j) { 21 if (p[i] == '?' || s[j] == p[i]) { 22 m[i + 1][j + 1] = m[i][j]; 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 28 return m[n2][n1]; 29 }
二维DP会报MLE,但是阿牧遥 用了一个dp[500][500]倒是可以通过。。。
优化
因为其实每次都是更新一行,可以将两维dp改成一维的dp。将上面的代码对应转换就行,不过要注意的是,不满足条件更新值的,需要设成默认值false;
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isMatch(const char *s, const char *p) { 4 if (p == '\0') return (s == '\0'); 5 int n1 = strlen(s); 6 int n2 = strlen(p); 7 int chars = 0; 8 for(int i=0; p[i] != '\0'; ++i) if(p[i] != '*' && n1<++chars) return false; 9 10 vector<bool> m(n1 + 1, false); 11 m[0] = true; 12 13 for (int i = 0; i < n2; ++i) { 14 if (p[i] == '*') { 15 int j = 0; 16 for (j = 0; j <= n1; ++j) { 17 if (m[j]) break; 18 } 19 for (; j <= n1; ++j) { 20 m[j] = true; 21 } 22 } else { 23 for (int j = n1 - 1; j >= 0; --j) { 24 if (p[i] == '?' || s[j] == p[i]) { 25 m[j + 1] = m[j]; 26 } else { 27 m[j + 1] = 0; 28 } 29 } 30 m[0] = false; 31 } 32 } 33 34 return m[n1]; 35 } 36 };
注意第8行,如果没有这一句就会TLE。主要是计算p里面的非*的字符,如果这个数目都比s的长度大,那么肯定匹配不完。直接返回true。这是为了过一个大数据。
Method II
遇到*的时候是可能需要回溯的。但是回溯是不是一定要回到回溯前的位置呢。比如s="aacb",p="a*a*b"。结果应该是为true的。
第一次遇到p[1]='*',从s[1]开始匹配,s[1]=p[2], 第二次遇到p[3] ='*',s[2]!=p[4],此路不通,要回溯,是不是要回溯到p[2]和s[2]呢,其实不用。
因为我们最后面撞见了p[3]='*',证明s[0...1]和p[0...2]是匹配的,那么直接从p[4]和s[3]回溯就可以了。p[4]=s[3],所以返回true。
因为遇到*都是先将*从区配空串开始的,所以当*把s都一直匹配到末尾有三种情况:
1. p后面还有,但是都是*,还是返回true;
2. p后面还有,但不全是*,返回false;
3. p后面没有,匹配刚刚好。
1 lass Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isMatch(const char *s, const char *p) { 4 if (p == '\0') return (s == '\0'); 5 6 const char *backP = NULL, *backS = NULL; 7 8 while (*s) { 9 if (*p == '*') { 10 while (*p != '\0' && *p == '*') p++; 11 if (*p == NULL) return true; 12 backS = s; 13 backP = p; 14 } else if (*s == *p || *p == '?') { 15 s++; p++; 16 } else if (backP) { 17 s = ++backS; 18 p = backP; 19 } else { 20 return false; 21 } 22 } 23 24 while (*p) { 25 if (*p != '*') return false; 26 p++; 27 } 28 29 return true; 30 } 31 };
这里第10行,是压缩了p连续*的情况。多个*相连其实相同于一个*。backP指向的*的下一个字符。backS就是从S当前的位置开始。
third time.
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isMatch(const char *s, const char *p) { 4 if (p == NULL || *p == '\0') return (s == NULL || *s == '\0'); 5 const char* lastS = NULL, *lastP = NULL; 6 7 while (*s != '\0') { 8 if (*p != '\0' && (*s == *p || *p == '?')) { 9 s++, p++; 10 } else if (*p == '*') { 11 for (; *p != '\0' && *p == '*'; p++); 12 lastP = p; 13 lastS = s; 14 } else if (lastP != NULL) { 15 p = lastP; 16 s = ++lastS; 17 } else { 18 break; 19 } 20 } 21 22 for (; *p != '\0' && *p == '*'; p++); 23 return *p == '\0' && *s == '\0'; 24 } 25 };