shiro源码分析(六)CredentialsMatcher 的案例分析
有了上一篇文章的原理分析,这一篇文章主要结合原理来进行使用。
shiro.ini配置为:
代码为:
此案例,对于jdbcRealm并没有配置CredentialsMatcher,它会使用默认的CredentialsMatcher即SimpleCredentialsMatcher,如下:
从上一篇文章中知道SimpleCredentialsMatcher不进行加密,仅仅匹配密码对应的字节数组。
所以代码中用户lg的登陆密码为123,则数据库中的密码也是明文123。
下面我们就开始进行加密,首先从CredentialsMatcher的第三个分支来说,使用HashedCredentialsMatcher来进行加密。加密方式为salt自定义、hash次数为2、加密算法为md5的加密过程。配置文件如下所示:
如用户"lg"明文密码为"123",假如salt为"www",hash次数为2,加密算法为"MD5",则密文可如下方式算出:
经过md5加密后变成byte数组,存在Hash的bytes属性中,然后使用hash.toHex()将byte数组转换成16进制的字符串,最终结果为"9bfe7c447c6c58389824bd8f1719b0bb",然后将该结果作为密码的密文存到数据库中,同时我们把salt也存到数据库中,则数据库中是如下记录:
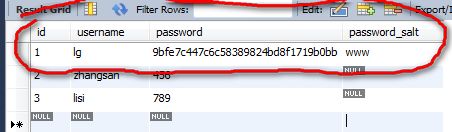
数据库的数据准备完毕,然后就开始代码设置。第一个设置就是,读取用户"lg"的记录的时候要把password_salt读取出来,即sql语句应该为DEFAULT_SALTED_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY =select password, password_salt from users where username = ?
然而默认的sql语句是:DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY=select password from users where username = ?
如何才能达到上述替换结果呢?
从上面代码中可以看到,需要设置JdbcRealm的saltStyle 为SaltStyle.COLUMN。saltStyle 是一个枚举类型,然而在ini配置文件中,并不支持设置枚举类型,只能暂时在代码中如下解决:
或者开涛大神又给出另外一种解决方案:注册一个Enum转换器,这个我准备在下一篇文章中给出ini配置文件的源码解析。
上述设置,就会使JdbcRealm 从数据库中读出用户"lg"的AuthenticationInfo信息中含有密文和salt。JdbcRealm下一步就要进行AuthenticationToken token(含有用户提交的明文密码"123") AuthenticationInfo info(含有密文密码"9bfe7c447c6c58389824bd8f1719b0bb",和salt "www")的匹配过程
hashProvidedCredentials方法:HashedCredentialsMatcher会将明文密码"123"进行如下类似的操作:
其中md5算法和hash次数2为我们所配置的,www则是从数据库中读出来的。
得到tokenHashedCredentials =上述的结果。
getCredentials方法:会将AuthenticationInfo info的密文密码先进行decode,如下:
为什么呢?因为我们之前算出的密文是byte数组,然后进行了16进制转换变成字符串,所以这里要将密文密码"9bfe7c447c6c58389824bd8f1719b0bb"先decode还原出byte数组
isStoredCredentialsHexEncoded()方法返回HashedCredentialsMatcher的storedCredentialsHexEncoded属性,默认为true,即会进行16进制的decode,正好符合我们的要求。如果设置为false,则要进行Base64解码。
tokenHashedCredentials 和上述getCredentials(AuthenticationInfo info)的结果的byte数组内容都是进过相同的算法和salt和hash次数,所以他们会匹配上,进而验证通过。
再来看下CredentialsMatcher的另一个分支PasswordMatcher的使用:
我们知道,根据上一篇文章的原理,PasswordMatcher会对AuthenticationInfo的密码进行String和Hash的判断。而我们的JdbcRealm在创建获取用户的AuthenticationInfo时,默认采用的是char数组的形式存储的,如下:
所以如果想让AuthenticationInfo存储的密码存储形式为Hash,则需要我们来自定义JdbcRealm。虽然是char数组,但PasswordMatcher对char数组转换成了String,如下:
所以会调用PasswordService的boolean passwordsMatch(Object submittedPlaintext, String encrypted)。
案例如下:
ini配置为:
第一个过程就是用户注册,对密码进行加密然后存到数据库的过程,我们全部使用PasswordMatcher最简单的默认配置,获取密文过程即用户注册的过程,先根据SecurityManager拿到JdbcRealm,再由JdbcRealm拿到PasswordMatcher,再根据PasswordMatcher拿到PasswordService,有了PasswordService就可以对明文密码进行加密了,打印的密文密码结果为:$shiro1$SHA-256$500000$y37r7l1qqEoIVXprJBfvbA==$065oJsZajS1yhGBUYYyxV1ThQ8brGw/9Koa6sDMmKAw=(每执行一次加密过程都会变,内部使用了随机生成salt的机制)
存到数据库中。如下截图:
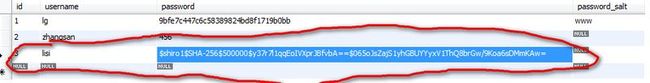
然后就可以直接用账号"lisi"和上述明文密码"456"来进行登陆,也可以登陆成功。
然后我们就分析下使用PasswordService对明文加密的过程和用户登录时的匹配过程(有了前一篇文章的原理分析,然后就能够更改默认配置,实现自己的需求)
先是PasswordService的各项默认配置:
我们jdbcRealm配置的credentialsMatcher是org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.PasswordMatcher,它的配置如下:
再看DefaultPasswordService的配置:
它内部使用的HashService:算法为DEFAULT_HASH_ALGORITHM即"SHA-256",hash次数为DEFAULT_HASH_ITERATIONS即500000,是否产生publicSalt为true,即一定会产生publicSalt(我们知道最终要参与计算的salt是publicSalt和privateSalt的合并,这里默认并没有设置DefaultHashService 的privateSalt)。
它内部使用的HashFormat:为Shiro1CryptFormat,它的format方法能将一个Hash格式化成一个字符串,它的parse方法能将一个上述格式化的字符串解析成一个Hash。
它内部使用的HashFormatFactory:为经过HashFormat格式化的字符串找到对应的HashFormat。
看完了DefaultPasswordService的基本配置,然后就来看下对明文密码的加密过程:
第一个过程,即将明文密码通过HashService的算法等配置加密成一个Hash
先创建一个HashRequest ,最终为new SimpleHashRequest(this.algorithmName, this.source, this.salt, this.iterations);这个Request只有明文密码不为空,其他都为空,iterations为0。通过hashService.computeHash(request)过程来生成一个new SimpleHash(algorithmName, source, salt, iterations);
algorithmName:来自hashService的算法名即SHA-256
source:即来自明文密码
salt:是hashService的privateSalt(从上文知道为空)和publicSalt的合并。由于hashService的generatePublicSalt属性为true(从上文知道),所以会生成publicSalt,是如下方式随机生成的
hash次数:上述SimpleHashRequest的hash次数为0,所以采用的是hashService的hash次数即500000
综上所述,hashService产生了一个new SimpleHashRequest("SHA-256", this.source, this.salt, 500000)的一个hash。
接下来就是用hashFormat来格式化这个Hash,过程如下:
MCF_PREFIX为:$shiro1$,TOKEN_DELIMITER为:$
格式化的字符串为: $shiro1$算法名字$hash次数$salt的base64编码$hash的base64编码
所以得到的加密密文的结果为:
$shiro1$SHA-256$500000$y37r7l1qqEoIVXprJBfvbA==$065oJsZajS1yhGBUYYyxV1ThQ8brGw/9Koa6sDMmKAw=
所以这个密文每一部分都代表着一定的内容,从而可以实现parse,得到采用的算法、hash次数、salt信息。所以在用户登陆的时候,就可以将用户的明文密码仍按照此配置进行一次加密来匹配,即可断定用户的密码是否正确,这其实就是密码匹配过程所采用的方式。
上述案例是使用PasswordMatcher默认配置,现在如果我们想更改算法、salt、和hash次数来满足我们的需求。
PasswordMatcher是依靠PasswordService,默认的PasswordService是DefaultPasswordService,DefaultPasswordService又是靠HashService(默认是DefaultHashService)的算法、salt、hash次数等配置来加密的,所以我们要更改算法、salt、hash次数则要DefaultHashService进行设置,如我们想用md5算法来加密、publicSalt为随机生成,hash次数为3次,则ini配置文件要如下更改:
PasswordMatcher是依靠PasswordService来实现加密和匹配的,所以我们可以自定义一个PasswordService来按照我们自己约定的加密规则来实现加密,如下所示:
加密过程和匹配过程都采用相同的步骤来实现匹配。以上便是一个简单的PasswordService实现,ini配置更改为:
作者: 乒乓狂魔
shiro.ini配置为:
[main] #realm dataSource=com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource dataSource.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver dataSource.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro dataSource.user=XXXXXX dataSource.password=XXXXX jdbcRealm=org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm jdbcRealm.dataSource=$dataSource jdbcRealm.permissionsLookupEnabled=true securityManager.realms=$jdbcRealm
代码为:
public class ShiroTest {
@Test
public void testHelloworld() {
init();
Subject subject=login("lg","123");
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("role1"));
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("role2"));
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("role3"));
}
private Subject login(String userName,String password){
//3、得到Subject及创建用户名/密码身份验证Token(即用户身份/凭证)
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName,password);
subject.login(token);
return subject;
}
private void init(){
//1、获取SecurityManager工厂,此处使用Ini配置文件初始化SecurityManager
Factory<org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager> factory =
new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
//2、得到SecurityManager实例 并绑定给SecurityUtils
org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
}
}
此案例,对于jdbcRealm并没有配置CredentialsMatcher,它会使用默认的CredentialsMatcher即SimpleCredentialsMatcher,如下:
public AuthenticatingRealm() {
this(null, new SimpleCredentialsMatcher());
}
public AuthenticatingRealm(CacheManager cacheManager) {
this(cacheManager, new SimpleCredentialsMatcher());
}
从上一篇文章中知道SimpleCredentialsMatcher不进行加密,仅仅匹配密码对应的字节数组。
所以代码中用户lg的登陆密码为123,则数据库中的密码也是明文123。
下面我们就开始进行加密,首先从CredentialsMatcher的第三个分支来说,使用HashedCredentialsMatcher来进行加密。加密方式为salt自定义、hash次数为2、加密算法为md5的加密过程。配置文件如下所示:
[main] #realm dataSource=com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource dataSource.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver dataSource.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro dataSource.user=XXXX dataSource.password=XXXX jdbcRealm=org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm jdbcRealm.dataSource=$dataSource jdbcRealm.permissionsLookupEnabled=true credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher.hashAlgorithmName=MD5 credentialsMatcher.hashIterations=2 jdbcRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher securityManager.realms=$jdbcRealm
如用户"lg"明文密码为"123",假如salt为"www",hash次数为2,加密算法为"MD5",则密文可如下方式算出:
Hash hash=new SimpleHash("MD5", new SimpleByteSource("123"),new SimpleByteSource("www"),2);
System.out.println(hash.toHex());
经过md5加密后变成byte数组,存在Hash的bytes属性中,然后使用hash.toHex()将byte数组转换成16进制的字符串,最终结果为"9bfe7c447c6c58389824bd8f1719b0bb",然后将该结果作为密码的密文存到数据库中,同时我们把salt也存到数据库中,则数据库中是如下记录:

数据库的数据准备完毕,然后就开始代码设置。第一个设置就是,读取用户"lg"的记录的时候要把password_salt读取出来,即sql语句应该为DEFAULT_SALTED_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY =select password, password_salt from users where username = ?
然而默认的sql语句是:DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY=select password from users where username = ?
如何才能达到上述替换结果呢?
public void setSaltStyle(SaltStyle saltStyle) {
this.saltStyle = saltStyle;
if (saltStyle == SaltStyle.COLUMN && authenticationQuery.equals(DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY)) {
authenticationQuery = DEFAULT_SALTED_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY;
}
}
从上面代码中可以看到,需要设置JdbcRealm的saltStyle 为SaltStyle.COLUMN。saltStyle 是一个枚举类型,然而在ini配置文件中,并不支持设置枚举类型,只能暂时在代码中如下解决:
Collection<Realm> realms=((RealmSecurityManager) securityManager).getRealms();
JdbcRealm jdbcRealm=(JdbcRealm)realms.toArray()[0];
jdbcRealm.setSaltStyle(SaltStyle.COLUMN);
或者开涛大神又给出另外一种解决方案:注册一个Enum转换器,这个我准备在下一篇文章中给出ini配置文件的源码解析。
上述设置,就会使JdbcRealm 从数据库中读出用户"lg"的AuthenticationInfo信息中含有密文和salt。JdbcRealm下一步就要进行AuthenticationToken token(含有用户提交的明文密码"123") AuthenticationInfo info(含有密文密码"9bfe7c447c6c58389824bd8f1719b0bb",和salt "www")的匹配过程
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
Object tokenHashedCredentials = hashProvidedCredentials(token, info);
Object accountCredentials = getCredentials(info);
return equals(tokenHashedCredentials, accountCredentials);
}
hashProvidedCredentials方法:HashedCredentialsMatcher会将明文密码"123"进行如下类似的操作:
new SimpleHash("MD5", new SimpleByteSource("123"),new SimpleByteSource("www"),2)
其中md5算法和hash次数2为我们所配置的,www则是从数据库中读出来的。
得到tokenHashedCredentials =上述的结果。
getCredentials方法:会将AuthenticationInfo info的密文密码先进行decode,如下:
protected Object getCredentials(AuthenticationInfo info) {
Object credentials = info.getCredentials();
byte[] storedBytes = toBytes(credentials);
if (credentials instanceof String || credentials instanceof char[]) {
//account.credentials were a char[] or String, so
//we need to do text decoding first:
if (isStoredCredentialsHexEncoded()) {
storedBytes = Hex.decode(storedBytes);
} else {
storedBytes = Base64.decode(storedBytes);
}
}
AbstractHash hash = newHashInstance();
hash.setBytes(storedBytes);
return hash;
}
为什么呢?因为我们之前算出的密文是byte数组,然后进行了16进制转换变成字符串,所以这里要将密文密码"9bfe7c447c6c58389824bd8f1719b0bb"先decode还原出byte数组
isStoredCredentialsHexEncoded()方法返回HashedCredentialsMatcher的storedCredentialsHexEncoded属性,默认为true,即会进行16进制的decode,正好符合我们的要求。如果设置为false,则要进行Base64解码。
tokenHashedCredentials 和上述getCredentials(AuthenticationInfo info)的结果的byte数组内容都是进过相同的算法和salt和hash次数,所以他们会匹配上,进而验证通过。
再来看下CredentialsMatcher的另一个分支PasswordMatcher的使用:
我们知道,根据上一篇文章的原理,PasswordMatcher会对AuthenticationInfo的密码进行String和Hash的判断。而我们的JdbcRealm在创建获取用户的AuthenticationInfo时,默认采用的是char数组的形式存储的,如下:
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
String username = upToken.getUsername();
// Null username is invalid
if (username == null) {
throw new AccountException("Null usernames are not allowed by this realm.");
}
Connection conn = null;
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = null;
try {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
String password = null;
String salt = null;
switch (saltStyle) {
case NO_SALT:
password = getPasswordForUser(conn, username)[0];
break;
case CRYPT:
// TODO: separate password and hash from getPasswordForUser[0]
throw new ConfigurationException("Not implemented yet");
//break;
case COLUMN:
String[] queryResults = getPasswordForUser(conn, username);
password = queryResults[0];
salt = queryResults[1];
break;
case EXTERNAL:
password = getPasswordForUser(conn, username)[0];
salt = getSaltForUser(username);
}
if (password == null) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("No account found for user [" + username + "]");
}
//重点在这里在这里在这里在这里在这里在这里在这里 password.toCharArray()变成了char数组
info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, password.toCharArray(), getName());
if (salt != null) {
info.setCredentialsSalt(ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
final String message = "There was a SQL error while authenticating user [" + username + "]";
if (log.isErrorEnabled()) {
log.error(message, e);
}
// Rethrow any SQL errors as an authentication exception
throw new AuthenticationException(message, e);
} finally {
JdbcUtils.closeConnection(conn);
}
return info;
}
所以如果想让AuthenticationInfo存储的密码存储形式为Hash,则需要我们来自定义JdbcRealm。虽然是char数组,但PasswordMatcher对char数组转换成了String,如下:
protected Object getStoredPassword(AuthenticationInfo storedAccountInfo) {
Object stored = storedAccountInfo != null ? storedAccountInfo.getCredentials() : null;
//fix for https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SHIRO-363
if (stored instanceof char[]) {
stored = new String((char[])stored);
}
return stored;
}
所以会调用PasswordService的boolean passwordsMatch(Object submittedPlaintext, String encrypted)。
案例如下:
@Test
public void testHelloworld() {
init();
register("lisi","456");
Subject subject=login("lisi","456");
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("role1"));
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("role2"));
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("role3"));
}
public void register(String username,String password){
JdbcRealm jdbcRealm=getJdbcRelam();
PasswordMatcher passwordMatcher=(PasswordMatcher) jdbcRealm.getCredentialsMatcher();
String encryptPassword=passwordMatcher.getPasswordService().encryptPassword(password);
//保存用户名和密文到数据库,这里不再做
System.out.println(encryptPassword);
}
private Subject login(String userName,String password){
//3、得到Subject及创建用户名/密码身份验证Token(即用户身份/凭证)
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName,password);
subject.login(token);
return subject;
}
private void init(){
//1、获取SecurityManager工厂,此处使用Ini配置文件初始化SecurityManager
Factory<org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager> factory =
new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
//2、得到SecurityManager实例 并绑定给SecurityUtils
org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
JdbcRealm jdbcRealm=getJdbcRelam();
jdbcRealm.setSaltStyle(SaltStyle.COLUMN);
}
public JdbcRealm getJdbcRelam(){
Collection<Realm> realms=((RealmSecurityManager)SecurityUtils.getSecurityManager()).getRealms();
return (JdbcRealm)realms.toArray()[0];
}
ini配置为:
[main] #realm dataSource=com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource dataSource.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver dataSource.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro dataSource.user=XXXX dataSource.password=XXXX jdbcRealm=org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm jdbcRealm.dataSource=$dataSource jdbcRealm.permissionsLookupEnabled=true credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.PasswordMatcher jdbcRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher securityManager.realms=$jdbcRealm
第一个过程就是用户注册,对密码进行加密然后存到数据库的过程,我们全部使用PasswordMatcher最简单的默认配置,获取密文过程即用户注册的过程,先根据SecurityManager拿到JdbcRealm,再由JdbcRealm拿到PasswordMatcher,再根据PasswordMatcher拿到PasswordService,有了PasswordService就可以对明文密码进行加密了,打印的密文密码结果为:$shiro1$SHA-256$500000$y37r7l1qqEoIVXprJBfvbA==$065oJsZajS1yhGBUYYyxV1ThQ8brGw/9Koa6sDMmKAw=(每执行一次加密过程都会变,内部使用了随机生成salt的机制)
存到数据库中。如下截图:

然后就可以直接用账号"lisi"和上述明文密码"456"来进行登陆,也可以登陆成功。
然后我们就分析下使用PasswordService对明文加密的过程和用户登录时的匹配过程(有了前一篇文章的原理分析,然后就能够更改默认配置,实现自己的需求)
先是PasswordService的各项默认配置:
我们jdbcRealm配置的credentialsMatcher是org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.PasswordMatcher,它的配置如下:
public class PasswordMatcher implements CredentialsMatcher {
private PasswordService passwordService;
public PasswordMatcher() {
this.passwordService = new DefaultPasswordService();
}
//内部使用了DefaultPasswordService
}
再看DefaultPasswordService的配置:
public class DefaultPasswordService implements HashingPasswordService {
public static final String DEFAULT_HASH_ALGORITHM = "SHA-256";
public static final int DEFAULT_HASH_ITERATIONS = 500000; //500,000
private HashService hashService;
private HashFormat hashFormat;
private HashFormatFactory hashFormatFactory;
private volatile boolean hashFormatWarned; //used to avoid excessive log noise
public DefaultPasswordService() {
this.hashFormatWarned = false;
DefaultHashService hashService = new DefaultHashService();
hashService.setHashAlgorithmName(DEFAULT_HASH_ALGORITHM);
hashService.setHashIterations(DEFAULT_HASH_ITERATIONS);
hashService.setGeneratePublicSalt(true); //always want generated salts for user passwords to be most secure
this.hashService = hashService;
this.hashFormat = new Shiro1CryptFormat();
this.hashFormatFactory = new DefaultHashFormatFactory();
}
//略
}
它内部使用的HashService:算法为DEFAULT_HASH_ALGORITHM即"SHA-256",hash次数为DEFAULT_HASH_ITERATIONS即500000,是否产生publicSalt为true,即一定会产生publicSalt(我们知道最终要参与计算的salt是publicSalt和privateSalt的合并,这里默认并没有设置DefaultHashService 的privateSalt)。
它内部使用的HashFormat:为Shiro1CryptFormat,它的format方法能将一个Hash格式化成一个字符串,它的parse方法能将一个上述格式化的字符串解析成一个Hash。
它内部使用的HashFormatFactory:为经过HashFormat格式化的字符串找到对应的HashFormat。
看完了DefaultPasswordService的基本配置,然后就来看下对明文密码的加密过程:
public String encryptPassword(Object plaintext) {
Hash hash = hashPassword(plaintext);
checkHashFormatDurability();
return this.hashFormat.format(hash);
}
第一个过程,即将明文密码通过HashService的算法等配置加密成一个Hash
public Hash hashPassword(Object plaintext) {
ByteSource plaintextBytes = createByteSource(plaintext);
if (plaintextBytes == null || plaintextBytes.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
HashRequest request = createHashRequest(plaintextBytes);
return hashService.computeHash(request);
}
protected HashRequest createHashRequest(ByteSource plaintext) {
return new HashRequest.Builder().setSource(plaintext).build();
}
先创建一个HashRequest ,最终为new SimpleHashRequest(this.algorithmName, this.source, this.salt, this.iterations);这个Request只有明文密码不为空,其他都为空,iterations为0。通过hashService.computeHash(request)过程来生成一个new SimpleHash(algorithmName, source, salt, iterations);
algorithmName:来自hashService的算法名即SHA-256
source:即来自明文密码
salt:是hashService的privateSalt(从上文知道为空)和publicSalt的合并。由于hashService的generatePublicSalt属性为true(从上文知道),所以会生成publicSalt,是如下方式随机生成的
publicSalt = getRandomNumberGenerator().nextBytes();
hash次数:上述SimpleHashRequest的hash次数为0,所以采用的是hashService的hash次数即500000
综上所述,hashService产生了一个new SimpleHashRequest("SHA-256", this.source, this.salt, 500000)的一个hash。
接下来就是用hashFormat来格式化这个Hash,过程如下:
public String format(Hash hash) {
if (hash == null) {
return null;
}
String algorithmName = hash.getAlgorithmName();
ByteSource salt = hash.getSalt();
int iterations = hash.getIterations();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(MCF_PREFIX).append(algorithmName).append(TOKEN_DELIMITER).append(iterations).append(TOKEN_DELIMITER);
if (salt != null) {
sb.append(salt.toBase64());
}
sb.append(TOKEN_DELIMITER);
sb.append(hash.toBase64());
return sb.toString();
}
MCF_PREFIX为:$shiro1$,TOKEN_DELIMITER为:$
格式化的字符串为: $shiro1$算法名字$hash次数$salt的base64编码$hash的base64编码
所以得到的加密密文的结果为:
$shiro1$SHA-256$500000$y37r7l1qqEoIVXprJBfvbA==$065oJsZajS1yhGBUYYyxV1ThQ8brGw/9Koa6sDMmKAw=
所以这个密文每一部分都代表着一定的内容,从而可以实现parse,得到采用的算法、hash次数、salt信息。所以在用户登陆的时候,就可以将用户的明文密码仍按照此配置进行一次加密来匹配,即可断定用户的密码是否正确,这其实就是密码匹配过程所采用的方式。
上述案例是使用PasswordMatcher默认配置,现在如果我们想更改算法、salt、和hash次数来满足我们的需求。
PasswordMatcher是依靠PasswordService,默认的PasswordService是DefaultPasswordService,DefaultPasswordService又是靠HashService(默认是DefaultHashService)的算法、salt、hash次数等配置来加密的,所以我们要更改算法、salt、hash次数则要DefaultHashService进行设置,如我们想用md5算法来加密、publicSalt为随机生成,hash次数为3次,则ini配置文件要如下更改:
[main] #realm dataSource=com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource dataSource.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver dataSource.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro dataSource.user=root dataSource.password=ligang jdbcRealm=org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm jdbcRealm.dataSource=$dataSource jdbcRealm.permissionsLookupEnabled=true hashService=org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.DefaultHashService hashService.hashAlgorithmName=MD5 hashService.hashIterations=3 hashService.generatePublicSalt=true passwordService=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.DefaultPasswordService passwordService.hashService=$hashService credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.PasswordMatcher credentialsMatcher.passwordService=$passwordService jdbcRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher securityManager.realms=$jdbcRealm
PasswordMatcher是依靠PasswordService来实现加密和匹配的,所以我们可以自定义一个PasswordService来按照我们自己约定的加密规则来实现加密,如下所示:
public class MyPasswordService implements PasswordService{
private String algorithmName="MD5";
private int iterations=5;
private String salt="2014";
private HashFormat hashFormat=new Shiro1CryptFormat();
@Override
public String encryptPassword(Object plaintextPassword)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
Hash hash=new SimpleHash(algorithmName,ByteSource.Util.bytes(plaintextPassword),ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt), iterations);
return hashFormat.format(hash);
}
@Override
public boolean passwordsMatch(Object submittedPlaintext, String encrypted) {
Hash hash=new SimpleHash(algorithmName,ByteSource.Util.bytes(submittedPlaintext),ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt), iterations);
String password=hashFormat.format(hash);
return encrypted.equals(password);
}
}
加密过程和匹配过程都采用相同的步骤来实现匹配。以上便是一个简单的PasswordService实现,ini配置更改为:
[main] #realm dataSource=com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource dataSource.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver dataSource.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro dataSource.user=root dataSource.password=ligang jdbcRealm=org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm jdbcRealm.dataSource=$dataSource jdbcRealm.permissionsLookupEnabled=true passwordService=com.lg.shiro.MyPasswordService credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.PasswordMatcher credentialsMatcher.passwordService=$passwordService jdbcRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher securityManager.realms=$jdbcRealm
作者: 乒乓狂魔