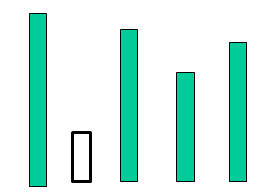LeetCode:Container With Most Water
LeetCode:Container With Most Water
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an, where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container.
算法1:枚举容器的两个边界,时间复杂度O(n^2)。大数据超时
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class
Solution {
public
:
int
maxArea(vector<
int
> &height) {
int
res = 0, n = height.size();
for
(
int
i = 0; i < n; i++)
//左边界
for
(
int
j = i+1; j < n; j++)
//右边界
{
int
tmp = (j-i)*min(height[i],height[j]);
if
(res < tmp)res = tmp;
}
return
res;
}
};
|
对上面的稍加改进,根据当前的已经计算出来的结果以及左边界的值,可以算出右边界下界。不过还是超时
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class
Solution {
public
:
int
maxArea(vector<
int
> &height) {
int
res = 0, n = height.size();
for
(
int
i = 0; i < n; i++)
//左边界
{
if
(height[i] == 0)
continue
;
for
(
int
j = max(i+1, res/height[i]+i); j < n; j++)
//右边界
{
int
tmp = (j-i)*min(height[i],height[j]);
if
(res < tmp)res = tmp;
}
}
return
res;
}
};
|
算法2:时间复杂度O(nlogn)。
构建结构体包含height和height在原数组中的位置
struct Node
{
int height;
int index;
};
对该结构体数组按照height的值递增排序,假设排序后的数组为vec.
假设f[i] 表示数组vec[i,i+1,…]内所有height按照原来的位置顺序排列好以后的最大水量
那么f[i-1]可以在O(1)时间内计算出来:因为vec[i-1].height 小于vec[i,i+1,…]内的所有height,所以以vec[i-1].index为边界的容器高度为vec[i-1].height,最大水量只需要分别计算vec[i,i+1,…]内按原始位置排列最前面和最后面的height,取两者的较大值。即下图中,黑色是最低的,要计算以黑色为边界的容器的最大水量,只需要分别和第一个和最后一个计算,去两者较大值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class
Solution {
struct
Node
{
int
height;
int
index;
Node(
int
h,
int
i):height(h),index(i){}
Node(){}
bool
operator < (
const
Node &a)
const
{
return
height < a.height;
}
};
public
:
int
maxArea(vector<
int
> &height) {
int
res = 0, n = height.size();
if
(n <= 1)
return
0;
vector<Node>vec(n);
for
(
int
i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
vec[i].index = i;
vec[i].height = height[i];
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
int
start = vec[n-1].index, end = start;
//记录已经处理完的height的原始位置的左右端点
for
(
int
i = n-2; i >= 0 ; i--)
{
start = min(start, vec[i].index);
end = max(end, vec[i].index);
res = max(res, max(vec[i].height*(vec[i].index - start), vec[i].height*(end - vec[i].index)));
}
return
res;
}
};
|
算法3:时间复杂度O(n),两个指针i, j分别从前后向中间移动,两个指针分别表示容器的左右边界。每次迭代用当前的容量更新最大容量,然后把高度小的边界对应的指针往中间移动一位。 本文地址
正确性证明:由于水的容量是有较小的那个边界决定的,因此某次迭代中,假设height[i] < height[j],那么j 减小肯定不会使水的容量增大,只有i 增加才有可能使水的容量增大。但是会不会有这种可能:当前的i 和 某个k (k > j)是最大容量, 这也是不可能的,因为按照我们的移动规则,既然右指针从k 移动到了j,说明i 的左边一定存在一个边界 m,使m > k,那么[m, k]的容量肯定大于[i, k],所以[i,k]不可能是最大容量。可以参考here
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class
Solution {
public
:
int
maxArea(vector<
int
> &height) {
int
res = 0, n = height.size();
int
left = 0, right = n-1;
while
(left < right)
{
res = max(res, (right-left)*min(height[left], height[right]));
if
(height[left] < height[right])
left++;
else
right--;
}
return
res;
}
};
|
【版权声明】转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/TenosDoIt/p/3812880.html