Flex与Java通信之HttpService方式
Flex用RemoteObject方式与Java通信是最常用的方式,这是一种最直观的方式。当然Flex也可以用HttpService与服务器类如servlet通信,这也是本次学习的重点。
这次学习是在上节的基础上进行的。本节学习用到的LoginEvent.as,LoginModule.sa文件代码如上节所示。
好了,新建一个servlet类LoginServlet.java,代码如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
package com.it161.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
publicclass LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protectedvoid service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generatedmethod stub
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter out=resp.getWriter();
String username=req.getParameter("username");
String passworld=req.getParameter("passworld");
//System.out.println(username+":"+passworld);
if(username.equals("admin")&&passworld.equals("123")){
out.print(true);
}else{
out.print(false);
}
}
}
|
这个servlet在web.xml中的配置如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<servlet>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.yqsn.servlet.LoginServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/LoginServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
|
将MyEclipse切换到flash视图,新建一个application文件HttpServiceDemo.mxml,代码如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<s:Application xmlns:fx=" http://ns.adobe.com/mxml/2009"
xmlns:s=" library://ns.adobe.com/flex/spark"
xmlns:mx=" library://ns.adobe.com/flex/mx" minWidth="955" minHeight="600">
<fx:Script>
<![CDATA[
import com.flex.ases.LoginEvent;
import com.flex.ases.LoginMess;
import com.flex.module.LoginModule;
import mx.controls.Alert;
import mx.managers.PopUpManager;
import mx.rpc.events.FaultEvent;
import mx.rpc.events.ResultEvent;
privatevar loginModule:LoginModule=new LoginModule();
[Bindable]
private var username:String;
[Bindable]
private varpassworld:String;
protectedfunction login_clickHandler(event:MouseEvent):void
{
// TODOAuto-generated method stub
PopUpManager.addPopUp(loginModule,this,true);
PopUpManager.centerPopUp(this.loginModule);
loginModule.addEventListener(LoginEvent.LOGIN_EVENT,loginHander);
}
publicfunction loginHander(event:LoginEvent):void{
//varobj:Object=event.loginMess as Object;
username=event.loginMess['username'];
passworld=event.loginMess['passworld'];
httpServiceSend.send();
}
protectedfunction httpServiceSend_faultHandler(event:FaultEvent):void
{
// TODOAuto-generated method stub
Alert.show(event.fault.message as String,"提示");
}
protectedfunction httpServiceSend_resultHandler(event:ResultEvent):void
{
// TODOAuto-generated method stub
var result:Boolean=event.result as Boolean;
if(result==true){
Alert.show(username+",欢迎您回来!","提示");
aaa.text=username+",欢迎您回来!";
login.label="";
bbb.text="";
}else{
Alert.show("对不起,用户名或密码不存在!","提示");
}
//Alert.show("成功了!");
}
]]>
</fx:Script>
<fx:Declarations>
<!-- Place non-visualelements (e.g., services, value objects) here -->
<s:HTTPService id="httpServiceSend" url=" http://localhost:8000/JavaAndFlexDemo/LoginServlet" useProxy="false"fault="httpServiceSend_faultHandler(event)"result="httpServiceSend_resultHandler(event)" >
<s:request>
<username>{username}</username>
<passworld>{passworld}</passworld>
</s:request>
</s:HTTPService>
</fx:Declarations>
<s:Label x="200" y="150" width="182" height="27" fontSize="18" id="aaa" text="您还没有登陆,现在就" verticalAlign="middle"/>
<mx:LinkButton x="393" y="150" width="57" height="27" label="登陆" id="login" fontSize="18"click="login_clickHandler(event)"/>
<s:Label x="459" y="150" width="37" height="27" id="bbb" fontSize="18" text="吧!" verticalAlign="middle"/>
</s:Application>
|
从代码中我们可以看出,我们先定义一个HttpServlet发送请求httpServiceSend,然后通过下面这种方式存值:
|
1
2
3
4
|
<s:request >
<username>{username}</username>
<passworld>{passworld}</passworld>
</s:request>
|
这种方式很简单,我们在后台通过request. getParameter(“参数名”)取值就可以了,当然我们也可以在loginHander(event:LoginEvent)函数中通过下面方式存值并发送请求:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public functionloginHander(event:LoginEvent):void{
//varobj:Object=event.loginMess as Object;
username=event.loginMess['username'];
passworld=event.loginMess['passworld'];
var obj:Object=new Object;
obj.username=username;
obj.passworld=passworld;
httpServiceSend.send(obj);
}
|
运行结果是一样的,你可以试试。
好了,程序算是完成了,现在开始验收结果。
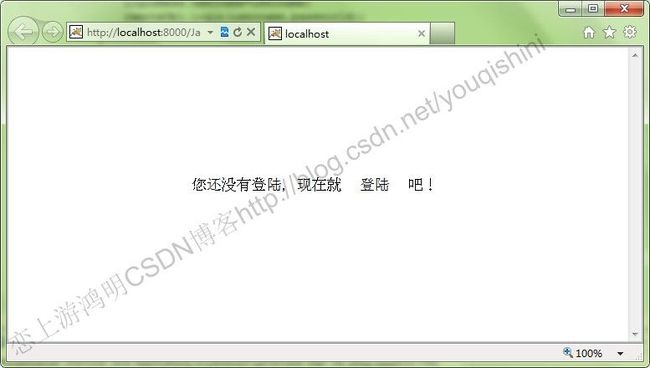
打开服务器并部署项目,运行felx页面RemoteObjectDemo.mxml,如下所示:
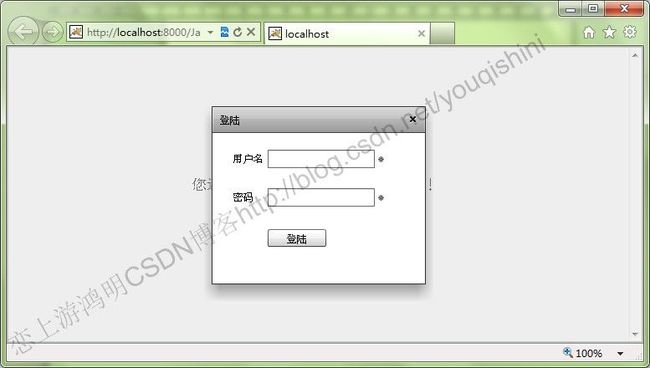
当我们点击“登陆”按钮后,弹出module页面,如下所示:
当我们输入的用户名和密码都正确时则提示你登陆正确:
输入错误则提示你输入不正确:
可以看出,我们输入的用户名与密码已经用httpservice方式发送到后台并且成功接受了并将结果返回给前台了。
好了,就学习这么多,下节将学习WebService方式。
原创文章,转载请注明出处:http://www.it161.com/article/webDetail?articleid=140111230433
更多原创内容,请访问:http://www.it161.com/