mochiweb 源码阅读(十四)
大家好,下了一天雨,十分凉爽,继续来看mochiweb源码,这一篇,我们来消化下上一篇留下的问题。
首先是mochiweb_socket_server:handle_cast/2关于{accepted, Pid, Timing}消息的处理:
handle_cast({accepted, Pid, Timing}, State=#mochiweb_socket_server{active_sockets=ActiveSockets}) -> State1 = State#mochiweb_socket_server{active_sockets=1 + ActiveSockets}, case State#mochiweb_socket_server.profile_fun of undefined -> undefined; F when is_function(F) -> catch F([{timing, Timing} | state_to_proplist(State1)]) end, {noreply, recycle_acceptor(Pid, State1)};
这个分支比较简单,首先,修改了State#mochiweb_socket_server记录active_sockets字段的值,增加1;
接着判断是否定义了State#mochiweb_socket_server.profile_fun字段,如果之前的配置文件中存在该选项,且该选项是函数,则调用该函数,传递类似这样的参数值:[{name, Name}, {port, Port}, {active_sockets, ActiveSockets}, {timing, Timing}]。
而mochiweb_socket_server:state_to_proplist/1函数代码如下,一眼就能看明白:
state_to_proplist(#mochiweb_socket_server{name=Name,
port=Port,
active_sockets=ActiveSockets}) ->
[{name, Name}, {port, Port}, {active_sockets, ActiveSockets}].
关于这个配置项,我们可以从mochiweb_http:start/1函数的注释上了解到,如下:
%% @spec start(Options) -> ServerRet %% Options = [option()] %% Option = {name, atom()} | {ip, string() | tuple()} | {backlog, integer()} %% | {nodelay, boolean()} | {acceptor_pool_size, integer()} %% | {ssl, boolean()} | {profile_fun, undefined | (Props) -> ok} %% | {link, false} %% @doc Start a mochiweb server. %% profile_fun is used to profile accept timing. %% After each accept, if defined, profile_fun is called with a proplist of a subset of the mochiweb_socket_server state and timing information. %% The proplist is as follows: [{name, Name}, {port, Port}, {active_sockets, ActiveSockets}, {timing, Timing}]. %% @end start(Options) -> mochiweb_socket_server:start(parse_options(Options)).
这里我们修改下mochiweb_example_web:start/1,增加profile_fun选项来测试下这个功能,代码如下:
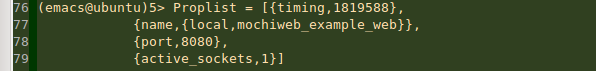
start(Options) -> {DocRoot, Options1} = get_option(docroot, Options), Loop = fun (Req) -> ?MODULE:loop(Req, DocRoot) end, Profile_fun = fun (Proplist) -> io:format("Proplist = ~p~n", [Proplist]) end, mochiweb_http:start([{name, ?MODULE}, {loop, Loop}, {profile_fun, Profile_fun} | Options1]).
重新编译并启动,然后用浏览器访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/,接着我们就能看到如下打印结果了:
最后该分支返回如下结果:{noreply, recycle_acceptor(Pid, State1)};
这里我们主要看下:mochiweb_socket_server:recycle_acceptor/2函数:
recycle_acceptor(Pid, State=#mochiweb_socket_server{ acceptor_pool=Pool, listen=Listen, loop=Loop, active_sockets=ActiveSockets}) -> case sets:is_element(Pid, Pool) of true -> Acceptor = mochiweb_acceptor:start_link(self(), Listen, Loop), Pool1 = sets:add_element(Acceptor, sets:del_element(Pid, Pool)), State#mochiweb_socket_server{acceptor_pool=Pool1}; false -> State#mochiweb_socket_server{active_sockets=ActiveSockets - 1} end.
可以看到,这个函数最后返回State#mochiweb_socket_server记录;
首先,调用sets:is_element/2判断Pid是否在Pool中存在;如果存在,则调用mochiweb_acceptor:start_link/3生成一个新的acceptor进程,并从Pool中移除Pid,添加新的acceptor进程,最后修改State#mochiweb_socket_server.acceptor_pool字段的值。
如果不存在,则修改State#mochiweb_socket_server.active_sockets的值减少1。
注意:这里可以看出每当有个客户端连接上来,Pool池就会把当前负责的acceptor进程移除,同时添加一个新的acceptor进程,也就是保证Pool池,始终和启动时拥有的数量一致。
第一个问题解决了,接下来是第二个问题,调用mochiweb_http:loop/2函数,完整代码如下:
loop(Socket, Body) -> ok = mochiweb_socket:setopts(Socket, [{packet, http}]), request(Socket, Body).
从上下文,我们可以知道这里的Body是个匿名函数,它就是mochiweb_example_web:start/1定义的Loop变量,大家可以翻看前一篇文章,回忆下。
这个函数,首先调用mochiweb_socket:setopts/2修改Socket的配置项,该函数完整代码如下:
setopts({ssl, Socket}, Opts) ->
ssl:setopts(Socket, Opts);
setopts(Socket, Opts) ->
inet:setopts(Socket, Opts).
同样是分SSL协议和非SSL协议来调用不同系统函数设置。
erlang doc 地址:http://www.erlang.org/doc/man/ssl.html#setopts-2,http://www.erlang.org/doc/man/inet.html#setopts-2
关于{packet, http}选项,大家可以查看上面第二个地址的文档,如下图:
最后调用函数mochiweb_http:request/2:
request(Socket, Body) -> ok = mochiweb_socket:setopts(Socket, [{active, once}]), receive {Protocol, _, {http_request, Method, Path, Version}} when Protocol == http orelse Protocol == ssl -> ok = mochiweb_socket:setopts(Socket, [{packet, httph}]), headers(Socket, {Method, Path, Version}, [], Body, 0); {Protocol, _, {http_error, "\r\n"}} when Protocol == http orelse Protocol == ssl -> request(Socket, Body); {Protocol, _, {http_error, "\n"}} when Protocol == http orelse Protocol == ssl -> request(Socket, Body); {tcp_closed, _} -> mochiweb_socket:close(Socket), exit(normal); {ssl_closed, _} -> mochiweb_socket:close(Socket), exit(normal); _Other -> handle_invalid_request(Socket) after ?REQUEST_RECV_TIMEOUT -> mochiweb_socket:close(Socket), exit(normal) end.
好了,这一篇就到这里,这个函数我们留到下一篇继续跟大家分享。
晚安。