UVALive 6602 Counting Lattice Squares
给定一个n*m的网格,求面积为奇数的正方形有多少个.
首先是n*m个面积为1的,然后剩下的要么是边长为奇数,要么被这样一个奇数边长所包围。
原因如下:
对于一个边长不平行于坐标抽的正方形,其边长一定是某个长方形的对角线,而且长方形长宽a,b一定是一奇数,一偶数,这样area = a^2+b^2才是奇数。
所以可以对任何奇数i <= min(n, m) 求出这样的边长正方形以及被包围的正方形个数。
注意对于一个奇数例如5,被包围的正方形可以是以1和4的对角线,2和3的对角线为边,这样对任何一个奇数i,被包围的正方形有i/2个,根据对称性还应该*2。
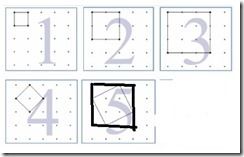
w-i+1表示宽方向能够移动的次数,l-i+1表示长度方向能够移动的次数,例如图5,长和宽方向均能移动2次。
ans = n*m(单位正方形) +
{2*(w-i+1)*(l-i+1)*(i/2) + (w-i+1)*(l-i+1)} i为 3<=i<=min(n, m)的奇数。
后来在最后完成这篇博客的时候想到能不能把式子简化一下呢,然后化简就得到这个:ans = ∑{ (w*l+w+l+1)*i – (w+l+2)*i*i + i*i*i} i为1到min(l,w)之间的奇数。
甚至可以推广到面积为偶数的情况:
公式:ans = ∑{ (w*l+w+l+1)*i – (w+l+2)*i*i + i*i*i} i为1到min(l,w)之间的偶数。
如果是求所有的正方形个数的话,只要把i从1取到min(w,l)就行了。
注意程序中预处理一下i,i*i,i*i*i的和。
下面只上化简后公式实现的代码好了。
time:29ms
//Date: 20140211 #include <iostream> #include <sstream> #include <cstdio> #include <climits> #include <ctime> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #define esp 1e-3 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define inf 0x0f0f0f0f #define pb push_back #define lson l, m, rt<<1 #define rson m+1, r, rt<<1|1 #define mp(a, b) make_pair((a), (b)) #define in freopen("test_in.txt", "r", stdin); #define out freopen("test_out.txt", "w", stdout); #define bug puts("********))))))"); #define inout in out #define stop system("pause"); #define PRD(a) printf("%d\n",(a)) #define PRLD(a) printf("%lld\n", (a)) #define PRID(a) printf("%I64d\n", (a)) #define PRU(a) printf("%u\n", (a)) #define PRLU(a) printf("%llu\n", (a)) #define PRIU(a) printf("%I64u\n", (a)) #define SET(a, v) memset(a, (v), sizeof(a)) #define READ(a, n) {REP(i, n) cin>>a[i];} #define REP(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < (n); i++) #define Rep(i, base, n) for(int i = base; i < n; i++) #define REPS(s) for(int i = 0; s[i]; i++) #define pf(x) ((x)*(x)) #define Log(a, b) (log((double)b)/log((double)a)) #define Srand() srand((int)time(0)) #define random(number) (rand()%number) #define random_range(a, b) (int)(((double)rand()/RAND_MAX)*(b-a) + a) /* 1. 点分治,atan和atan2返回弧度值,atan值域为(-pi/2, pi/2), atan2值域为(-pi, pi) ; 2. exp(x)用于计算e^x ; 3. log2和log10分别用来计算对数, log默认以e为底 ; 4. sort中比较函数的原型:bool cmp(const Type &a, const Type &b); 5. lower_bound和upper_bound返回的是相应下标对应的指针 ; 6. dfs时注意利用强剪枝和避免重复状态进行优化 ; 7. 尽量减少不必要的状态表示的维度 ; 8. greater<T> () less<T> () ; 9. 尽量少用strlen,尤其是在递归深度较大,字符串较长的时候,容易超时;少用memset ; 10.不要在函数里面开数组,易暴栈 ; */ using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef vector<int> VI; typedef pair<int,int> pii; typedef vector<pii> VII; typedef vector<pii, int> VIII; typedef VI:: iterator IT; typedef map<string, int> Mps; typedef map<int, int> Mpi; typedef map<int, pii> Mpii; typedef map<pii, int> Mpiii; template<class T> inline const T& Max(const T& a, const T& b) { return a < b ? b : a; } template<class T> inline const T& Min(const T& a, const T& b) { return a < b ? a : b; } template<class T> inline void checkMax(T& a, const T& b) { if(a < b) a = b; } template<class T> inline void checkMin(T& a, const T& b) { if(a > b) a = b; } const int maxn = 100000 + 100; LL f[maxn], g[maxn], h[maxn]; void pre() { f[1] = g[1] = h[1] = 1; for(int i = 3; i < maxn; i += 2) { f[i] = f[i-2] + i; g[i] = g[i-2] + (LL)i*i; h[i] = h[i-2] + (LL)i*i*i; } } int main() { LL n, m; pre(); while(scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m), n||m) { LL k = min(n, m); if((k&1) == 0) k--; LL ans = (n*m+n+m+1)*f[k]-(n+m+2)*g[k]+h[k]; printf("%lld\n", ans); } return 0; }