IOS网络编程:HTTP
IOS网络编程:HTTP
HTTP定义了一种在服务器和客户端之间传递数据的途径。
URL定义了一种唯一标示资源在网络中位置的途径。
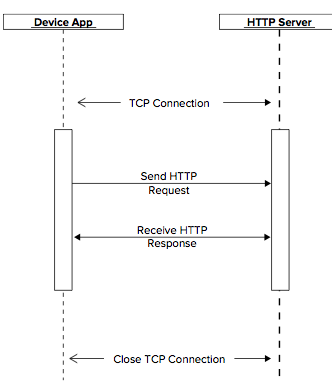
客户端先建立一个TCP连接,然后发送一个请求。服务器受到请求处理后发送一个响应向客户端传递数据。然后客户端可以继续发送请求或者关闭这个TCP连接。
HTTPS:
在TCP连接建立后,发送请求之前,需要建立一个一个SSL会话。
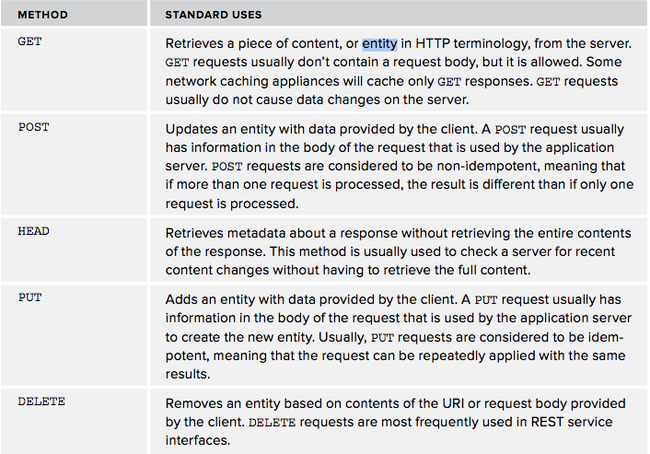
request方法和它们的用途
iOS的NSURLRequest和它的子类NSMutableURLRequest提供了建立HTTP请求的方法。
NSURLResponse 和 它的子类NSHTTPURLResponse 处理返回的数据。
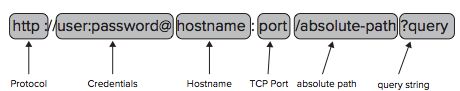
URL:
Protocol包括HTTP、FTP和file。
URL编码:
NSString *urlString = @"http://myhost.com?query=This is a question";
NSString *encoded = [urlString stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSURL用来管理URL。
IOS HTTP APIS:
涉及到下面一些类:
NSURL, NSURLRequest, NSURLConnection, 和 NSURLResponse.
1、NSURL
NSURL可以定义本地文件和网络文件
NSURL *url = [NSURL urlWithString:@"http://www.google.com"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
NSURL定义了很多访问器:
if (url.port == nil) {
NSLog(@"Port is nil"); } else { NSLog(@"Port is not nil"); }
2、NSURLRequest
创建了NSURL后,就可以用NSURLRequest建立请求了:
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString: @"https://gdata.youtube.com/feeds/api/standardfeeds/top_rated"]; if (url == nil) { NSLog(@"Invalid URL");
return; } NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
if (request == nil) { NSLog(@"Invalid Request"); return; }
NSMutableURLRequest是NSURLRequest 的子类,提供了改变请求的属性的方法:
NSURL *url = [NSURL urlWithString@"http://server.com/postme"];
NSMutableURLRequest *req = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
[req setHTTPMethod:@"POST"]; [req setHTTPBody:[@"Post body" dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
如果你要发送一个图片或者视频,那么用需要用NSInputStream,它没有把数据全部加在到内存。
NSMutableURLRequest *request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url]; NSInputStream *inStream = [NSInputStream inputStreamWithFileAtPath:srcFilePath]; [request setHTTPBodyStream:inStream]; [request setHTTPMethod:@"POST"];
3、NSURLConnection
提供了初始化、开始、和取消一个连接。
4、NSURLResponse
发送同步请求:
- (NSArray *) doSyncRequest:(NSString *)urlString { // make the NSURL object from the string NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString]; // Create the request object with a 30 second timeout and a cache policy to always retrieve the // feed regardless of cachability. NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData timeoutInterval:30.0]; // Send the request and wait for a response NSHTTPURLResponse *response; NSError *error; NSData *data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request returningResponse:&response error:&error]; // check for an error if (error != nil) { NSLog(@"Error on load = %@", [error localizedDescription]); return nil; } // check the HTTP status if ([response isKindOfClass:[NSHTTPURLResponse class]]) { NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response; if (httpResponse.statusCode != 200) { return nil; } NSLog(@"Headers: %@", [httpResponse allHeaderFields]); } // Parse the data returned into an NSDictionary NSDictionary *dictionary = [XMLReader dictionaryForXMLData:data error:&error]; // Dump the dictionary to the log file NSLog(@"feed = %@", dictionary); NSArray *entries =[self getEntriesArray:dictionary]; // return the list if items from the feed. return entries; }
Queued Asynchronous Requests:
- (void) doQueuedRequest:(NSString *)urlString delegate:(id)delegate { // make the NSURL object NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString]; // create the request object with a no cache policy and a 30 second timeout. NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData timeoutInterval:30.0]; // If the queue doesn't exist, create one. if (queue == nil) { queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init]; } // send the request and specify the code to execute when the request completes or fails. [NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:request queue:queue completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse *response, NSData *data, NSError *error) { if (error != nil) { NSLog(@"Error on load = %@", [error localizedDescription]); } else { // check the HTTP status if ([response isKindOfClass:[NSHTTPURLResponse class]]) { NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response; if (httpResponse.statusCode != 200) { return; } NSLog(@"Headers: %@", [httpResponse allHeaderFields]); } // parse the results and make a dictionary NSDictionary *dictionary = [XMLReader dictionaryForXMLData:data error:&error]; NSLog(@"feed = %@", dictionary); // get the dictionary entries. NSArray *entries =[self getEntriesArray:dictionary]; // call the delegate if ([delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(setVideos:)]) { [delegate performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(setVideos:) withObject:entries waitUntilDone:YES]; } } }]; }
Asynchronous Requests:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #define kDownloadComplete @"downloadComplete" @class DownloadProgressView; @interface AsyncDownloader : NSObject <NSURLConnectionDelegate> { // The number of bytes that need to be downloaded long long downloadSize; // the total amount downloaded thus far long long totalDownloaded; } // A reference to the progress view to show the user how things are progressing @property (assign) DownloadProgressView *progressView; // The target MP4 file @property (strong) NSString *targetFile; // The original URL to download. Due to redirects the actual content may come from another URL @property (strong) NSString *srcURL; // The open file to which the content is written @property (strong) NSFileHandle *outputHandle; // The name of the temp file to which the content is streamed. This file is moved to the target file when // the download is complete @property (strong) NSString *tempFile; @property (strong) NSURLConnection *conn; // instructs the class to start the download. - (void) start; @end
// // AsyncDownloader.m // VideoDownloader // // Created by Jack Cox on 4/7/12. // // #import "AsyncDownloader.h" #import "DownloadProgressView.h" @implementation AsyncDownloader @synthesize targetFile; @synthesize srcURL; @synthesize outputHandle; @synthesize tempFile; @synthesize progressView; @synthesize conn; - (void) start { NSLog(@"Starting to download %@", srcURL); // create the URL NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:srcURL]; // Create the request NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url]; // create the connection with the target request and this class as the delegate self.conn = [NSURLConnection connectionWithRequest:request delegate:self]; // start the connection [self.conn start]; } /** * Creates a UUID to use as the temporary file name during the download */ - (NSString *)createUUID { CFUUIDRef uuidRef = CFUUIDCreate(NULL); CFStringRef uuidStringRef = CFUUIDCreateString(NULL, uuidRef); CFRelease(uuidRef); NSString *uuid = [NSString stringWithString:(__bridge NSString *) uuidStringRef]; CFRelease(uuidStringRef); return uuid; } #pragma mark NSURLConnectionDelegate methods /** * This delegate method is called when the NSURLConnection gets a 300 series response that indicates * that the request needs to be redirected. It is implemented here to display any redirects that might * occur. This method is optional. If omitted the client will follow all redirects. **/ - (NSURLRequest *)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection willSendRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request redirectResponse:(NSURLResponse *)redirectResponse { // Dump debugging information NSLog(@"Redirect request for %@ redirecting to %@", srcURL, request.URL); NSLog(@"All headers = %@", [(NSHTTPURLResponse*) redirectResponse allHeaderFields]); // Follow the redirect return request; } /** * This delegate method is called when the NSURLConnection connects to the server. It contains the * NSURLResponse object with the headers returned by the server. This method may be called multiple times. * Therefore, it is important to reset the data on each call. Do not assume that it is the first call * of this method. **/ - (void) connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response { NSLog(@"Received response from request to url %@", srcURL); NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response; NSLog(@"All headers = %@", [httpResponse allHeaderFields]); if (httpResponse.statusCode != 200) {// something went wrong, abort the whole thing // reset the download counts if (downloadSize != 0L) { [progressView addAmountToDownload:-downloadSize]; [progressView addAmountDownloaded:-totalDownloaded]; } [connection cancel]; return; } NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; // If we have a temp file already, close it and delete it if (self.tempFile != nil) { [self.outputHandle closeFile]; NSError *error; [fm removeItemAtPath:self.tempFile error:&error]; } // remove any pre-existing target file NSError *error; [fm removeItemAtPath:targetFile error:&error]; // get the temporary directory name and make a temp file name NSString *tempDir = NSTemporaryDirectory(); self.tempFile = [tempDir stringByAppendingPathComponent:[self createUUID]]; NSLog(@"Writing content to %@", self.tempFile); // create and open the temporary file [fm createFileAtPath:self.tempFile contents:nil attributes:nil]; self.outputHandle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:self.tempFile]; // prime the download progress view NSString *contentLengthString = [[httpResponse allHeaderFields] objectForKey:@"Content-length"]; // reset the download counts if (downloadSize != 0L) { [progressView addAmountToDownload:-downloadSize]; [progressView addAmountDownloaded:-totalDownloaded]; } downloadSize = [contentLengthString longLongValue]; totalDownloaded = 0L; [progressView addAmountToDownload:downloadSize]; } /** * This delegate method is called for each chunk of data received from the server. The chunk size * is dependent on the network type and the server configuration. */ - (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveData:(NSData *)data { // figure out how many bytes in this chunk totalDownloaded+=[data length]; // Uncomment if you want a packet by packet log of the bytes received. NSLog(@"Received %lld of %lld (%f%%) bytes of data for URL %@", totalDownloaded, downloadSize, ((double)totalDownloaded/(double)downloadSize)*100.0, srcURL); // inform the progress view that data is downloaded [progressView addAmountDownloaded:[data length]]; // save the bytes received [self.outputHandle writeData:data]; } /** * This delegate methodis called if the connection cannot be established to the server. * The error object will have a description of the error **/ - (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didFailWithError:(NSError *)error { NSLog(@"Load failed with error %@", [error localizedDescription]); NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; // If we have a temp file already, close it and delete it if (self.tempFile != nil) { [self.outputHandle closeFile]; NSError *error; [fm removeItemAtPath:self.tempFile error:&error]; } // reset the progress view if (downloadSize != 0L) { [progressView addAmountToDownload:-downloadSize]; [progressView addAmountDownloaded:-totalDownloaded]; } } /** * This delegate method is called when the data load is complete. The delegate will be released * following this call **/ - (void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection { // close the file [self.outputHandle closeFile]; // Move the file to the target location NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; NSError *error; [fm moveItemAtPath:self.tempFile toPath:self.targetFile error:&error]; // Notify any concerned classes that the download is complete [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:kDownloadComplete object:nil userInfo:nil]; } @end
"付出努力的过程也许是举步维艰的,但必须是开心和充实的。“
----火星人
在挖掘工程代码的过程中,仅仅游走在header文件和源代码文件中往往是意犹未尽的感觉,尤其在实际环境中很难确定某一版本的开源代码真的就是当前系统运行的代码,反正无论怎样,对库文件的汇编追踪都是必不可少的。
汇编代码中的symbol追踪是非常重要的一环,一旦要对库函数做实验,编译测试代码,通过binary tool分析目标代码去hunt down真正的库函数细节!
此篇就是介绍在Mac OS X下这个过程的操作,let's do it.!
最近Mars在研究关于NaN的问题(Orz,写这篇的时候NaN的那篇还不到50%完成度,崩溃中......),那就用相关的代码来介绍一下吧!假设现在写下了下面个这个小羔羊程序:
#include <math.h> int main() { double d0 = nan("0xfff0000000001230"); return 0; }
这个程序的目标是追踪一下nan这个libc标准函数的实现,在库header里面大家是看不到他嘀~,因为他的实现代码是编译代码。
gcc -g -o nan nan.c
看一下编译后汇编代码的主体,因为没有-O选项,所以能看到没有任何优化的原貌:
_main: Leh_func_begin1: pushq %rbp Ltmp0: movq %rsp, %rbp Ltmp1: subq $16, %rsp Ltmp2: leaq L_.str(%rip), %rax movq %rax, %rdi callq _nan movsd %xmm0, -16(%rbp) movl $0, -8(%rbp) movl -8(%rbp), %eax movl %eax, -4(%rbp) movl -4(%rbp), %eax addq $16, %rsp popq %rbp ret Leh_func_end1:
从汇编码中看到了"callq _nan",毫无挑战的行踪败露。下一步常规的手段可能会这样做:
otool -L nan
但这样的结果如下:
但事实上在/usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib中根本不存在_nan的代码,只需要:
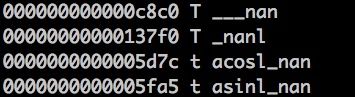
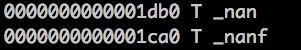
nm -a /usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib | grep _nan
就可以知道:
完全没有,就算是存在符号连接也会被nm -a输出来的。
为什么会出现这么奇怪的情况,明明有外部符号,但otool输出的库缺没有这个外部符号的信息?这个问题目前还没找到答案,当另一种追踪符号的方法反而被脑补出来了。
因为下一步要gdb调试,所以带上-g,添加调试符号信息。OK~let's gdb it.
下面分别截图gdb的整个过程:
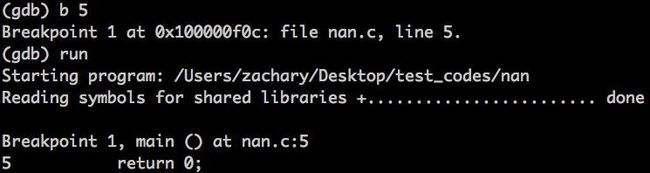
1)启动gdb看看代码
2)设置断点让程序运行,至于运行到哪里似乎没什么所谓(因为在实验中,把nan的调用嵌入到三重函数嵌套调用中,把断点设置在最外层函数调用之前,也同样可以),因为程序一旦开始执行,就会加载动态链接库的符号。
3)秘密武器出来~
在最后一步,通过info symbol nan就把这个未定义的外部符号最终归属给找出来了!!稍微检验一下:
nm -a /usr/lib/system/libmathCommon.A.dylib | grep "_nan"
搞定~找到~接下来就看_nan的代码吧!!
otool -p "_nan" -tV /usr/lib/system/libmathCommon.A.dylib
好啦,到这里已经完成对symbol追踪过程的阐述,也故意列出一些otool和nm的使用方法,希望大家受乐啦~毕竟Mac OS X下二进制文件的处理真不太方便,没有了objdump和readelf,虽然可以安装传说中的binutils,但一直没装上,Mars土鳖了。