webx学习
环境为ubuntu14.04 maven3, jdk1.6
使用maven构造一个webx项目,命令如下
mvn archetype:generate \ -DgroupId=com.alibaba.webx \ -DartifactId=tutorial1 \ -Dversion=1.0-SNAPSHOT \ -Dpackage=com.alibaba.webx.tutorial1 \ -DarchetypeArtifactId=archetype-webx-quickstart \ -DarchetypeGroupId=com.alibaba.citrus.sample \ -DarchetypeVersion=1.8 \ -DinteractiveMode=false
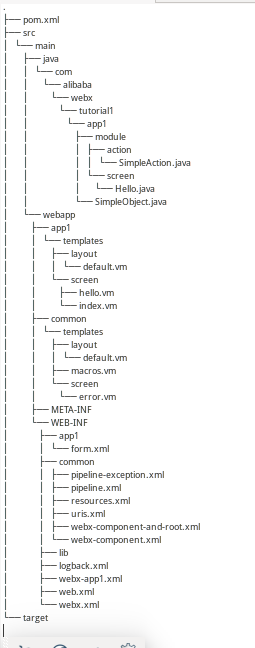
项目结构如下
1.listener
在web.xml中,配置了WebxContextLoaderListener,作用是用来启动root context的listener.
<!-- 装载/WEB-INF/webx.xml, /WEB-INF/webx-*.xml --> <listener> <listener-class>com.alibaba.citrus.webx.context.WebxContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
WebxContextLoaderListener继承了Spring的ContextLoaderListener,ContextLoaderListener继承了ContextLoader
并实现了ServletContextListener.
1.1ContextLoade,ContextLoader中存在静态代码块,加载默认的资源文件DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
1.2ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener的contextInitialized和contextDestroyed两个方法,所以容器将会在启动时调用contextInitialized方法.
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
ContextLoaderListener的createContextLoader方法返回的是空值,WebxContextLoaderListener重写了该方法,调用的是WebxContextLoaderListener的createContextLoader方法,该方法返回的是一个重写了getDefaultContextClass方法的WebxComponentsLoader对象.然后调用了该对象的initWebApplicationContext方法,根据调试结果来看,servletContext.getInitParameter("webxConfigurationName")的返回结果为null.
@Override
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) throws IllegalStateException,
BeansException {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
init();
return super.initWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
protected void init() {
setWebxConfigurationName(servletContext.getInitParameter("webxConfigurationName"));
}
/** 设置context中<code>WebxConfiguration</code>的名称。 */
public void setWebxConfigurationName(String webxConfigurationName) {
this.webxConfigurationName = trimToNull(webxConfigurationName);
}
然后调用父类ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法,在这里将会单步调试逐行注释说明
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//判断是否已经初始化,已初始化则抛出异常
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
//获取日志相关
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Determine parent for root web application context, if any.
//判断是否存在共享的父上下文容器,有则将其加载.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
//加载上下文,下面给出该方法的执行过程
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);
将此上下文和共享的父上下文保存.
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
/**
* Instantiate the root WebApplicationContext for this loader, either the
* default context class or a custom context class if specified.
* <p>This implementation expects custom contexts to implement the
* {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} interface.
* Can be overridden in subclasses.
* <p>In addition, {@link #customizeContext} gets called prior to refreshing the
* context, allowing subclasses to perform custom modifications to the context.
* @param sc current servlet context
* @param parent the parent ApplicationContext to use, or <code>null</code> if none
* @return the root WebApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, ApplicationContext parent) {
//从WebxComponentsLoader中调用determineContextClass方法加载上下文,determineContextClass见下面,
//最后返回结果为WebxComponentsContext.class
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
//判断该类是否实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// Assign the best possible id value.
//设置contextId,用于给底层的BeanFactory序列化使用
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
if (sc.getMajorVersion() == 2 && sc.getMinorVersion() < 5) {
// Servlet <= 2.4: resort to name specified in web.xml, if any.
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getServletContextName()));
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setServletContext(sc);
wac.setConfigLocation(sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM));
//调用WebxComponentsLoader的customizeContext方法,见下面
//在WebxComponentsLoader和WebxComponents中互相设置
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//根据WebxComponentsContext的一层层父类调用方法加载了webx的配置文件.
wac.refresh();
return wac;
}
@Override
protected final Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) throws ApplicationContextException {
//读取配置,调试结果为null
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]",
ex);
}
} else {
//该方法调用的就是重写过的getDefaultContextClass方法,具体看下面.
return getDefaultContextClass();
}
}
@Override
protected final ContextLoader createContextLoader() {
return new WebxComponentsLoader() {
@Override
protected Class<? extends WebxComponentsContext> getDefaultContextClass() {
//WebxContextLoaderListener.this.getDefaultContextClass()返回的是null
Class<? extends WebxComponentsContext> defaultContextClass = WebxContextLoaderListener.this
.getDefaultContextClass();
if (defaultContextClass == null) {
//调用父类即WebxComponentsLoader的getDefaultContextClass,返回WebxComponentsContext.class
defaultContextClass = super.getDefaultContextClass();
}
return defaultContextClass;
}
};
}
/** 在componentsContext.refresh()之前被调用。 */
@Override
protected void customizeContext(ServletContext servletContext, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext componentsContext) {
this.componentsContext = componentsContext;
if (componentsContext instanceof WebxComponentsContext) {
((WebxComponentsContext) componentsContext).setLoader(this);
}
}
refresh执行完成后,全部web应用会话和Spring容器初始化完成,后面再慢慢补充WebxComponentsContext的结构和拦截请求的过程