用户手势检测-GestureDetector使用详解
一、概述
当用户触摸屏幕的时候,会产生许多手势,例如down,up,scroll,filing等等。
一般情况下,我们知道View类有个View.OnTouchListener内部接口,通过重写他的onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event)方法,我们可以处理一些touch事件,但是这个方法太过简单,如果需要处理一些复杂的手势,用这个接口就会很麻烦(因为我们要自己根据用户触摸的轨迹去判断是什么手势)。
Android sdk给我们提供了GestureDetector(Gesture:手势Detector:识别)类,通过这个类我们可以识别很多的手势,主要是通过他的onTouchEvent(event)方法完成了不同手势的识别。虽然他能识别手势,但是不同的手势要怎么处理,应该是提供给程序员实现的。
GestureDetector这个类对外提供了两个接口和一个外部类
接口:OnGestureListener,OnDoubleTapListener
内部类:SimpleOnGestureListener
这个外部类,其实是两个接口中所有函数的集成,它包含了这两个接口里所有必须要实现的函数而且都已经重写,但所有方法体都是空的;不同点在于:该类是static class,程序员可以在外部继承这个类,重写里面的手势处理方法。
下面我们先看OnGestureListener接口;
二、GestureDetector.OnGestureListener---接口
1、基本讲解
如果我们写一个类并implements OnGestureListener,会提示有几个必须重写的函数,加上之后是这个样子的:
private class gesturelistener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}
可见,这里总共重写了六个函数,这些函数都在什么情况下才会触发呢,下面讲一下:
OnDown(MotionEvent e):用户按下屏幕就会触发;
onShowPress(MotionEvent e):如果是按下的时间超过瞬间,而且在按下的时候没有松开或者是拖动的,那么onShowPress就会执行,具体这个瞬间是多久,我也不清楚呃……
onLongPress(MotionEvent e):长按触摸屏,超过一定时长,就会触发这个事件
触发顺序:
onDown->onShowPress->onLongPress
onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e):从名子也可以看出,一次单独的轻击抬起操作,也就是轻击一下屏幕,立刻抬起来,才会有这个触发,当然,如果除了Down以外还有其它操作,那就不再算是Single操作了,所以也就不会触发这个事件
触发顺序:
点击一下非常快的(不滑动)Touchup:
onDown->onSingleTapUp->onSingleTapConfirmed
点击一下稍微慢点的(不滑动)Touchup:
onDown->onShowPress->onSingleTapUp->onSingleTapConfirmed
onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,float velocityY) :滑屏,用户按下触摸屏、快速移动后松开,由1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多个ACTION_MOVE, 1个ACTION_UP触发
参数解释:
e1:第1个ACTION_DOWN MotionEvent
e2:最后一个ACTION_MOVE MotionEvent
velocityX:X轴上的移动速度,像素/秒
velocityY:Y轴上的移动速度,像素/秒
onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,float distanceX, float distanceY):在屏幕上拖动事件。无论是用手拖动view,或者是以抛的动作滚动,都会多次触发,这个方法 在ACTION_MOVE动作发生时就会触发
滑屏:手指触动屏幕后,稍微滑动后立即松开
onDown-----》onScroll----》onScroll----》onScroll----》………----->onFling
拖动
onDown------》onScroll----》onScroll------》onFiling
可见,无论是滑屏,还是拖动,影响的只是中间OnScroll触发的数量多少而已,最终都会触发onFling事件!
2、实例
要使用GestureDetector,有三步要走:
1、创建OnGestureListener监听函数:
可以使用构造实例:
GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener = new GestureDetector.OnGestureListener(){
};
也可以构造类:
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
}
2、创建GestureDetector实例mGestureDetector:
构造函数有下面三个,根据需要选择:
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener); GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener); GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener listener);
3、onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event)中拦截:
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
4、控件绑定
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv); tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
现在进入实例阶段:
首先,在主布局页面添加一个textView,并将其放大到整屏,方便在其上的手势识别,代码为:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.gesturedetectorinterface.MainActivity" > <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_margin="50dip" android:background="#ff00ff" android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout>
然后在JAVA代码中,依据上面的三步走原则,写出代码,并在所有的手势下添加上Toast提示并写上Log
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener{
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new gestureListener()); //使用派生自OnGestureListener
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
/*
* 在onTouch()方法中,我们调用GestureDetector的onTouchEvent()方法,将捕捉到的MotionEvent交给GestureDetector
* 来分析是否有合适的callback函数来处理用户的手势
*/
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
// 用户轻触触摸屏,由1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN触发
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDown");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDown", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return false;
}
/*
* 用户轻触触摸屏,尚未松开或拖动,由一个1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN触发
* 注意和onDown()的区别,强调的是没有松开或者拖动的状态
*
* 而onDown也是由一个MotionEventACTION_DOWN触发的,但是他没有任何限制,
* 也就是说当用户点击的时候,首先MotionEventACTION_DOWN,onDown就会执行,
* 如果在按下的瞬间没有松开或者是拖动的时候onShowPress就会执行,如果是按下的时间超过瞬间
* (这块我也不太清楚瞬间的时间差是多少,一般情况下都会执行onShowPress),拖动了,就不执行onShowPress。
*/
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onShowPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onShowPress", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
// 用户(轻触触摸屏后)松开,由一个1个MotionEvent ACTION_UP触发
///轻击一下屏幕,立刻抬起来,才会有这个触发
//从名子也可以看出,一次单独的轻击抬起操作,当然,如果除了Down以外还有其它操作,那就不再算是Single操作了,所以这个事件 就不再响应
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapUp");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapUp", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
// 用户按下触摸屏,并拖动,由1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多个ACTION_MOVE触发
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.i("MyGesture22", "onScroll:"+(e2.getX()-e1.getX()) +" "+distanceX);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onScroll", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
// 用户长按触摸屏,由多个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN触发
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onLongPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onLongPress", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
// 用户按下触摸屏、快速移动后松开,由1个MotionEvent ACTION_DOWN, 多个ACTION_MOVE, 1个ACTION_UP触发
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onFling");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onFling", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
};
}
三、GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener---接口
有两种方式设置双击监听:
方法一:新建一个类同时派生自OnGestureListener和OnDoubleTapListener:
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener,GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
}
方法二:使用GestureDetector::setOnDoubleTapListener();函数设置监听:
//构建GestureDetector实例
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new gestureListener()); //使用派生自OnGestureListener
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
}
//设置双击监听器
mGestureDetector.setOnDoubleTapListener(new doubleTapListener());
private class doubleTapListener implements GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
}
注意:大家可以看到无论在方法一还是在方法二中,都需要派生自GestureDetector.OnGestureListener,前面我们说过GestureDetector 的构造函数,如下:
GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener); GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.OnGestureListener listener); GestureDetector gestureDetector=new GestureDetector(Context context,GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener listener);
可以看到,在构造函数中,除了后面要讲的SimpleOnGestureListener 以外的其它两个构造函数都必须是OnGestureListener的实例。所以要想使用OnDoubleTapListener的几个函数,就必须先实现OnGestureListener。
2、函数讲解:
首先看一下OnDoubleTapListener接口必须重写的三个函数:
private class doubleTapListener implements GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}
onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e):单击事件。用来判定该次点击是SingleTap而不是DoubleTap,如果连续点击两次就是DoubleTap手势,如果只点击一次,系统等待一段时间后没有收到第二次点击则判定该次点击为SingleTap而不是DoubleTap,然后触发SingleTapConfirmed事件。触发顺序是:OnDown->OnsingleTapUp->OnsingleTapConfirmed
关于onSingleTapConfirmed和onSingleTapUp的一点区别: OnGestureListener有这样的一个方法onSingleTapUp,和onSingleTapConfirmed容易混淆。二者的区别是:onSingleTapUp,只要手抬起就会执行,而对于onSingleTapConfirmed来说,如果双击的话,则onSingleTapConfirmed不会执行。
onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e):双击事件
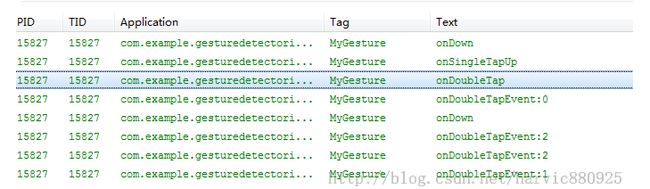
onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e):双击间隔中发生的动作。指触发onDoubleTap以后,在双击之间发生的其它动作,包含down、up和move事件;下图是双击一下的Log输出:
两点总结:
1、从上图可以看出,在第二下点击时,先触发OnDoubleTap,然后再触发OnDown(第二次点击)
2、其次在触发OnDoubleTap以后,就开始触发onDoubleTapEvent了,onDoubleTapEvent后面的数字代表了当前的事件,0指ACTION_DOWN,1指ACTION_UP,2 指ACTION_MOVE
在上一个例子的基础上,我们再添加一个双击监听类,实现如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener{
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new gestureListener()); //使用派生自OnGestureListener
mGestureDetector.setOnDoubleTapListener(new doubleTapListener());
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
/*
* 在onTouch()方法中,我们调用GestureDetector的onTouchEvent()方法,将捕捉到的MotionEvent交给GestureDetector
* 来分析是否有合适的callback函数来处理用户的手势
*/
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
//OnGestureListener监听
private class gestureListener implements GestureDetector.OnGestureListener{
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDown");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDown", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return false;
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onShowPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onShowPress", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapUp");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapUp", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.i("MyGesture22", "onScroll:"+(e2.getX()-e1.getX()) +" "+distanceX);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onScroll", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onLongPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onLongPress", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onFling");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onFling", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
};
//OnDoubleTapListener监听
private class doubleTapListener implements GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener{
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapConfirmed");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapConfirmed", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTap");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTap", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTapEvent");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTapEvent", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
};
}
四、GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener---类
它与前两个不同的是:
1、这是一个类,在它基础上新建类的话,要用extends派生而不是用implements继承!
2、OnGestureListener和OnDoubleTapListener接口里的函数都是强制必须重写的,即使用不到也要重写出来一个空函数但在SimpleOnGestureListener类的实例或派生类中不必如此,可以根据情况,用到哪个函数就重写哪个函数,因为SimpleOnGestureListener类本身已经实现了这两个接口的所有函数,只是里面全是空的而已。
下面利用SimpleOnGestureListener类来重新实现上面的几个效果,代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener {
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new simpleGestureListener());
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private class simpleGestureListener extends
GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener {
/*****OnGestureListener的函数*****/
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDown");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDown", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
return false;
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onShowPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onShowPress", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapUp");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapUp",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onScroll:" + (e2.getX() - e1.getX()) + " "
+ distanceX);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onScroll", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
return true;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onLongPress");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onLongPress", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onFling");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onFling", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
return true;
}
/*****OnDoubleTapListener的函数*****/
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onSingleTapConfirmed");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onSingleTapConfirmed",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTap");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTap", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
return true;
}
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
Log.i("MyGesture", "onDoubleTapEvent");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "onDoubleTapEvent",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
}
}
到此,有关GestureDetector的所有基础知识都讲解完了,下面给出一个小应用——识别用户是向左滑还是向右滑!
五、OnFling应用——识别向左滑还是向右滑
这部分就有点意思了,可以说是上面知识的一个小应用,我们利用OnFling函数来识别当前用户是在向左滑还是向右滑,从而打出日志。先看下OnFling的参数:
boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,float velocityY) 参数解释: e1:第1个ACTION_DOWN MotionEvent e2:最后一个ACTION_MOVE MotionEvent velocityX:X轴上的移动速度,像素/秒 velocityY:Y轴上的移动速度,像素/秒
首先,先说一下实现的功能:当用户向左滑动距离超过100px,且滑动速度超过100 px/s时,即判断为向左滑动;向右同理.代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnTouchListener {
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new simpleGestureListener());
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
tv.setFocusable(true);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setLongClickable(true);
}
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private class simpleGestureListener extends
GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener {
/*****OnGestureListener的函数*****/
final int FLING_MIN_DISTANCE = 100, FLING_MIN_VELOCITY = 200;
// 触发条件 :
// X轴的坐标位移大于FLING_MIN_DISTANCE,且移动速度大于FLING_MIN_VELOCITY个像素/秒
// 参数解释:
// e1:第1个ACTION_DOWN MotionEvent
// e2:最后一个ACTION_MOVE MotionEvent
// velocityX:X轴上的移动速度,像素/秒
// velocityY:Y轴上的移动速度,像素/秒
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
if (e1.getX() - e2.getX() > FLING_MIN_DISTANCE
&& Math.abs(velocityX) > FLING_MIN_VELOCITY) {
// Fling left
Log.i("MyGesture", "Fling left");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Fling Left", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else if (e2.getX() - e1.getX() > FLING_MIN_DISTANCE
&& Math.abs(velocityX) > FLING_MIN_VELOCITY) {
// Fling right
Log.i("MyGesture", "Fling right");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Fling Right", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
return true;
}
}
}