使用网站作为WCF服务宿主的几种做法
内容摘要
这一篇文章探讨使用网站作为WCF服务宿主的几种做法,我将从最基本的svc文件的方式,演化成为无svc文件的方式,并且在最后介绍REST与路由规则结合的做法。
本文所讲解的WCF功能,是基于WCF 4.0这个版本。我所采用的开发工具是Visual Studio 2012. 本文范例代码可以通过 Web-host-sample.zip 下载。
本文不是WCF的入门文档,有关WCF的典型使用场景和一些基础知识,可以参考我之前的两篇文章
范例说明
本文所采用的范例是相当简单的,我已经定义的合约和服务如下
using System.ServiceModel; namespace Web { [ServiceContract] public interface IHelloService { [OperationContract] string SayHello(); } public class HelloService : IHelloService { public string SayHello() { return "Hello,world"; } } }
基本做法(采用svc文件的方式)
WCF 4.0以前的版本,我们都是采用svc文件作为服务的宿主文件。例如,我们可以定义如下这样一个HelloService.svc,其内容如下
<%@ ServiceHost Service="Web.HelloService" %>
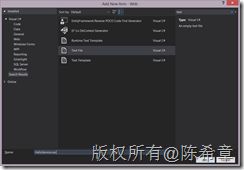
需要注意的是,你在Visual Studio中无法直接添加一个空白的svc文件,我一般是选择Text File这个模板,但是在命名的时候,将其修改为svc后缀。如下图所示
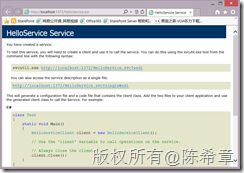
定义好这个文件后,可以直接在浏览器中查看该服务的描述,如下图所示。此时表示该服务已经被正确地宿主了。
无svc文件的做法
上面这个做法虽然不难,但每次都要手工创建那个svc文件,总是觉得有些多余。那么是否有办法免去这个步骤呢?WCF 4.0提供了这种可能性。
我们需要做的是,在配置文件中指定一个虚拟的文件路径,并且将其与服务进行关联起来。如下所示(请重点关心粗体部分)
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!-- For more information on how to configure your ASP.NET application, please visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=169433 --> <configuration> <system.web> <compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5" /> <httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5" /> </system.web> <system.serviceModel> <behaviors> <serviceBehaviors> <behavior> <serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/> </behavior> </serviceBehaviors> </behaviors> <serviceHostingEnvironment aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true" multipleSiteBindingsEnabled="true"> <serviceActivations> <add service="Web.HelloService" relativeAddress="MyService.svc"/> </serviceActivations> </serviceHostingEnvironment> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>
为了与上面的例子区分,我特意在这里定义relativeAddress的时候,用了不一样的名称。你没有看错,只需要这样定义就可以直接访问到MyService.svc,而不要求你实际去创建这个文件。
看起来挺不错的,但仍然有一点点美中不足就是,这个虚拟地址,必须有一个后缀名(而且推荐使用svc),对于一般的用户而言,可能并不是特别友好。是否有办法将这个地址进一步地简化呢?
对于标准的SOAP服务来说,应该是没有办法了。但是如果是REST服务,倒是有另外一个方法来实现。请继续阅读下面的说明。
REST与路由规则
为了做演示,我将服务稍作修改,使得其成为所谓的RESTful的服务。请注意红色粗体部分。
using System.ServiceModel; using System.ServiceModel.Web; namespace Web { [ServiceContract] public interface IHelloService { [OperationContract] [WebGet] string SayHello(); } public class HelloService : IHelloService { public string SayHello() { return "Hello,world"; } } }
然后我们还需要添加有关的配置文件设置(请注意粗体部分)
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!-- For more information on how to configure your ASP.NET application, please visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=169433 --> <configuration> <system.web> <compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5" /> <httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5" /> </system.web> <system.serviceModel> <services> <service name="Web.HelloService"> <endpoint contract="Web.IHelloService" binding="webHttpBinding"></endpoint> </service> </services> <behaviors> <serviceBehaviors> <behavior> <serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/> </behavior> </serviceBehaviors> <endpointBehaviors> <behavior> <webHttp helpEnabled="true"></webHttp> </behavior> </endpointBehaviors> </behaviors> <serviceHostingEnvironment aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true" multipleSiteBindingsEnabled="true"> <serviceActivations> <add service="Web.HelloService" relativeAddress="MyService.svc"/> </serviceActivations> </serviceHostingEnvironment> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>
为了使用我们自己想要的地址(虚拟地址)来访问这个服务,我们可以结合路由规则来实现(这个也是WCF 4.0新增的特性)
将如下代码添加到Global.asax文件中
using System; using System.ServiceModel.Activation; using System.Web.Routing; namespace Web { public class Global : System.Web.HttpApplication { private void RegisterRoutes() { WebServiceHostFactory factory = new WebServiceHostFactory(); RouteTable.Routes.Add(new ServiceRoute("HelloService", factory, typeof(HelloService))); } protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { RegisterRoutes(); } protected void Session_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { } protected void Application_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { } protected void Application_AuthenticateRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { } protected void Application_Error(object sender, EventArgs e) { } protected void Session_End(object sender, EventArgs e) { } protected void Application_End(object sender, EventArgs e) { } } }
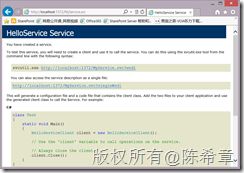
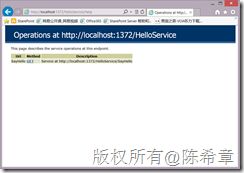
我们在这里是定义了一个路由规则,凡是请求HelloService这个虚拟路径的(注意,没有带任何后缀),就路由到我们的服务。在浏览器中我们可以看到效果如下