深入理解WCF系统体系(之二:WCF客户端如何构建?(下))
通过之前的介绍,大家都应该有个共识:客户端通过透明代理建立对应的实际代理对服务进行调用,而在WCF在实际代理对象类型为ServiceChannelProxy。实际代理对象ServiceChannelProxy的建立又是通过它的构造函数完成。先来看看它的构造函数:
{
if (!MessageDirectionHelper.IsDefined(direction))
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( " direction "));
}
this.interfaceType = interfaceType;
this.proxiedType = proxiedType;
this.serviceChannel = serviceChannel;
this.proxyRuntime = serviceChannel.ClientRuntime.GetRuntime();
this.methodDataCache = new MethodDataCache();
this.objectWrapper = new MbrObject( this, proxiedType);
}
在WCF客户端中,ChannelFactory通过绑定创建; 在 ChannelFactory创建的过程中,会初始化ServiceEndpoint;通过ServiceEndpoint又创建ServiceChannelFactory;通过ServiceChannelFactory
创建ServiceChannel。而ServiceChannelProxy接口中的Type类型就是契约接口类型,MessageDirection
是一个枚举类型,有Input\Output两个枚举值。这些类型,真实代理对象就创建成功。
通过以上述过程,真实代理对象就创建成功。
首先看看一下代码:
using ( var channkeFactory = new DuplexChannelFactory<ICalculator>(instanceContext, " calculator "))
{
ICalculator proxy = channkeFactory.CreateChannel();
}
码分析得出:
{
public TChannel CreateChannel(InstanceContext callbackInstance)
{
return this.CreateChannel(callbackInstance, base.CreateEndpointAddress( base.Endpoint), null);
}
public static TChannel CreateChannel( object callbackObject, string endpointConfigurationName)
{
return DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>.CreateChannel(DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>.GetInstanceContextForObject(callbackObject), endpointConfigurationName);
}
public override TChannel CreateChannel(EndpointAddress address, Uri via)
{
return this.CreateChannel( base.CallbackInstance, address, via);
}
public TChannel CreateChannel(InstanceContext callbackInstance, EndpointAddress address)
{
if (address == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperArgumentNull( " address ");
}
return this.CreateChannel(callbackInstance, address, address.Uri);
}
public static TChannel CreateChannel(InstanceContext callbackInstance, string endpointConfigurationName)
{
TChannel channel = new DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>(callbackInstance, endpointConfigurationName).CreateChannel();
ChannelFactory<TChannel>.SetFactoryToAutoClose(channel);
return channel;
}
public static TChannel CreateChannel( object callbackObject, Binding binding, EndpointAddress endpointAddress)
{
return DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>.CreateChannel(DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>.GetInstanceContextForObject(callbackObject), binding, endpointAddress);
}
public static TChannel CreateChannel(InstanceContext callbackInstance, Binding binding, EndpointAddress endpointAddress)
{
TChannel channel = new DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>(callbackInstance, binding, endpointAddress).CreateChannel();
ChannelFactory<TChannel>.SetFactoryToAutoClose(channel);
return channel;
}
public virtual TChannel CreateChannel(InstanceContext callbackInstance, EndpointAddress address, Uri via)
{
if (address == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperArgumentNull( " address ");
}
if (( base.CallbackType != null) && (callbackInstance == null))
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " SFxCreateDuplexChannelNoCallback1 ")));
}
if (callbackInstance == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " SFxCreateDuplexChannelNoCallback ")));
}
if (callbackInstance.UserObject == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " SFxCreateDuplexChannelNoCallbackUserObject ")));
}
if (! base.HasDuplexOperations())
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " SFxCreateDuplexChannel1 ", new object[] { base.Endpoint.Contract.Name })));
}
Type c = callbackInstance.UserObject.GetType();
Type callbackContractType = base.Endpoint.Contract.CallbackContractType;
if ((callbackContractType != null) && !callbackContractType.IsAssignableFrom(c))
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " SFxCreateDuplexChannelBadCallbackUserObject ", new object[] { callbackContractType })));
}
base.EnsureOpened();
TChannel local = (TChannel) base.ServiceChannelFactory.CreateChannel( typeof(TChannel), address, via);
IDuplexContextChannel channel = local as IDuplexContextChannel;
if (channel != null)
{
channel.CallbackInstance = callbackInstance;
}
return local;
}
public static TChannel CreateChannel( object callbackObject, Binding binding, EndpointAddress endpointAddress, Uri via)
{
return DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>.CreateChannel(DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>.GetInstanceContextForObject(callbackObject), binding, endpointAddress, via);
}
public static TChannel CreateChannel(InstanceContext callbackInstance, Binding binding, EndpointAddress endpointAddress, Uri via)
{
TChannel channel = new DuplexChannelFactory<TChannel>(callbackInstance, binding).CreateChannel(endpointAddress, via);
ChannelFactory<TChannel>.SetFactoryToAutoClose(channel);
return channel;
}
}
{
public TChannel CreateChannel()
{
return this.CreateChannel( base.CreateEndpointAddress( base.Endpoint), null);
}
public virtual TChannel CreateChannel(EndpointAddress address, Uri via)
{
TChannel local;
bool traceOpenAndClose = base.TraceOpenAndClose;
try
{
using (ServiceModelActivity activity = (DiagnosticUtility.ShouldUseActivity && base.TraceOpenAndClose) ? ServiceModelActivity.CreateBoundedActivity() : null)
{
if (DiagnosticUtility.ShouldUseActivity)
{
ServiceModelActivity.Start(activity, this.OpenActivityName, this.OpenActivityType);
base.TraceOpenAndClose = false;
}
if (address == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperArgumentNull( " address ");
}
if ( base.HasDuplexOperations())
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " SFxCreateNonDuplexChannel1 ", new object[] { base.Endpoint.Contract.Name })));
}
base.EnsureOpened();
local = (TChannel) this.ServiceChannelFactory.CreateChannel( typeof(TChannel), address, via);
}
}
finally
{
base.TraceOpenAndClose = traceOpenAndClose;
}
return local;
}
}
注意到这一句:
local = (TChannel) this.ServiceChannelFactory.CreateChannel(typeof(TChannel), address, via);
继续分析ServiceChannelFactory.CreateChannel(typeof(TChannel), address, via)的过程:
{
public object CreateChannel(Type channelType, EndpointAddress address, Uri via)
{
if (via == null)
{
via = this.ClientRuntime.Via;
if (via == null)
{
via = address.Uri;
}
}
ServiceChannel serviceChannel = this.CreateServiceChannel(address, via);
serviceChannel.Proxy = CreateProxy(channelType, channelType, MessageDirection.Input, serviceChannel);
serviceChannel.ClientRuntime.GetRuntime().InitializeChannel((IClientChannel) serviceChannel.Proxy);
OperationContext current = OperationContext.Current;
if ((current != null) && (current.InstanceContext != null))
{
current.InstanceContext.WmiChannels.Add((IChannel) serviceChannel.Proxy);
serviceChannel.WmiInstanceContext = current.InstanceContext;
}
return serviceChannel.Proxy;
}
[SecuritySafeCritical]
internal static object CreateProxy(Type interfaceType, Type proxiedType, MessageDirection direction, ServiceChannel serviceChannel)
{
if (!proxiedType.IsInterface)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " SFxChannelFactoryTypeMustBeInterface ")));
}
ServiceChannelProxy proxy = new ServiceChannelProxy(interfaceType, proxiedType, direction, serviceChannel);
return proxy.GetTransparentProxy();
}
}
CreateChannel方法返回的是serviceChannel.Proxy,而serviceChannel.Proxy又是
proxy.GetTransparentProxy()获取到的TransparentProxy.
下面来看看Invoke方法。
{
IMessage message3;
try
{
IMethodCallMessage methodCall = message as IMethodCallMessage;
if (methodCall == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new ArgumentException(SR.GetString( " SFxExpectedIMethodCallMessage ")));
}
MethodData methodData = this.GetMethodData(methodCall);
switch (methodData.MethodType)
{
case MethodType.Service:
return this.InvokeService(methodCall, methodData.Operation);
case MethodType.BeginService:
return this.InvokeBeginService(methodCall, methodData.Operation);
case MethodType.EndService:
return this.InvokeEndService(methodCall, methodData.Operation);
case MethodType.Channel:
return this.InvokeChannel(methodCall);
case MethodType.Object:
return this.InvokeObject(methodCall);
case MethodType.GetType:
return this.InvokeGetType(methodCall);
}
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException( string.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, " Invalid proxy method type ", new object[ 0])));
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
if (Fx.IsFatal(exception))
{
throw;
}
message3 = this.CreateReturnMessage(exception, message as IMethodCallMessage);
}
return message3;
}
3.1、MethodData的Service类型
MethodType.Service为同步调用方式;MethodType.BeginService、MethodType.EndService为异步方式。
首先看看MethodType.Service,它调用了ServiceChannelProxy的InvokeService方法完成。InvokeService方法定义如下:
{
object[] objArray;
object[] ins = operation.MapSyncInputs(methodCall, out objArray);
object ret = this.serviceChannel.Call(operation.Action, operation.IsOneWay, operation, ins, objArray);
object[] returnArgs = operation.MapSyncOutputs(methodCall, objArray, ref ret);
return this.CreateReturnMessage(ret, returnArgs, methodCall);
}
可以看出,在 InvokeService中,通过serviceChannel.Call返回调用结果,最有又通过ServerChannelProxy的
CreateReturnMessage方法返回Message。
ProxyOperationRuntime在WCF中也是很重要的对象。它的定义以及构造函数如下:
{
// Fields
private string action;
private MethodInfo beginMethod;
private bool deserializeReply;
internal static readonly object[] EmptyArray = new object[ 0];
private ParameterInfo[] endOutParams;
private readonly IClientFaultFormatter faultFormatter;
private readonly IClientMessageFormatter formatter;
private ParameterInfo[] inParams;
private readonly bool isInitiating;
private readonly bool isOneWay;
private readonly bool isTerminating;
private readonly string name;
internal static readonly ParameterInfo[] NoParams = new ParameterInfo[ 0];
private ParameterInfo[] outParams;
private readonly IParameterInspector[] parameterInspectors;
private readonly ImmutableClientRuntime parent;
private string replyAction;
private ParameterInfo returnParam;
private bool serializeRequest;
private MethodInfo syncMethod;
// Methods
internal ProxyOperationRuntime(ClientOperation operation, ImmutableClientRuntime parent)
{
if (operation == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperArgumentNull( " operation ");
}
if (parent == null)
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperArgumentNull( " parent ");
}
this.parent = parent;
this.formatter = operation.Formatter;
this.isInitiating = operation.IsInitiating;
this.isOneWay = operation.IsOneWay;
this.isTerminating = operation.IsTerminating;
this.name = operation.Name;
this.parameterInspectors = EmptyArray<IParameterInspector>.ToArray(operation.ParameterInspectors);
this.faultFormatter = operation.FaultFormatter;
this.serializeRequest = operation.SerializeRequest;
this.deserializeReply = operation.DeserializeReply;
this.action = operation.Action;
this.replyAction = operation.ReplyAction;
this.beginMethod = operation.BeginMethod;
this.syncMethod = operation.SyncMethod;
if ( this.beginMethod != null)
{
this.inParams = ServiceReflector.GetInputParameters( this.beginMethod, true);
if ( this.syncMethod != null)
{
this.outParams = ServiceReflector.GetOutputParameters( this.syncMethod, false);
}
else
{
this.outParams = NoParams;
}
this.endOutParams = ServiceReflector.GetOutputParameters(operation.EndMethod, true);
this.returnParam = operation.EndMethod.ReturnParameter;
}
else if ( this.syncMethod != null)
{
this.inParams = ServiceReflector.GetInputParameters( this.syncMethod, false);
this.outParams = ServiceReflector.GetOutputParameters( this.syncMethod, false);
this.returnParam = this.syncMethod.ReturnParameter;
}
if (( this.formatter == null) && ( this.serializeRequest || this.deserializeReply))
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString( " ClientRuntimeRequiresFormatter0 ", new object[] { this.name })));
}
}
[SecurityCritical]
internal object[] MapSyncInputs(IMethodCallMessage methodCall, out object[] outs)
{
if ( this.outParams.Length == 0)
{
outs = EmptyArray;
}
else
{
outs = new object[ this.outParams.Length];
}
if ( this.inParams.Length == 0)
{
return EmptyArray;
}
return methodCall.InArgs;
}
[SecurityCritical]
internal object[] MapSyncOutputs(IMethodCallMessage methodCall, object[] outs, ref object ret)
{
return this.MapOutputs( this.outParams, methodCall, outs, ref ret);
}
[SecurityCritical]
private object[] MapOutputs(ParameterInfo[] parameters, IMethodCallMessage methodCall, object[] outs, ref object ret)
{
if ((ret == null) && ( this.returnParam != null))
{
ret = GetDefaultParameterValue(TypeLoader.GetParameterType( this.returnParam));
}
if (parameters.Length == 0)
{
return null;
}
object[] args = methodCall.Args;
for ( int i = 0; i < parameters.Length; i++)
{
if (outs[i] == null)
{
args[parameters[i].Position] = GetDefaultParameterValue(TypeLoader.GetParameterType(parameters[i]));
}
else
{
args[parameters[i].Position] = outs[i];
}
}
return args;
}
/
****/
}
IMethodCallMessage的InArgs:获取未标记为 out 参数的参数数组;Args:获取传递给该方法的参数数组(MSDN中的定义)。
{
return this.Call(action, oneway, operation, ins, outs, this.operationTimeout);
}
internal object Call( string action, bool oneway, ProxyOperationRuntime operation, object[] ins, object[] outs, TimeSpan timeout)
{
this.ThrowIfDisallowedInitializationUI();
this.ThrowIfIdleAborted(operation);
ProxyRpc rpc = new ProxyRpc( this, operation, action, ins, timeout);
using (rpc.Activity = DiagnosticUtility.ShouldUseActivity ? ServiceModelActivity.CreateBoundedActivity() : null)
{
if (DiagnosticUtility.ShouldUseActivity)
{
ServiceModelActivity.Start(rpc.Activity, SR.GetString( " ActivityProcessAction ", new object[] { action }), ActivityType.ProcessAction);
}
this.PrepareCall(operation, oneway, ref rpc);
if (! this.explicitlyOpened)
{
this.EnsureDisplayUI();
this.EnsureOpened(rpc.TimeoutHelper.RemainingTime());
}
else
{
this.ThrowIfOpening();
base.ThrowIfDisposedOrNotOpen();
}
try
{
ConcurrencyBehavior.UnlockInstanceBeforeCallout(OperationContext.Current);
if (oneway)
{
this.binder.Send(rpc.Request, rpc.TimeoutHelper.RemainingTime());
}
else
{
rpc.Reply = this.binder.Request(rpc.Request, rpc.TimeoutHelper.RemainingTime());
if (rpc.Reply == null)
{
base.ThrowIfFaulted();
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError( new CommunicationException(SR.GetString( " SFxServerDidNotReply ")));
}
}
}
finally
{
this.CompletedIOOperation();
CallOnceManager.SignalNextIfNonNull( this.autoOpenManager);
ConcurrencyBehavior.LockInstanceAfterCallout(OperationContext.Current);
}
rpc.OutputParameters = outs;
this.HandleReply(operation, ref rpc);
}
return rpc.ReturnValue;
}
上面代码中有至关重要的一段:
{
this.binder.Send(rpc.Request, rpc.TimeoutHelper.RemainingTime());
}
else
{
rpc.Reply = this.binder.Request(rpc.Request, rpc.TimeoutHelper.RemainingTime());
}
通过是否单程oneway,来进行Send或者Request。那binder由是什么对象呢。。?
在ServiceChannel中,定义:
privatereadonly IChannelBinder binder。这点可以从RealProxy对象中可以看出来:
binder就不一样。以wsHttpBinding为例,它的binder为RequestChannelBinder。
DuplexChannelBinder的Send与Request定义如下:
{
this.channel.Send(message, timeout);
}
public Message Request(Message message, TimeSpan timeout)
{
SyncDuplexRequest request = null;
bool flag = false;
RequestReplyCorrelator.PrepareRequest(message);
lock (this.ThisLock)
{
if (!this.Pumping)
{
flag = true;
this.syncPumpEnabled = true;
}
if (!flag)
{
request = new SyncDuplexRequest(this);
}
this.RequestStarting(message, request);
}
if (flag)
{
TimeoutHelper helper = new TimeoutHelper(timeout);
UniqueId messageId = message.Headers.MessageId;
try
{
this.channel.Send(message, helper.RemainingTime());
if ((DiagnosticUtility.ShouldUseActivity && (ServiceModelActivity.Current != null)) && (ServiceModelActivity.Current.ActivityType == ActivityType.ProcessAction))
{
ServiceModelActivity.Current.Suspend();
}
while (true)
{
Message message2;
do
{
TimeSpan span = helper.RemainingTime();
if (!this.channel.TryReceive(span, out message2))
{
throw TraceUtility.ThrowHelperError(this.GetReceiveTimeoutException(timeout), message);
}
if (message2 == null)
{
this.AbortRequests();
return null;
}
if (message2.Headers.RelatesTo == messageId)
{
this.ThrowIfInvalidReplyIdentity(message2);
return message2;
}
}
while (this.HandleRequestAsReply(message2));
if (DiagnosticUtility.ShouldTraceInformation)
{
EndpointDispatcher endpointDispatcher = null;
if ((this.ChannelHandler != null) && (this.ChannelHandler.Channel != null))
{
endpointDispatcher = this.ChannelHandler.Channel.EndpointDispatcher;
}
TraceUtility.TraceDroppedMessage(message2, endpointDispatcher);
}
message2.Close();
}
}
finally
{
lock (this.ThisLock)
{
this.RequestCompleting(null);
this.syncPumpEnabled = false;
if (this.pending > 0)
{
this.EnsurePumping();
}
}
}
}
TimeoutHelper helper2 = new TimeoutHelper(timeout);
this.channel.Send(message, helper2.RemainingTime());
this.EnsurePumping();
return request.WaitForReply(helper2.RemainingTime());
}
在Request中,除了调用Channel的Send方法以外,还调用了SyncDuplexRequest的WaitForReply返回消息。
{
try
{
if (!TimeoutHelper.WaitOne(this.wait, timeout))
{
throw DiagnosticUtility.ExceptionUtility.ThrowHelperError(this.parent.GetReceiveTimeoutException(timeout));
}
}
finally
{
this.CloseWaitHandle();
}
this.parent.ThrowIfInvalidReplyIdentity(this.reply);
return this.reply;
}
3.2MethodData的Channel类型:
{
string str = null;
ActivityType unknown = ActivityType.Unknown;
if (DiagnosticUtility.ShouldUseActivity && ((ServiceModelActivity.Current == null) || (ServiceModelActivity.Current.ActivityType != ActivityType.Close)))
{
MethodData methodData = this.GetMethodData(methodCall);
if ((methodData.MethodBase.DeclaringType == typeof(ICommunicationObject)) && methodData.MethodBase.Name.Equals( " Close ", StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
str = SR.GetString( " ActivityClose ", new object[] { this.serviceChannel.GetType().FullName });
unknown = ActivityType.Close;
}
}
using (ServiceModelActivity activity = string.IsNullOrEmpty(str) ? null : ServiceModelActivity.CreateBoundedActivity())
{
if (DiagnosticUtility.ShouldUseActivity)
{
ServiceModelActivity.Start(activity, str, unknown);
}
return this.ExecuteMessage( this.serviceChannel, methodCall);
}
}
private IMethodReturnMessage ExecuteMessage( object target, IMethodCallMessage methodCall)
{
MethodBase methodBase = methodCall.MethodBase;
object[] args = methodCall.Args;
object ret = null;
try
{
ret = methodBase.Invoke(target, args);
}
catch (TargetInvocationException exception)
{
return this.CreateReturnMessage(exception.InnerException, methodCall);
}
return this.CreateReturnMessage(ret, args, args.Length, null, methodCall);
}
对于Channel,直接调用methodBase.Invoke进行调用
3.3、MethodData的Object类型
{
return RemotingServices.ExecuteMessage( this.objectWrapper, methodCall);
}
RemotingServices中ExecuteMessage的定义如下:
[SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.Infrastructure)]
public static IMethodReturnMessage ExecuteMessage(MarshalByRefObject target, IMethodCallMessage reqMsg)
{
if (target == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException( " target ");
}
RealProxy realProxy = GetRealProxy(target);
if ((realProxy is RemotingProxy) && !realProxy.DoContextsMatch())
{
throw new RemotingException(Environment.GetResourceString( " Remoting_Proxy_WrongContext "));
}
StackBuilderSink sink = new StackBuilderSink(target);
return (IMethodReturnMessage) sink.SyncProcessMessage(reqMsg, 0, true);
}
StackBuilderSink中SyncProcessMessage的处理过程:
public virtual IMessage SyncProcessMessage(IMessage msg)
{
return this.SyncProcessMessage(msg, 0, false);
}
internal virtual IMessage SyncProcessMessage(IMessage msg, int methodPtr, bool fExecuteInContext)
{
IMessage message3;
IMessage message = InternalSink.ValidateMessage(msg);
if (message != null)
{
return message;
}
IMethodCallMessage message2 = msg as IMethodCallMessage;
LogicalCallContext threadCallContext = null;
object obj2 = CallContext.GetLogicalCallContext().GetData( " __xADCall ");
bool flag = false;
try
{
object server = this._server;
VerifyIsOkToCallMethod(server, message2);
LogicalCallContext callCtx = null;
if (message2 != null)
{
callCtx = message2.LogicalCallContext;
}
else
{
callCtx = (LogicalCallContext) msg.Properties[ " __CallContext "];
}
threadCallContext = CallContext.SetLogicalCallContext(callCtx);
flag = true;
callCtx.PropagateIncomingHeadersToCallContext(msg);
PreserveThreadPrincipalIfNecessary(callCtx, threadCallContext);
if ( this.IsOKToStackBlt(message2, server) && ((Message) message2).Dispatch(server, fExecuteInContext))
{
message3 = new StackBasedReturnMessage();
((StackBasedReturnMessage) message3).InitFields((Message) message2);
LogicalCallContext context4 = CallContext.GetLogicalCallContext();
context4.PropagateOutgoingHeadersToMessage(message3);
((StackBasedReturnMessage) message3).SetLogicalCallContext(context4);
return message3;
}
MethodBase methodBase = GetMethodBase(message2);
object[] outArgs = null;
object ret = null;
RemotingMethodCachedData reflectionCachedData = InternalRemotingServices.GetReflectionCachedData(methodBase);
object[] args = Message.CoerceArgs(message2, reflectionCachedData.Parameters);
ret = this.PrivateProcessMessage(methodBase.MethodHandle, args, server, methodPtr, fExecuteInContext, out outArgs);
this.CopyNonByrefOutArgsFromOriginalArgs(reflectionCachedData, args, ref outArgs);
LogicalCallContext logicalCallContext = CallContext.GetLogicalCallContext();
if (((obj2 != null) && (( bool) obj2)) && (logicalCallContext != null))
{
logicalCallContext.RemovePrincipalIfNotSerializable();
}
message3 = new ReturnMessage(ret, outArgs, (outArgs == null) ? 0 : outArgs.Length, logicalCallContext, message2);
logicalCallContext.PropagateOutgoingHeadersToMessage(message3);
CallContext.SetLogicalCallContext(threadCallContext);
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
message3 = new ReturnMessage(exception, message2);
((ReturnMessage) message3).SetLogicalCallContext(message2.LogicalCallContext);
if (flag)
{
CallContext.SetLogicalCallContext(threadCallContext);
}
}
return message3;
3.4MethodData的GetType类型
{
return this.CreateReturnMessage( this.proxiedType, null, 0, SetActivityIdInLogicalCallContext(methodCall.LogicalCallContext), methodCall);
}
private IMethodReturnMessage CreateReturnMessage( object ret, object[] outArgs, int outArgsCount, LogicalCallContext callCtx, IMethodCallMessage mcm)
{
return new ReturnMessage(ret, outArgs, outArgsCount, callCtx, mcm);
}
它调用了ReturnMessage的如下构造函数:
{
this._ret = ret;
this._outArgs = outArgs;
this._outArgsCount = outArgsCount;
if (callCtx != null)
{
this._callContext = callCtx;
}
else
{
this._callContext = CallContext.GetLogicalCallContext();
}
if (mcm != null)
{
this._URI = mcm.Uri;
this._methodName = mcm.MethodName;
this._methodSignature = null;
this._typeName = mcm.TypeName;
this._hasVarArgs = mcm.HasVarArgs;
this._methodBase = mcm.MethodBase;
}
}
4、总结:
了一些介绍。下面对这些对象做个总结以认清它们之间的关系。
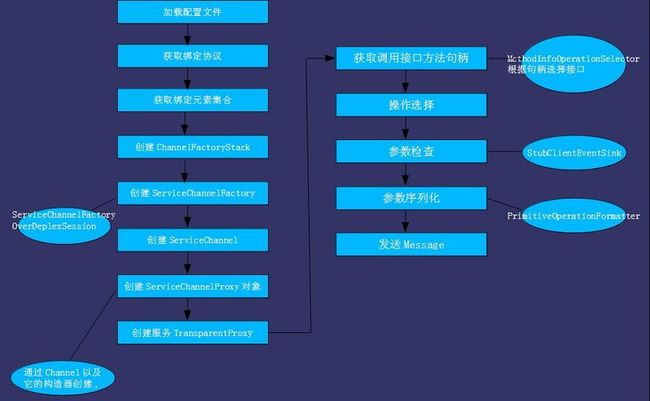
4.1、WCF客户端流程:
WCF客户端流程如下图:
上图流程说明:
1、由DuplexChannelFactory的父类:ChannelFactory<TChannel>的父类ChannelFactory初始化
Endpoint。
2、ChannelFactory调用ServiceChannelFactroy的BuildChannelFactory,通过初始化的Endpoint创建
ServiceChannelFactroy。(根据契约需要的通道形状,会生成继承自ServiceChannelFactory的
ServiceChannelFactoryOverX,)
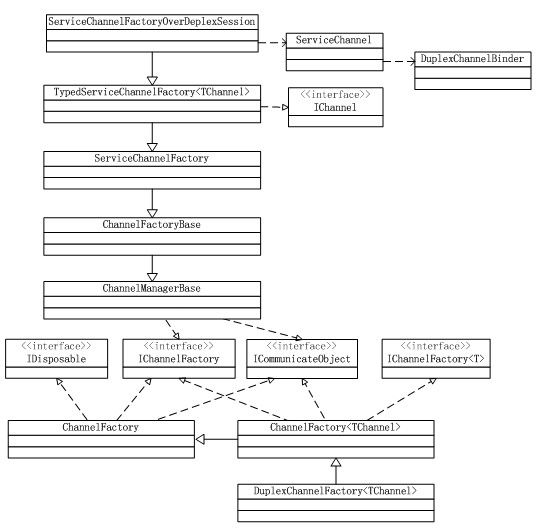
4.2、WCF客户端使用到的对象关系
在这两节分析WCF客户端时,介绍了很多内部 对象。通过UML关系图描述一下这些类型之间的关系:
在上图中,以接口为分界线,上半部分生成ServiceChannel;下半部分生成调用服务的代理。
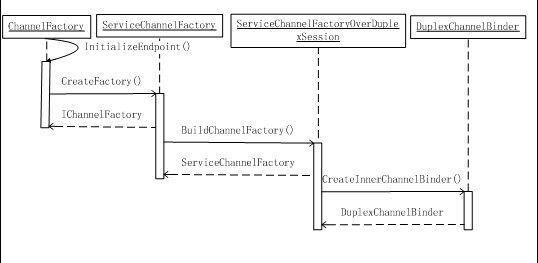
4.3、ServiceChannel生成时序图
最后后通过时序图介绍一下ServiceChannel、IChannelBinder对象生成过程:
备注:本节以及前一节中所有流程的说明都是以netTcpBiding作为传输协议来进行的,其他协议也类似。