通过源代码研究ASP.NET MVC中的Controller和View(二)
通过源代码研究ASP.NET MVC中的Controller和View(一)
在开始之前,先来温习下上一篇文章中的结论(推论):
- IView是所有HTML视图的抽象
- ActionResult是Controller对View的控制的抽象,也是View的入口。
- ViewResult用于指明呈现某个HTML视图(IView实例)。
- ViewResult是IView实例的使用者,查找、呈现和释放IView实例。
- IViewEngine是IView的管理者,被ViewResult调用,用于查找和释放IView实例。
三个类型已经可以得出初步的结论:
ViewResult
- 创建者:Controller
- 职责:呈现HTML视图
- 公开接口:ExecuteResult( ControllerContext ) : void
IViewEngine
- 创建者:全局
- 职责:查找和管理IView(视图)对象
- 公开接口:FindView( controllerContext : ControllerContext, viewName : string, masterName : string, useCache : bool ) : ViewEngineResult,ReleaseView( IView ) : void
IView
- 创建者:IViewEngine
- 职责:呈现HTML
- 公开接口:Render( TextWriter ) : void
在呈现视图这个过程中,ViewResult是主控,IView是操作执行,IViewEngine是查找映射。如果类比到其他的架构(如ASP.NET),则可以建立这样的类比:
ViewResult 类比为 HttpApplication,是呈现视图的主控对象。
IView 类比为 IHttpHandler,是呈现视图的操作执行。
IViewEngine 类比为 IHttpHandlerFactory,负责视图的查找映射。
PS:大家可以比较一下类比类型的公开接口是何其相似。
同时我发现到,ViewResult调用IViewEngine.FindView接口参数里,除了ControllerContext,没有开放类型(非sealed类型)。这意味着这个接口很难存在“私有协议”(自创名称)这种手法。
简单的说“私有协议”这种手法就是指假设有两个类型A和B(A和B都是开放类型),A是B的某个接口的使用者,同时这个接口中存在一个开放类型C(非sealed类型)。那么我们就可以写出两个类型A'和B',同时写一个私有的(internal)类型C'。由于C'是私有的,非A'和B'便不能访问其扩展成员,此时在A'和B'之间就建立了一个“私有协议”。
显然举例说明更好,由于IView类型是一个开放类型(非sealed),我们可以建立一个IViewEngine到ViewResult之间的私有协议,如下:
public class MyViewResult : ViewResult
{
protected override ViewEngineResult FindView( ControllerContext context )
{
var result = base.FindView( context );
var myView = result.View as PrivateView;
if ( myView != null )
myView.ControllerContext = context;
return result;
}
}
public class MyViewEngine : IViewEngine
{
//...
public ViewEngineResult FindView( ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache )
{
return new ViewEngineResult( new PrivateView(), this );
}
//...
}
internal class PrivateView : IView
{
public ControllerContext ControllerContext
{
get;
internal set;
}
#region IView 成员
public void Render( ViewContext viewContext, System.IO.TextWriter writer )
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
#endregion
}
注意这里的PrivateView 类型,这是一个internal的类型,只有我们的MyViewResult和MyViewEngine才能使用和发现。在使用中我们利用私有协议传输了更多的信息:ControllerContext,而这些信息对于这个程序集之外的代码是不可见的(因为携带的类型根本就不可见),这就形成了私有协议。这个例子仅为说明这种手法,并无实际意义(因为事实上IViewEngine在创建IView对象的时候就可以把ControllerContext传进去了,而无需这么复杂)。
在IViewEngine.FindView的参数里,只有ControllerContext是开放类型,私有协议只能在这之上建立。但从设计上来说,在Context上建立私有协议并不是一个好的idea。
或者说这种接口的设计透露出来设计者的思想:我不太愿意ViewResult和IViewEngine之间存在强耦合关系。
最后来看看ViewEngineResult的设计:
public class ViewEngineResult
{
public ViewEngineResult( IEnumerable<string> searchedLocations )
{
if ( searchedLocations == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException( "searchedLocations" );
}
SearchedLocations = searchedLocations;
}
public ViewEngineResult( IView view, IViewEngine viewEngine )
{
if ( view == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException( "view" );
}
if ( viewEngine == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException( "viewEngine" );
}
View = view;
ViewEngine = viewEngine;
}
public IEnumerable<string> SearchedLocations
{
get;
private set;
}
public IView View
{
get;
private set;
}
public IViewEngine ViewEngine
{
get;
private set;
}
}
这个类型除了属性啥都没有,难道就是传说中的贫血对象?
顺带提一句我对某些胡乱发明(至少我认为是)的诸如“贫血对象”这样的词汇相当不满。尽管这里的设计明显有一些坏味道。
OK,那么很显然的这个对象只是为了IViewEngine的FindView方法不至于多一个out IEnumerable<string> searchedLocations而已,这种设计存在的意义更多的在于改善编码体验,同时,避免在公开接口中定义out参数。
结合ViewResult.FindView和ViewEngineCollection.FindView的实现,我能够搞清楚这个类型对我们来说唯一有价值的东西就是View属性,如果这个属性为null,则表示没有找到视图。
那么对于架构设计的研究就到此为止了。接下来研究下ASP.NET MVC的默认视图模型实现。
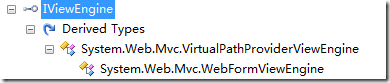
由于IViewEngine是IView对象的管理者,所以先用Reflector查找一下IViewEngine的实现类有哪些:
OK,只有一个类型,看来问题变得很简单了。
FindView是IViewEngine的主要方法,这个方法在VirtualPathProviderViewEngine里面实现:
public virtual ViewEngineResult FindView( ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache )
{
if ( controllerContext == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException( "controllerContext" );
}
if ( String.IsNullOrEmpty( viewName ) )
{
throw new ArgumentException( MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "viewName" );
}
string[] viewLocationsSearched;
string[] masterLocationsSearched;
string controllerName = controllerContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString( "controller" );
string viewPath = GetPath( controllerContext, ViewLocationFormats, AreaViewLocationFormats, "ViewLocationFormats", viewName, controllerName, _cacheKeyPrefix_View, useCache, out viewLocationsSearched );
string masterPath = GetPath( controllerContext, MasterLocationFormats, AreaMasterLocationFormats, "MasterLocationFormats", masterName, controllerName, _cacheKeyPrefix_Master, useCache, out masterLocationsSearched );
if ( String.IsNullOrEmpty( viewPath ) || (String.IsNullOrEmpty( masterPath ) && !String.IsNullOrEmpty( masterName )) )
{
return new ViewEngineResult( viewLocationsSearched.Union( masterLocationsSearched ) );
}
return new ViewEngineResult( CreateView( controllerContext, viewPath, masterPath ), this );
}
逻辑很简单,首先是得到controllerName,然后调用GetPath方法,这个方法的参数数量,呃,,,那个,,,,(private的方法也不能写成这样啊!怒!)
GetPath方法会返回一个字符串,看起来这个字符串应该是path,然后是一个if,他的逻辑是判断GetPath返回的结果是不是空。如果是空,则返回一个没有View的ViewEngineResult,否则调用CreateView方法来创建视图返回。
简单说:
- 获取路径
- 路径为空则返回没有视图的ViewEngineResult
- 否则创建视图返回
那么我发现CreateView方法是一个抽象的方法,这意味着我大体上能推测出VirtualPathProviderViewEngine类型的主要职责便是将ViewResult通过FindView方法传递来的信息转换成路径信息交由派生类创建视图对象:
viewName -> viewPath
masterName -> masterPath
这就是主要工作,这个工作是由GetPath方法完成的:
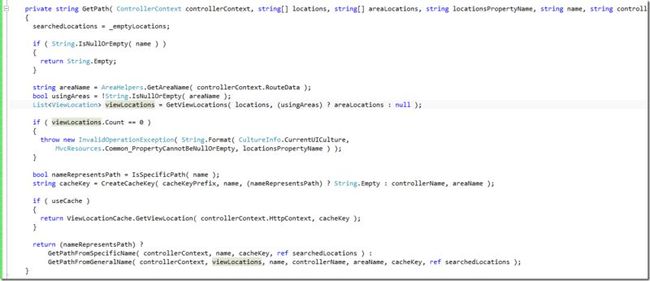
private string GetPath( ControllerContext controllerContext, string[] locations, string[] areaLocations, string locationsPropertyName, string name, string controllerName, string cacheKeyPrefix, bool useCache, out string[] searchedLocations )
{
searchedLocations = _emptyLocations;
if ( String.IsNullOrEmpty( name ) )
{
return String.Empty;
}
string areaName = AreaHelpers.GetAreaName( controllerContext.RouteData );
bool usingAreas = !String.IsNullOrEmpty( areaName );
List<ViewLocation> viewLocations = GetViewLocations( locations, (usingAreas) ? areaLocations : null );
if ( viewLocations.Count == 0 )
{
throw new InvalidOperationException( String.Format( CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture,
MvcResources.Common_PropertyCannotBeNullOrEmpty, locationsPropertyName ) );
}
bool nameRepresentsPath = IsSpecificPath( name );
string cacheKey = CreateCacheKey( cacheKeyPrefix, name, (nameRepresentsPath) ? String.Empty : controllerName, areaName );
if ( useCache )
{
return ViewLocationCache.GetViewLocation( controllerContext.HttpContext, cacheKey );
}
return (nameRepresentsPath) ?
GetPathFromSpecificName( controllerContext, name, cacheKey, ref searchedLocations ) :
GetPathFromGeneralName( controllerContext, viewLocations, name, controllerName, areaName, cacheKey, ref searchedLocations );
}
我的神,这个方法有够复杂,我们慢慢看。
首先是入口检查和out变量初始化,尽管那个_emptyLocations明白无误的告诉了我们他是一个空的数组,我还是去瞄了一眼:
private static readonly string[] _emptyLocations = new string[0];
然后获取了areaName,useAreas标识是不是使用了区域,然后获取了viewLocations,大体上这些变量从名称就能推测其意义。
如果viewLocations没有,那么抛了个异常,这个异常大体上的意思是属性不能为空,属性名则是locationsPropertyName,这是个参数,对应到调用的地方的那个字符串:"ViewLocationFormats"
显然这个字符串和GetViewLocations方法存在某种微妙的联系,这个联系并不难找,我们发现调用的地方是这样的:
string viewPath = GetPath( controllerContext, ViewLocationFormats, AreaViewLocationFormats, "ViewLocationFormats", viewName, controllerName, _cacheKeyPrefix_View, useCache, out viewLocationsSearched );
string masterPath = GetPath( controllerContext, MasterLocationFormats, AreaMasterLocationFormats, "MasterLocationFormats", masterName, controllerName, _cacheKeyPrefix_Master, useCache, out masterLocationsSearched );
这个字符串的值和第二个参数是一样的,第二个参数就是locations,看看locations用来干啥了?唔,,,GetViewLocations的参数,所以,,,,
好吧,这个设计有点坏味道了,,,,
继续我们的探索,回头我会帮大家把这些方法全掰碎了看清楚。
然后有一个判断,IsSpecificPath,下面的cacheKey和if ( useCache )是缓存用的,暂且不管。然后我们看到下面是return了。
先来摸清楚那个判断干啥的,nameRepresentsPath的意思应该是:“名称代表路径”,IsSpecificPath的意思是:“是特定的路径”,传入的参数是name,结合起来分析。
IsSpecificPath方法的参数应该是一个path,那么这意味着name和path在某些时候是一个东西(nameRepresentsPath)。来看看IsSpecificPath的实现:
private static bool IsSpecificPath( string name )
{
char c = name[0];
return (c == '~' || c == '/');
}
极为简洁。在这里顺带稍微提一下,写成return name.StartsWith( "~" ) || name.StartsWith( "/" );语义岂不更为明确。
这个方法大体上来说可以描述成,判断name是不是一个绝对路径。结合参数名,我大体上可以这样猜测,如果name是以"/"或者"~"开头,则VirtualPathProviderViewEngine则会当作路径来看待,否则当作名称来看待。向上追溯,我们就能发现这个name其实就是viewName或matserName。
现在我们大体上理清了VirtualPathProviderViewEngine.GetPath的逻辑:
- 获取区域名(areaName)和视图位置(viewLocations)
- 检查名称是不是一个绝对路径
- 如果useCache为true,尝试从缓存中获取路径
- 否则,根据名称是不是一个绝对路径调用相应的方法获取路径。
修剪和归纳一下大体是这样:
- 获取视图位置
- 缓存检索
- 获取路径
接下来探索GetPathFromSpecificName和GetPathFromGeneralName两个方法,直觉告诉我GetPathFromSpecificName应该会比较简单:
private string GetPathFromSpecificName( ControllerContext controllerContext, string name, string cacheKey, ref string[] searchedLocations )
{
string result = name;
if ( !FileExists( controllerContext, name ) )
{
result = String.Empty;
searchedLocations = new[] { name };
}
ViewLocationCache.InsertViewLocation( controllerContext.HttpContext, cacheKey, result );
return result;
}
的确很简单,简单的判断了一下文件是否存在(FileExists),然后就是插入缓存和返回结果了,而这个结果(result),就是name。哈,还真是nameRepresentsPath。
那么看看GetPathFromGeneralName:
private string GetPathFromGeneralName( ControllerContext controllerContext, List<ViewLocation> locations, string name, string controllerName, string areaName, string cacheKey, ref string[] searchedLocations )
{
string result = String.Empty;
searchedLocations = new string[locations.Count];
for ( int i = 0; i < locations.Count; i++ )
{
ViewLocation location = locations[i];
string virtualPath = location.Format( name, controllerName, areaName );
if ( FileExists( controllerContext, virtualPath ) )
{
searchedLocations = _emptyLocations;
result = virtualPath;
ViewLocationCache.InsertViewLocation( controllerContext.HttpContext, cacheKey, result );
break;
}
searchedLocations[i] = virtualPath;
}
return result;
}
- 循环获取locations(就是viewLocations)里面的所有项,进行了一个Format的操作(注意这里调用的是ViewLocation.Format方法)得到virtualPath(虚拟路径)。
- 如果某个虚拟路径的文件是存在的(FileExists),则返回这个虚拟路径(同时会清空searchedLocations)。
- 否则,会返回一个空字符串(最上面初始化的结果)。
在循环过程中,如果虚拟路径不存在,那么他会被添加到searchedLocations(查找过的位置)。唔,,,,这里又有坏味道了?
简单解释下,因为如果在循环过程中找到了任何一个正确的结果,searchedLocations就会被置为空数组,所以最终searchedLocations只可能有两种结果:空,或者所有循环过的virtualPath。
OK,现在获取路径的逻辑已经基本搞清,唯一不明白的是ViewLocation.Format方法的实现,而ViewLocation这个对象则是从这里来的:
List<ViewLocation> viewLocations = GetViewLocations( locations, (usingAreas) ? areaLocations : null );
这个viewLocations后来成为了GetPathFromGeneralName的locations参数,如果注意观察的话,事实上这个东西仅用在了GetPathFromGeneralName方法:
先来看看ViewLocation这个类型:
private class ViewLocation
{
protected string _virtualPathFormatString;
public ViewLocation( string virtualPathFormatString )
{
_virtualPathFormatString = virtualPathFormatString;
}
public virtual string Format( string viewName, string controllerName, string areaName )
{
return String.Format( CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, _virtualPathFormatString, viewName, controllerName );
}
}
呃,简单的说,这个类型就是对string的一个包装,提供一个特定的Format方法。。。。
不过,好像areaName参数没有被用到,,,,
还好在这个类型定义的下面我很快发现了另一个东西:
private class AreaAwareViewLocation : ViewLocation
{
public AreaAwareViewLocation( string virtualPathFormatString )
: base( virtualPathFormatString )
{
}
public override string Format( string viewName, string controllerName, string areaName )
{
return String.Format( CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, _virtualPathFormatString, viewName, controllerName, areaName );
}
}
这一对父子都是string的一个包装。他们包装了类似于:"abc{0}shy{1}uin{2}"这样的字符串,然后提供一个Format方法映射到String.Format。
没有更多信息了。去创建这些类型的GetViewLocations方法去看看:
private static List<ViewLocation> GetViewLocations( string[] viewLocationFormats, string[] areaViewLocationFormats )
{
List<ViewLocation> allLocations = new List<ViewLocation>();
if ( areaViewLocationFormats != null )
{
foreach ( string areaViewLocationFormat in areaViewLocationFormats )
{
allLocations.Add( new AreaAwareViewLocation( areaViewLocationFormat ) );
}
}
if ( viewLocationFormats != null )
{
foreach ( string viewLocationFormat in viewLocationFormats )
{
allLocations.Add( new ViewLocation( viewLocationFormat ) );
}
}
return allLocations;
}
神,这个方法也是如此的简洁,简单说就是把两个string[]类型的参数包装成ViewLocation然后再合并输出了。
好吧,我大体上可以弄明白了,这些GetViewLocations方法和ViewLocation类型全部都是障眼法。真正的逻辑可以简单的描述成,有若干个字符串模版,然后在GetPathFromGeneralName对这些模版调用了String.Format方法来产生virtualPath。
结合之前的研究可以得到结论了:
GetPath方法干的事情:
- 获取视图位置(GetViewLocations)
- 检查是否使用了区域(Area)
- 如果使用了区域,则把areaLocations传入
- GetViewLocations方法会将locations和areaLocations这两个字符串数组包装和合并成一个ViewLocation的集合
- 如果集合没有东西,那么抛异常
- 缓存检索
- 获取路径
- 如果名称像是一个绝对路径("/"或"~"开头)
- 检查虚拟路径所指向的文件是否存在(FileExists)
- 存在则返回名称(当作路径)。
- 否则返回空字符串。
- 如果名称不像是一个绝对路径
- 遍历所有的视图位置生成虚拟路径
- 如果虚拟路径所指向的文件存在,则返回这个虚拟路径。
- 如果所有生成的虚拟路径所指向的文件都不存在,则返回空字符串。
- 如果名称像是一个绝对路径("/"或"~"开头)
缓存处理部分我并不关心,现在从外部来看GetPath方法,那么它的参数分为三大部分:
- 缓存部分
- controllerContext(主要利用里面的HttpContext.Cache模块)
- cacheKeyPrefix
- useCache
- 位置部分:
- locations和areaLocations,这是虚拟路径的模版,使用的值是VirtualPathProviderViewEngine的公开属性。
- locationsPropertyName,这个用于抛异常的时候指示使用的哪个Property。
- 名称部分:
- name,这个参数会是viewName或者masterName
- controllerName,这个参数标识了控制器的名称
- areaName,没有出现在参数中,但利用controllerContext提取了出来,事实上controllerName也是从controllerContext中提取的,性质一样。
那么这里弥漫着一股很浓烈的坏味道了。
GetPath方法的参数真是一团糟。不应当传入ControllerContext而是传入areaName和Cache,locations、areaLocations和locationsPropertyName应该绑成一个对象。换言之,这样岂不更好:
private string GetPath( Cache cache, string cacheKeyPrefix, bool useCache, LocationsInfo locations, string name, string controllerName, string areaName );
最后用一句话来总结GetPath方法干的破事儿:
利用提供的虚拟路径模版和名称产生虚拟路径,并检查虚拟路径文件是否存在(FileExists),如果存在则返回虚拟路径。
那么,默认虚拟路径模版到底有哪些呢?这些东西是在派生类(WebFormViewEngine)中定义的。