java流操作
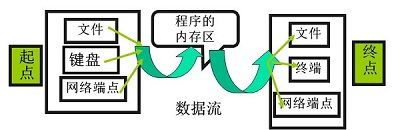
这是从csdn上粘贴过来的一张图片,很好的说明了流传输的整个过程。我现在所使用到的无非就是标准的输入输出流以及文件与内存之间的流的传输。其他的暂时还没有涉及到。
先来说明下几个概念吧:
字符流和字节流
字节流:数据流的传输过程中最小的传输单元是字节。比如音频、视频、ASSII码等传输过程中都以字节的形式来进行传输。
字符流:数据流的传输过程中最小的传输单元是字符。我们都知道java虚拟机中的编码方式是unicode编码,一个unicode编码方式是两个字节。在流的传输过程中汉字一般需要3个字节。
输入流和输出流
这里输入流和输出流是相对于当前程序来讲的,因为程序运行在内存中。模糊来说是相对于内存来讲的。
输入流:从其他地方如外存、标准输入到程序中为输入流。
输出流:程序输出到外存文件、标准输出等为输出流。
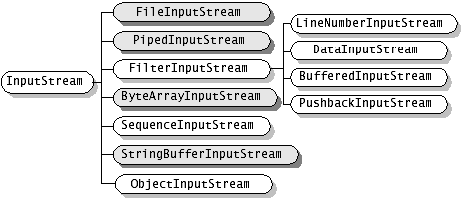
下图是字节流(来自别人)的分类:
下面通过查看jdk源码的形式来主要分析下
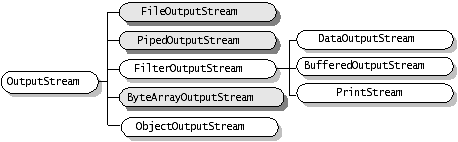
字节流:基类 InputStream 和OutputStream
InputStream 抽象类
主要使用属性和方法 jdk源码中粘贴出来
private static final int MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048;
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int c = read();
if (c == -1) {
return -1;
}
b[off] = (byte)c;
int i = 1;
try {
for (; i < len ; i++) {
c = read();
if (c == -1) {
break;
}
b[off + i] = (byte)c;
}
} catch (IOException ee) {
}
return i;
}
OutputStream 抽象类
public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException;
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if ((off < 0) || (off > b.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > b.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {
write(b[off + i]);
}
}
继承该抽象类的子类主要有:
对于文件的操作:FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
public void testFileInputAndOutput() throws IOException{
InputStream isFile = new FileInputStream("D:/testIO.txt");
byte b[] = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
int tmp = 0;
while ((tmp = isFile.read()) != -1) {
b[len] = (byte) tmp;
len++;
}
isFile.close();
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
OutputStream osFile = new FileOutputStream("D:\\testIO2.txt");
osFile.write(b, 0, len);
osFile.close();
}
对于Memory中Array的操作
public void ByteArrayInputAndOutput() throws IOException{
int a=1;
int b=2;
int c=3;
byte[] wArr = new byte[1024];
byte[] rArr = new byte[1024];
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(1024);
bos.write(a);
bos.write(b);
bos.write(c);
wArr = bos.toByteArray();
for(int i=0; i<wArr.length;i++){
System.out.println("写入到缓冲区里面去:"+wArr[i]);
}
bos.close();
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(wArr);
int len=0;
int tmp=0;
while((tmp = bis.read()) != -1){
//System.out.println(tmp);
rArr[len] = (byte) tmp;
len++;
}
bis.close();
for(int i=0; i<len;i++){
System.out.println("读回来放入另一个数组:"+ wArr[i]);
}
}
此外还有从管道来的PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream
以上三种都是属于节点流,这些流的操作都只具有读写字节的功能,但是在文件的操作中我们可以写入任何类型的数据,因此需要其他类型的流来进行包装过滤。这里可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/rcoder/article/details/6112973这篇文章。
public void testFilterStream() throws IOException{
File file = new File("D:\\testIO.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis);
String tmp=null;
while( (tmp = dis.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}
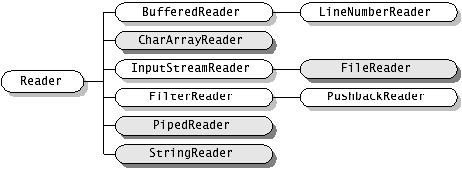
下面讲述下字符流
字符流跟字节流类似:其主要的节点流为:关于文件操作的FileReader和FileWriter,关于内存中字符数组的CharArrayReader和CharArrayWriter,关于管道的PipedReader和PipedWriter,唯一不同的是还有关于内存中字符串的StringReader和StringWriter.
public void testReaderAndWriter() throws IOException{
File file = new File("D:\\testIO.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String temp = null;
while((temp = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(temp);
}
}