相信接触过网络开发的人对HTTP、HttpWebRequest、Socket这些东西都不陌生吧。它们之间的一些介绍和关系我这里都忽略了。开我们平时开发过程中也是很少有机会接触大什么大并发这个东东,一般大并发我们都需要考虑异步和多线程以及对象池,这个我们以一个简单demo来讲解吧。
主要的调用关系图如下:
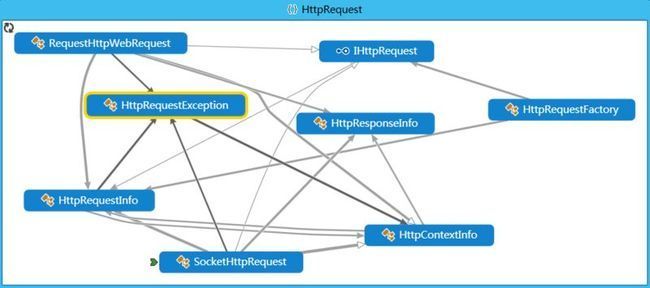
类的结构图如下:
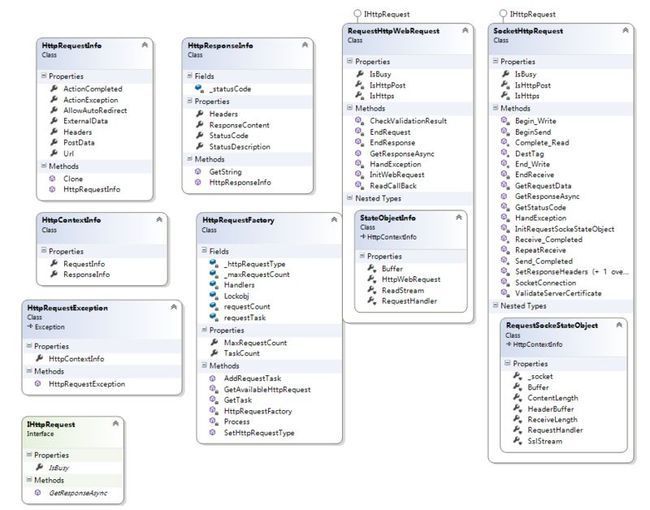
一:这里我们依次对这些类做一个简单的说明
HttpRequestInfo:
public string Url:http请求的url字符串,如http://www.baidu.com/
public byte[] PostData:Post请求中的数据
public WebHeaderCollection Headers:请求的头部数据
public bool AllowAutoRedirect :是否允许301、302自动跳转,如果你想获取请求返回的头部信息,建议一般设置为false
public Dictionary<string, string> ExternalData :请求过程中附加的数据(如数据记录的ID),便于在成功或失败回调函数中调用
public Action<HttpContextInfo> ActionCompleted :请求成功后所调用的函数
public Action<HttpRequestException> ActionException:请求失败所调用函数
public HttpRequestInfo Clone():返回当前对象的一个副本。
HttpResponseInfo:
public Stream ResponseContent :Http请求返回内容(除头部信息)的对象流
public HttpStatusCode StatusCode:Http返回的状态
public string StatusDescription :Http状态描述
public WebHeaderCollection Headers:Http返回的头部信息
public string GetString(Encoding coding):把http返回体中数据流转换为字符串,转换编码就是我们所传参数。
public interface IHttpRequest
{
void GetResponseAsync(HttpRequestInfo request);
bool IsBusy { set; get; }
}
在IHttpRequest接口中,IsBusy属性主要是判断当前对象是否正在使用中,GetResponseAsync方法是真正完成Http请求的方法。
这里我们主要看看HttpRequestFactory的封装吧,管理对象实例的个数,相当于一个对象池,这里的代码主要是基于。net framework2.0的,
首先我们需要2个集合分别管理HttpRequestInfo请求实例和IHttpRequest处理请求实例,
static Queue<HttpRequestInfo> requestTask = new Queue<HttpRequestInfo>();
static List<IHttpRequest> Handlers = new List<IHttpRequest>();
而我们暴露给外部的一个主要方法就是AddRequestTask,
public static void AddRequestTask(HttpRequestInfo info)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(info.Url))
{
lock (Lockobj)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref requestCount);
requestTask.Enqueue(info);
}
}
}
那么这些请求在什么时候被处理了,在一个叫Process方法中处理,
private static void Process(object obj)
{
while (true)
{
IHttpRequest handler = GetAvailableHttpRequest();
while (handler == null)
{
Thread.Sleep(100);
handler = GetAvailableHttpRequest();
}
HttpRequestInfo task = GetTask();
while (task == null)
{
Thread.Sleep(100);
task = GetTask();
}
if (task != null && handler != null)
{
Interlocked.Decrement(ref requestCount);
handler.GetResponseAsync(task);
}
// Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
在这个方法中我们需要调用GetAvailableHttpRequest来获取IHttpRequest处理对象实例,调用GetTask来获取HttpRequestInfo请求实例。如果这2个实例都存在我们调用 IHttpRequest.GetResponseAsync(HttpRequestInfo);方法开始处理http请求。
GetAvailableHttpRequest如下:
private static IHttpRequest GetAvailableHttpRequest()
{
lock (Lockobj)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Handlers.Count; i++)
{
if (!Handlers[i].IsBusy)
{
return Handlers[i];
}
}
if (Handlers.Count <= MaxRequestCount)
{
IHttpRequest handler = (IHttpRequest)Activator.CreateInstance(_httpRequestType);
Handlers.Add(handler);
return handler;
}
}
return null;
//return GetAvailableHttpRequest();
}
在GetAvailableHttpRequest方法中,我们首先在处理对象集合中查找是否有空闲对象,如果有就返回,否则检查当前对象实例个数个数是否达到最大个数,如果没有我们则创建新实例,且加入到集合中,再返回,否者返回null。所以在Process方法中有一个检查,看啊看你返回的IHttpRequest是否为null,请注意这里一定不要用递归来返回有效的IHttpRequest,建议用一个死循环来处理,如果用递归一般不会出现什么问题,但是递归层次嵌套太深就会出现栈溢出错误,我在测试的时候曾经出现过这个问题。GetTask和GetAvailableHttpRequest处理一样。
那么这里的Process方法有在什么地方调用了,在HttpRequestFactory的静态构造函数中调用。
static HttpRequestFactory()
{
MaxRequestCount = 10;
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(Process));
}
到这里我们的一个对象池就构造玩了。
二 现在我们来看看RequestHttpWebRequest是如何处理HTTP请求的。它主要使用HttpWebRequest来处理请求。
这里我们主要使用HttpWebRequest的异步方法,因此我们需要构造一个状态对象StateObjectInfo
class StateObjectInfo : HttpContextInfo
{
internal byte[] Buffer { set; get; } //把返回的流写到HttpResponseInfo.ResponseContent 时用到的暂存数组
internal Stream ReadStream { set; get; }//把返回的流写到HttpResponseInfo.ResponseContent
internal HttpWebRequest HttpWebRequest { set; get; }
internal RequestHttpWebRequest RequestHandler { set; get; }//主要便于后面改IsBusy属性。
}
其GetResponseAsync实现如下:
public void GetResponseAsync(HttpRequestInfo info)
{
HttpWebRequest webRequest;
StateObjectInfo state;
InitWebRequest(info, out webRequest, out state);
try
{
if (IsHttpPost)
{
webRequest.Method = "POST";
webRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
webRequest.BeginGetRequestStream(EndRequest, state);
}
else { webRequest.BeginGetResponse(EndResponse, state); }
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
其中InitWebRequest的实现如下:
private void InitWebRequest(HttpRequestInfo info, out HttpWebRequest webRequest, out StateObjectInfo state)
{
IsBusy = true;
if (info.PostData != null && info.PostData.Length > 0)
{
IsHttpPost = true;
}
else
{
IsHttpPost = false;
}
if (info.Url.ToLower().Trim().StartsWith("https"))
{
IsHttps = true;
ServicePointManager.ServerCertificateValidationCallback = new RemoteCertificateValidationCallback(CheckValidationResult);
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3;
}
else
{
IsHttps = false; }
webRequest = HttpWebRequest.CreateDefault(new Uri(info.Url)) as HttpWebRequest;
if (IsHttps)
{
/*基础连接已经关闭: 发送时发生错误 */
/*无法从传输连接中读取数据: 远程主机强迫关闭了一个现有的连接*/
webRequest.KeepAlive = false;
webRequest.ProtocolVersion = HttpVersion.Version10;
webRequest.UserAgent = "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.2; .NET CLR 1.0.3705;)";
}
webRequest.AllowAutoRedirect = info.AllowAutoRedirect;
if (info.Headers != null && info.Headers.Count > 0)
{
foreach (string key in info.Headers.Keys)
{
webRequest.Headers.Add(key, info.Headers[key]);
}
}
//webRequest.Proxy = WebProxy.GetDefaultProxy();
//webRequest.Proxy.Credentials = CredentialCache.DefaultCredentials;
//webResponse.Headers.Get("Set-Cookie");
state = new StateObjectInfo
{
Buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024],
HttpWebRequest = webRequest,
RequestHandler = this,
RequestInfo = info,
ResponseInfo = new HttpResponseInfo()
};
}
关于该类的EndRequest、EndResponse我想就没什么说的了,其中ReadCallBack的实现如下:
void ReadCallBack(IAsyncResult ar)
{
StateObjectInfo state = ar.AsyncState as StateObjectInfo;
try
{
int read = state.ReadStream.EndRead(ar);
if (read > 0)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, read);
state.ReadStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, ReadCallBack, state);
}
else
{
state.ReadStream.Close();
state.HttpWebRequest.Abort();
if (state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted != null)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted(state); }
state.Buffer = null;
state.RequestHandler.IsBusy = false;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
这里还有一个HandException方法需要我们注意:
private void HandException(Exception ex, StateObjectInfo state)
{
if (state.ReadStream != null)
state.ReadStream.Close();
if (state.HttpWebRequest != null)
state.HttpWebRequest.Abort();
state.Buffer = null;
if (state.RequestInfo.ActionException != null)
{
state.RequestInfo.ActionException(new HttpRequestException(state, ex));
}
state.RequestHandler.IsBusy = false;
}
这里我们在使用HttpWebRequest的时候,在完成使用后一定要关闭请求流。
在我们来看看一个简单的调用把:
public static void DownLoadFile(string remoteurl, string destinationFilePath, string id)
{
try
{
if (HasIllegalCharacters(destinationFilePath, false))
{
SetFileCopyed(id, "400", "HasIllegalCharacters");
return;
}
DirectoryInfo dir = new DirectoryInfo(destinationFilePath);
FileInfo destinationFile = new FileInfo(destinationFilePath);
if (!destinationFile.Directory.Exists)
{
destinationFile.Directory.Create();
}
HttpRequestInfo request = new HttpRequestInfo(remoteurl);
request.ActionCompleted = new Action<HttpContextInfo>(x =>
{
if (x.ResponseInfo.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
using (Stream wr = File.Open(destinationFilePath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write), sr = x.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent)
{
byte[] data = new byte[1024 * 1024];
int readcount = sr.Read(data, 0, data.Length);
while (readcount > 0)
{
wr.Write(data, 0, readcount);
readcount = sr.Read(data, 0, data.Length);
}
}
SetFileCopyed(id, "200", string.Empty);
}
else
{
SetFileCopyed(id, ((int)x.ResponseInfo.StatusCode).ToString(), x.ResponseInfo.StatusDescription);
string message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + remoteurl + " : " + x.ResponseInfo.StatusDescription;
LogManager.LogException(message);
}
});
request.ActionException = new Action<HttpRequestException>(ex =>
{
Regex reg = new Regex(@"\d{3}",RegexOptions.Compiled);
string message = ex.Message;
Match m = reg.Match(message);
if (m.Success)
{
SetFileCopyed(id, m.Value, message);
}
else
{
SetFileCopyed(id, "503", message);
HttpRequestInfo newRequest = ex.HttpContextInfo.RequestInfo.Clone();
request.ActionCompleted = null;
request.ActionException = null;
HttpRequestFactory.AddRequestTask(newRequest);
}
message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + ex.HttpContextInfo.RequestInfo.Url + " : " + message;
LogManager.LogException(message);
});
HttpRequestFactory.AddRequestTask(request);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SetFileCopyed(id, "-1", ex.Message);
string message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + remoteurl + " : " + ex.Message;
LogManager.LogException(message);
}
}
internal static bool HasIllegalCharacters(string path, bool checkAdditional)
{
for (int i = 0; i < path.Length; i++)
{
int num2 = path[i];
if (((num2 == 0x22) || (num2 == 60)) || (((num2 == 0x3e) || (num2 == 0x7c)) || (num2 < 0x20)))
{
return true;
}
if (checkAdditional && ((num2 == 0x3f) || (num2 == 0x2a)))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
对于这个调用的demo我这里就不多说,不过在调用的时候偶尔会出现:
/*基础连接已经关闭: 发送时发生错误 */
/*无法从传输连接中读取数据: 远程主机强迫关闭了一个现有的连接*/
这样的错误,网上有一些什么改良方法,我测试后都不管用,个人猜测是与网络有关的,即使我用socket来做偶尔也会有一些问题。所以当我们遇到这些网络问题的时候,我们把我们的请求再次加入请求队列中 HttpRequestFactory.AddRequestTask(newRequest);。这一很重要的哦。
HttpWebRequest类对我们做http请求做了很多封装,我们使用也很方便。但是它的性能比我们自己用socket要低很多,同时在一些处理上违背了我们的操作习惯。如我们上面的调用代码:
如果我们http返回状态是403、404...(除200以外)程序没有进入我的else,而是进入我的ActionException方法里面了,这点让我很是不爽。于是萌生了用socket来做http请求的念头。
三 现在我们来看看SocketHttpRequest是如何处理HTTP请求的。它主要使用Socket来处理请求。
SocketHttpRequest和RequestHttpWebRequest一样都是采用对象的异步模式,那么也需要一个状态对象:
class RequestSockeStateObject : HttpContextInfo
{
internal SocketHttpRequest RequestHandler { set; get; }
internal Socket _socket { set; get; } //普通http请求采用socket
internal List<byte> HeaderBuffer { set; get; }
internal byte[] Buffer { set; get; }
internal int ContentLength { set; get; }//http需要接收的数据长度
internal int ReceiveLength { set; get; }//http已经接收的数据长度
internal SslStream SslStream { set; get; }//https请求采用TcpClient,这里需要用到SslStream
}
public void GetResponseAsync(HttpRequestInfo info)
{
RequestSockeStateObject _state;
InitRequestSockeStateObject(info, out _state);
SocketConnection(_state);
}
这里的InitRequestSockeStateObject和RequestHttpWebRequest的InitWebRequest方法差不多,就不在累赘了。
主要看看SocketConnection方法:
void SocketConnection(RequestSockeStateObject _state)
{
try
{
Uri uri = new Uri(_state.RequestInfo.Url);
IPHostEntry hostEntry = Dns.GetHostEntry(uri.Host);
if (IsHttps)
{
TcpClient tcpclient = new TcpClient();
tcpclient.Connect(hostEntry.AddressList, uri.Port);
_state._socket = tcpclient.Client;
SslStream sslStream = new SslStream(tcpclient.GetStream(), false, new RemoteCertificateValidationCallback(ValidateServerCertificate), null);
sslStream.AuthenticateAsClient(hostEntry.HostName, new X509CertificateCollection(), SslProtocols.Ssl3 | SslProtocols.Tls, false);
_state.SslStream = sslStream;
Begin_Write(_state);
}
else
{
Socket client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); client.Connect(hostEntry.AddressList, uri.Port);
_state._socket = client;
BeginSend(_state);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, _state);
}
}
socket连接是需要IP和端口的,这里我们借用 Uri来获取所需端口,但是一台计算机的ip可能有很多个,实际只有一两个可以连接,所以我们这里需要调用 client.Connect(hostEntry.AddressList, uri.Port)方法,传递一个ip集合。如果是https的话,直接用socket我没有搞定,最后用SslStream搞定,不知道大家有没有其他方法。
其中Begin_Write、End_Write、Complete_Read方法是sslStream异步中所必需的方法,BeginSend、Send_Completed、Receive_Completed、RepeatReceive是socket异步中所需方法。其中Complete_Read和Receive_Completed方法相似。
protected virtual void Complete_Read(IAsyncResult ar)
{
RequestSockeStateObject state = ar.AsyncState as RequestSockeStateObject;
try
{
int byteCount = state.SslStream.EndRead(ar);
if (state.ResponseInfo.Headers.Count < 1)
{
SetResponseHeaders(state, byteCount); if ((state.ReceiveLength == state.ContentLength && state.ContentLength > 0))
{
EndReceive(state);
}
else
{
state.SslStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, Complete_Read, state);
}
}
else
{
if (byteCount > 0 && byteCount==state.Buffer.Length)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, byteCount);
state.SslStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, Complete_Read, state);
}
else
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, byteCount);
EndReceive(state);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
如果是第一次接收数据流,我们必须把数据流中http头部信息取出来,再把头部信息以外的数据流写到HttpResponseInfo.ResponseContent中,如果我们已经接收的数据等于我们需要接收的数据,就表示我们已经接收完毕了。如果没有就继续接收数据。在第二次及以后所接收数据过程中,我们需要判断接收数据长度是否小于接收数组的长度,如果小于就表示接收完毕了,否则继续接收。这里的EndReceive方法如下:
void EndReceive(RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
/*
* if (state.RequestInfo.AllowAutoRedirect &&
(state.ResponseInfo.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Found || state.ResponseInfo.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.MovedPermanently))
{
string location = state.ResponseInfo.Headers["Location"];
state.RequestInfo.Url = location;
state.RequestInfo.Headers = state.ResponseInfo.Headers;
state.RequestInfo.Headers.Remove("Location");
state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add("Referer", location);
Begin_Write(state);
}
*/
if (IsHttps)
{
state.SslStream.Close(); state.SslStream = null;
}
else
{
state._socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); state._socket.Close(); state._socket = null;
}
if (state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted != null)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted(state); }
state.RequestHandler.IsBusy = false;
}
EndReceive方法主要是关闭socket或则SslStream数据流,然后调用ActionCompleted方法。在这里 state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);这个方法非常重要,不然在外面的调用方法就必须调用Stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin)来吧数据流定位开始位置。
在SocketHttpRequest这个类中,我们是如何来获取发送的http请求信息以及如何解析http返回的header信息了?
首先来看一个GetRequestData方法,它主要是通过RequestInfo实例来获取请求信息:
byte[] GetRequestData(RequestSockeStateObject _state)
{
StringBuilder bufRequest = new StringBuilder();
Uri uri = new Uri(_state.RequestInfo.Url);
if (!IsHttpPost)
{
bufRequest.Append("GET ").Append(uri.OriginalString).AppendLine(" HTTP/1.1");
}
else
{
bufRequest.Append("POST ").Append(uri.OriginalString).AppendLine(" HTTP/1.1");
string contentLengthkey = "Content-Length";
string contentTypekey = "Content-Type";
List<string> headerKeys = new List<string>(_state.RequestInfo.Headers.AllKeys);
if (headerKeys.Contains(contentLengthkey))
{
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Remove(contentLengthkey);
}
if (headerKeys.Contains(contentTypekey))
{
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Remove(contentTypekey);
}
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add(contentTypekey, "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add(contentLengthkey, _state.RequestInfo.PostData.Length.ToString());
}
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add("Host", uri.Host);
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add("Connection", "keep-alive");
if (_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Count > 0)
{
bufRequest.Append(_state.RequestInfo.Headers.ToString());
}
byte[] byteData = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(bufRequest.ToString());
if (!IsHttpPost)
{
return byteData;
}
else
{
byte[] sendData = new byte[byteData.Length + _state.RequestInfo.PostData.Length];
Array.Copy(byteData, 0, sendData, 0, byteData.Length);
Array.Copy(_state.RequestInfo.PostData, 0, sendData, byteData.Length, _state.RequestInfo.PostData.Length);
return sendData;
}
}
有关请求和header信息的字符串建议不要自己拼接,用WebHeaderCollection实例的ToString方法来生成,并且它把最后那个回车换行也生成。
那么如何更具换回的流中的数据来设置它的返回头信息了,这里我们有一个方法SetResponseHeaders:
void SetResponseHeaders(RequestSockeStateObject state, int bytesRead)
{
try
{
byte[] tempArray = new byte[bytesRead];
Array.Copy(state.Buffer, 0, tempArray, 0, bytesRead);
state.HeaderBuffer.AddRange(tempArray);
tempArray = state.HeaderBuffer.ToArray();
string headerSpilt = "\r\n\r\n";
byte[] headerbyte = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(headerSpilt);
int contentindex = DestTag(tempArray, headerbyte, 0, tempArray.Length);
if (contentindex > 0)
{
string headerStr = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(tempArray, 0, contentindex);
int startIndex = contentindex + headerbyte.Length;
SetResponseHeaders(headerStr, state);
state.ReceiveLength = tempArray.Length - startIndex;
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(tempArray, startIndex, tempArray.Length - startIndex);
state.HeaderBuffer.Clear();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
这里的bytesRead时我第一次接收的数据流长度,首先我们需要在返回流中找到连续的\r\n\r\n 信息,它前面是返回头信息,后面的时返回体信息。这里我们用自定义的DestTag方法来查找。SetResponseHeaders方法如下:
void SetResponseHeaders(string headerStr, RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
try
{
string[] headers = headerStr.Split(new string[] { "\r\n" }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
string statline = headers[0];
state.ResponseInfo.StatusCode = GetStatusCode(statline);
for (int i = 1; i < headers.Length; i++)
{
int index = headers[i].IndexOf(":");
if (index > 1)
{
string key = headers[i].Substring(0, index);
string value = headers[i].Substring(index + 1);
state.ResponseInfo.Headers.Add(key.Trim(), value.Trim());
}
}
string contentLength = state.ResponseInfo.Headers["Content-Length"];
state.ContentLength = int.Parse(contentLength);
state.ReceiveLength = 0;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
以上就是这个类的主要方法,目前SocketHttpRequest对301、302暂不支持。
完整的代码如下:
namespace HttpRequest
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
[Serializable]
public class HttpRequestInfo
{
public HttpRequestInfo(string url)
{
Url = url;
Headers = new WebHeaderCollection();
ExternalData = new Dictionary<string, string>();
}
public string Url { set; get; }
public byte[] PostData { set; get; }
public WebHeaderCollection Headers { set; get; }
public bool AllowAutoRedirect { set; get; }
public Dictionary<string, string> ExternalData { set; get; }
public Action<HttpContextInfo> ActionCompleted { set; get; }
public Action<HttpRequestException> ActionException { set; get; }
public HttpRequestInfo Clone()
{
HttpRequestInfo newobj = new HttpRequestInfo(this.Url)
{
AllowAutoRedirect = this.AllowAutoRedirect,
ActionCompleted = this.ActionCompleted,
ActionException = this.ActionException
};
if (PostData != null && PostData.Length > 0)
{
newobj.PostData = new byte[this.PostData.Length];
Array.Copy(this.PostData, 0, newobj.PostData, 0, this.PostData.Length);
}
if (Headers.Count > 0)
{
foreach (string key in Headers.Keys)
{
newobj.Headers.Add(key, Headers[key]);
}
}
if (ExternalData.Count > 0)
{
foreach (string key in ExternalData.Keys)
{
newobj.ExternalData.Add(key, ExternalData[key]);
}
}
return newobj;
}
}
public class HttpRequestException : Exception
{
public HttpRequestException(HttpContextInfo context, Exception ex)
: base(ex.Message, ex)
{
HttpContextInfo = context;
}
public HttpContextInfo HttpContextInfo { set; get; }
}
}
namespace HttpRequest
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
[Serializable]
public class HttpResponseInfo
{
public HttpResponseInfo()
{
ResponseContent = new MemoryStream();
Headers = new WebHeaderCollection();
}
public Stream ResponseContent { set; get; }
HttpStatusCode _statusCode;
public HttpStatusCode StatusCode
{
set
{
_statusCode = value;
StatusDescription = System.Web.HttpWorkerRequest.GetStatusDescription((int)_statusCode);
}
get
{
return _statusCode;
}
}
public string StatusDescription { set; get; }
public WebHeaderCollection Headers { set; get; }
public string GetString(Encoding coding)
{
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
Stream sr = ResponseContent;
byte[] data = new byte[1024 * 1024];
int readcount = sr.Read(data, 0, data.Length);
while (readcount > 0)
{
str.Append(coding.GetString(data, 0, readcount));
readcount = sr.Read(data, 0, data.Length);
}
ResponseContent.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
return str.ToString();
}
}
public class HttpContextInfo
{
public HttpResponseInfo ResponseInfo { set; get; }
public HttpRequestInfo RequestInfo { set; get; }
}
public interface IHttpRequest
{
void GetResponseAsync(HttpRequestInfo request);
bool IsBusy { set; get; }
}
}
namespace HttpRequest
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.IO;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.OleDb;
using System.Net;
using System.Xml;
using System.Net.Security;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
public class RequestHttpWebRequest : IHttpRequest
{
class StateObjectInfo : HttpContextInfo
{
internal byte[] Buffer { set; get; }
internal Stream ReadStream { set; get; }
internal HttpWebRequest HttpWebRequest { set; get; }
internal RequestHttpWebRequest RequestHandler { set; get; }
}
private bool CheckValidationResult(object sender, X509Certificate certificate, X509Chain chain, SslPolicyErrors errors)
{
//直接确认,否则打不开
return true;
}
public void GetResponseAsync(HttpRequestInfo info)
{
HttpWebRequest webRequest;
StateObjectInfo state;
InitWebRequest(info, out webRequest, out state);
try
{
if (IsHttpPost)
{
webRequest.Method = "POST";
webRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
webRequest.BeginGetRequestStream(EndRequest, state);
}
else
{
webRequest.BeginGetResponse(EndResponse, state);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
void EndRequest(IAsyncResult ar)
{
StateObjectInfo state = ar.AsyncState as StateObjectInfo;
try
{
HttpWebRequest webRequest = state.HttpWebRequest as HttpWebRequest;
using (Stream stream = webRequest.EndGetRequestStream(ar))
{
byte[] data = state.RequestInfo.PostData;
stream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
}
webRequest.BeginGetResponse(EndResponse, state);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
void EndResponse(IAsyncResult ar)
{
StateObjectInfo state = ar.AsyncState as StateObjectInfo;
try
{
HttpWebResponse webResponse = state.HttpWebRequest.EndGetResponse(ar) as HttpWebResponse;
state.ResponseInfo.StatusCode = webResponse.StatusCode;
state.ResponseInfo.StatusDescription = webResponse.StatusDescription;
foreach (string key in webResponse.Headers.AllKeys)
{
state.ResponseInfo.Headers.Add(key, webResponse.Headers[key]);
}
state.ReadStream = webResponse.GetResponseStream();
state.ReadStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, ReadCallBack, state);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
void ReadCallBack(IAsyncResult ar)
{
StateObjectInfo state = ar.AsyncState as StateObjectInfo;
try
{
int read = state.ReadStream.EndRead(ar);
if (read > 0)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, read);
state.ReadStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, ReadCallBack, state);
}
else
{
state.ReadStream.Close();
state.HttpWebRequest.Abort();
if (state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted != null)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted(state);
}
state.Buffer = null;
state.RequestHandler.IsBusy = false;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
private void InitWebRequest(HttpRequestInfo info, out HttpWebRequest webRequest, out StateObjectInfo state)
{
IsBusy = true;
if (info.PostData != null && info.PostData.Length > 0)
{
IsHttpPost = true;
}
else
{
IsHttpPost = false;
}
if (info.Url.ToLower().Trim().StartsWith("https"))
{
IsHttps = true;
ServicePointManager.ServerCertificateValidationCallback = new RemoteCertificateValidationCallback(CheckValidationResult);
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3;
}
else
{
IsHttps = false;
}
webRequest = HttpWebRequest.CreateDefault(new Uri(info.Url)) as HttpWebRequest;
if (IsHttps)
{
/*基础连接已经关闭: 发送时发生错误 */
/*无法从传输连接中读取数据: 远程主机强迫关闭了一个现有的连接*/
webRequest.KeepAlive = false;
webRequest.ProtocolVersion = HttpVersion.Version10;
webRequest.UserAgent = "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.2; .NET CLR 1.0.3705;)";
}
webRequest.AllowAutoRedirect = info.AllowAutoRedirect;
if (info.Headers != null && info.Headers.Count > 0)
{
foreach (string key in info.Headers.Keys)
{
webRequest.Headers.Add(key, info.Headers[key]);
}
}
//webRequest.Proxy = WebProxy.GetDefaultProxy();
//webRequest.Proxy.Credentials = CredentialCache.DefaultCredentials;
//webResponse.Headers.Get("Set-Cookie");
state = new StateObjectInfo
{
Buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024],
HttpWebRequest = webRequest,
RequestHandler = this,
RequestInfo = info,
ResponseInfo = new HttpResponseInfo()
};
}
private bool IsHttpPost { set; get; }
private bool IsHttps { set; get; }
public bool IsBusy { set; get; }
private void HandException(Exception ex, StateObjectInfo state)
{
if (state.ReadStream != null)
state.ReadStream.Close();
if (state.HttpWebRequest != null)
state.HttpWebRequest.Abort();
state.Buffer = null;
if (state.RequestInfo.ActionException != null)
{
state.RequestInfo.ActionException(new HttpRequestException(state, ex));
}
state.RequestHandler.IsBusy = false;
}
}
}
namespace HttpRequest
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Net;
public class HttpRequestFactory
{
static HttpRequestFactory()
{
MaxRequestCount = 10;
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(Process));
}
static readonly object Lockobj = new object();
static long requestCount = 0;
static Queue<HttpRequestInfo> requestTask = new Queue<HttpRequestInfo>();
static List<IHttpRequest> Handlers = new List<IHttpRequest>();
public static void AddRequestTask(HttpRequestInfo info)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(info.Url))
{
lock (Lockobj)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref requestCount);
requestTask.Enqueue(info);
}
}
}
private static IHttpRequest GetAvailableHttpRequest()
{
lock (Lockobj)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Handlers.Count; i++)
{
if (!Handlers[i].IsBusy)
{
return Handlers[i];
}
}
if (Handlers.Count <= MaxRequestCount)
{
IHttpRequest handler = (IHttpRequest)Activator.CreateInstance(_httpRequestType);
Handlers.Add(handler);
return handler;
}
}
return null;
//return GetAvailableHttpRequest();
}
private static HttpRequestInfo GetTask()
{
HttpRequestInfo task = null;
lock (Lockobj)
{
if (requestTask.Count > 0)
{
task = requestTask.Dequeue();
return task;
}
}
return task;
}
private static void Process(object obj)
{
while (true)
{
IHttpRequest handler = GetAvailableHttpRequest();
while (handler == null)
{
Thread.Sleep(100);
handler = GetAvailableHttpRequest();
}
HttpRequestInfo task = GetTask();
while (task == null)
{
Thread.Sleep(100);
task = GetTask();
}
if (task != null && handler != null)
{
Interlocked.Decrement(ref requestCount);
handler.GetResponseAsync(task);
}
// Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
public static long TaskCount
{
get
{
return Interlocked.Read(ref requestCount);
}
}
static int _maxRequestCount = 2;
public static int MaxRequestCount
{
set
{
_maxRequestCount = value;
ServicePointManager.DefaultConnectionLimit = _maxRequestCount;
}
get
{
return _maxRequestCount;
}
}
static Type _httpRequestType = typeof(RequestHttpWebRequest);
public static void SetHttpRequestType(Type type)
{
if (type.IsClass && typeof(IHttpRequest).IsAssignableFrom(type))
{
_httpRequestType = type;
}
}
}
}
namespace HttpRequest
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Reflection;
using System.IO;
public class LogManager
{
static object lockobj = new object();
static Queue<string> Messages = new Queue<string>();
static LogManager()
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(Work));
}
public static void LogException(Exception ex)
{
Type type = ex.GetType();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine(type.ToString() + "--------" + DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
PropertyInfo[] properties = type.GetProperties();
foreach (PropertyInfo p in properties)
{
if (p.PropertyType == typeof(string))
{
object msg = p.GetValue(ex, null);
if (msg != null)
sb.AppendLine(p.Name + ":" + msg.ToString());
}
}
lock (lockobj)
{
Messages.Enqueue(sb.ToString());
}
}
public static void LogException(string msg)
{
lock (lockobj)
{
Messages.Enqueue(msg);
}
}
static void Work(object obj)
{
if (!File.Exists(ExceptionLogFilePath))
{
FileStream fs = File.Create(ExceptionLogFilePath);
fs.Close();
}
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(ExceptionLogFilePath, true, Encoding.UTF8))
{
while (true)
{
if (Messages.Count > 0)
{
string msg = string.Empty;
lock (lockobj)
{
msg = Messages.Dequeue();
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(msg))
{
sw.Write(msg);
sw.WriteLine();
sw.Flush();
// Console.WriteLine(msg);
}
}//end if
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
}//end
public static string ExceptionLogFilePath { set; get; }
}
}
SocketHttpRequest代码:
namespace HttpRequest
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Security;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Security.Authentication;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
public class SocketHttpRequest : IHttpRequest
{
class RequestSockeStateObject : HttpContextInfo
{
internal SocketHttpRequest RequestHandler { set; get; }
internal Socket _socket { set; get; }
internal List<byte> HeaderBuffer { set; get; }
internal byte[] Buffer { set; get; }
internal int ContentLength { set; get; }
internal int ReceiveLength { set; get; }
internal SslStream SslStream { set; get; }
}
public void GetResponseAsync(HttpRequestInfo info)
{
RequestSockeStateObject _state;
InitRequestSockeStateObject(info, out _state);
SocketConnection(_state);
}
void SocketConnection(RequestSockeStateObject _state)
{
try
{
Uri uri = new Uri(_state.RequestInfo.Url);
IPHostEntry hostEntry = Dns.GetHostEntry(uri.Host);
if (IsHttps)
{
TcpClient tcpclient = new TcpClient();
tcpclient.Connect(hostEntry.AddressList, uri.Port);
_state._socket = tcpclient.Client;
SslStream sslStream = new SslStream(tcpclient.GetStream(), false, new RemoteCertificateValidationCallback(ValidateServerCertificate), null);
sslStream.AuthenticateAsClient(hostEntry.HostName, new X509CertificateCollection(), SslProtocols.Ssl3 | SslProtocols.Tls, false);
_state.SslStream = sslStream;
Begin_Write(_state);
}
else
{
Socket client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
client.Connect(hostEntry.AddressList, uri.Port);
_state._socket = client;
BeginSend(_state);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, _state);
}
}
#region SSL Https
void Begin_Write(RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
try
{
byte[] requestData = GetRequestData(state);
state.SslStream.BeginWrite(requestData, 0, requestData.Length, End_Write, state);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
protected virtual void End_Write(IAsyncResult ar)
{
RequestSockeStateObject state = ar.AsyncState as RequestSockeStateObject;
try
{
state.SslStream.EndWrite(ar);
state.SslStream.Flush();
state.SslStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, Complete_Read, state);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
protected virtual void Complete_Read(IAsyncResult ar)
{
RequestSockeStateObject state = ar.AsyncState as RequestSockeStateObject;
try
{
int byteCount = state.SslStream.EndRead(ar);
if (state.ResponseInfo.Headers.Count < 1)
{
SetResponseHeaders(state, byteCount);
if ((state.ReceiveLength == state.ContentLength && state.ContentLength > 0))
{
EndReceive(state);
}
else
{
state.SslStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, Complete_Read, state);
}
}
else
{
if (byteCount > 0 && byteCount == state.Buffer.Length)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, byteCount);
state.SslStream.BeginRead(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length, Complete_Read, state);
}
else
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, byteCount);
EndReceive(state);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
#endregion
#region Http
void BeginSend(RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
try
{
byte[] byteData = GetRequestData(state);
SocketAsyncEventArgs arg = new SocketAsyncEventArgs
{
UserToken = state,
RemoteEndPoint = state._socket.RemoteEndPoint
};
arg.SetBuffer(byteData, 0, byteData.Length);
arg.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(Send_Completed);
bool send = state._socket.SendAsync(arg);
if (!send)
{
HandException(new SocketException((int)SocketError.NoData), state);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
protected virtual void Send_Completed(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
RequestSockeStateObject state = e.UserToken as RequestSockeStateObject;
try
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
SocketAsyncEventArgs arg = new SocketAsyncEventArgs
{
UserToken = state,
RemoteEndPoint = state._socket.RemoteEndPoint,
};
arg.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(Receive_Completed);
arg.SetBuffer(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length);
bool receive = state._socket.ReceiveAsync(arg);
if (!receive)
{
HandException(new SocketException((int)SocketError.NoData), state);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
protected virtual void Receive_Completed(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
RequestSockeStateObject state = e.UserToken as RequestSockeStateObject;
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
if (state.ResponseInfo.Headers.Count < 1)
{
SetResponseHeaders(state, e.BytesTransferred);
if ((state.ReceiveLength == state.ContentLength && state.ContentLength > 0))
{
EndReceive(state);
}
else
{
RepeatReceive(state);
}
}
else
{
if (e.BytesTransferred > 0 && e.BytesTransferred == state.Buffer.Length)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, e.BytesTransferred);
RepeatReceive(state);
}
else
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(state.Buffer, 0, e.BytesTransferred);
EndReceive(state);
}
}
}
else
{
HandException(new SocketException((int)e.SocketError), state);
}
}
//end
void RepeatReceive(RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
SocketAsyncEventArgs arg = new SocketAsyncEventArgs
{
UserToken = state,
RemoteEndPoint = state._socket.RemoteEndPoint,
};
arg.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(Receive_Completed);
arg.SetBuffer(state.Buffer, 0, state.Buffer.Length);
bool receive = state._socket.ReceiveAsync(arg);
if (!receive)
{
HandException(new SocketException((int)SocketError.SocketError), state);
}
}
#endregion
void EndReceive(RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
/*
* if (state.RequestInfo.AllowAutoRedirect &&
(state.ResponseInfo.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Found || state.ResponseInfo.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.MovedPermanently))
{
string location = state.ResponseInfo.Headers["Location"];
state.RequestInfo.Url = location;
state.RequestInfo.Headers = state.ResponseInfo.Headers;
state.RequestInfo.Headers.Remove("Location");
state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add("Referer", location);
Begin_Write(state);
}
*/
if (IsHttps)
{
state.SslStream.Close();
state.SslStream = null;
}
else
{
state._socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
state._socket.Close();
state._socket = null;
}
if (state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted != null)
{
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
state.RequestInfo.ActionCompleted(state);
}
state.RequestHandler.IsBusy = false;
}
#region Set Response Header
/// <summary>
/// 判断读取的信息中是否包含返回头的结束符,如果有则取出返回头的信息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="state">状态信息</param>
/// <param name="bytesRead">读取的字节数</param>
void SetResponseHeaders(RequestSockeStateObject state, int bytesRead)
{
try
{
byte[] tempArray = new byte[bytesRead];
Array.Copy(state.Buffer, 0, tempArray, 0, bytesRead);
state.HeaderBuffer.AddRange(tempArray);
tempArray = state.HeaderBuffer.ToArray();
string headerSpilt = "\r\n\r\n";
byte[] headerbyte = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(headerSpilt);
int contentindex = DestTag(tempArray, headerbyte, 0, tempArray.Length);
if (contentindex > 0)
{
string headerStr = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(tempArray, 0, contentindex);
int startIndex = contentindex + headerbyte.Length;
SetResponseHeaders(headerStr, state);
state.ReceiveLength = tempArray.Length - startIndex;
state.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent.Write(tempArray, startIndex, tempArray.Length - startIndex);
state.HeaderBuffer.Clear();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 设置ResponseInfo的返回头,并且检查返回头是否含有Keep-Alive和Content-Length
/// </summary>
/// <param name="headerStr">字符串形式的返回头</param>
/// <param name="state">整个异步处理过程中的对象</param>
void SetResponseHeaders(string headerStr, RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
try
{
string[] headers = headerStr.Split(new string[] { "\r\n" }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
string statline = headers[0];
state.ResponseInfo.StatusCode = GetStatusCode(statline);
for (int i = 1; i < headers.Length; i++)
{
int index = headers[i].IndexOf(":");
if (index > 1)
{
string key = headers[i].Substring(0, index);
string value = headers[i].Substring(index + 1);
state.ResponseInfo.Headers.Add(key.Trim(), value.Trim());
}
}
string contentLength = state.ResponseInfo.Headers["Content-Length"];
state.ContentLength = int.Parse(contentLength);
state.ReceiveLength = 0;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandException(ex, state);
}
}
HttpStatusCode GetStatusCode(string text)
{
Regex reg = new Regex(@"\d{3}");
Match m = reg.Match(text);
string code = m.Value;
HttpStatusCode statu = (HttpStatusCode)Enum.Parse(typeof(HttpStatusCode), code, true);
return statu;
}
/// <summary>
/// 在指定的数组中检索短数组
/// </summary>
/// <param name="buffer">要检索的大数组</param>
/// <param name="tag">待检索的小字数组</param>
/// <param name="startIndex">检完索的启始索引</param>
/// <param name="maxLength">大数组的有效长度</param>
/// <returns>如检索到,则返回启始索引,否则返回-1</returns>
protected int DestTag(byte[] buffer, byte[] tag, int startIndex, int maxLength)
{
bool temp = true;
int endIndex = maxLength - tag.Length;
while (startIndex < maxLength - tag.Length)
{
temp = true;
int pos = Array.IndexOf(buffer, tag[0], startIndex, endIndex - startIndex);
if (pos < 0)
{
return -1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < tag.Length; j++) //匹配所有字节
{
if (buffer[pos + j] != tag[j])
{
if (pos > startIndex)
startIndex = pos;
else
startIndex++;
temp = false;
break;
}
}
if (temp == true)
{
return pos;
}
}
return -1;
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// 根据指定的uri获取请求头
/// </summary>
/// <param name="uri">请求的uri</param>
/// <returns>以字符串的形式返回请求头</returns>
byte[] GetRequestData(RequestSockeStateObject _state)
{
StringBuilder bufRequest = new StringBuilder();
Uri uri = new Uri(_state.RequestInfo.Url);
if (!IsHttpPost)
{
bufRequest.Append("GET ").Append(uri.OriginalString).AppendLine(" HTTP/1.1");
}
else
{
bufRequest.Append("POST ").Append(uri.OriginalString).AppendLine(" HTTP/1.1");
string contentLengthkey = "Content-Length";
string contentTypekey = "Content-Type";
List<string> headerKeys = new List<string>(_state.RequestInfo.Headers.AllKeys);
if (headerKeys.Contains(contentLengthkey))
{
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Remove(contentLengthkey);
}
if (headerKeys.Contains(contentTypekey))
{
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Remove(contentTypekey);
}
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add(contentTypekey, "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add(contentLengthkey, _state.RequestInfo.PostData.Length.ToString());
}
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add("Host", uri.Host);
_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Add("Connection", "keep-alive");
if (_state.RequestInfo.Headers.Count > 0)
{
bufRequest.Append(_state.RequestInfo.Headers.ToString());
}
byte[] byteData = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(bufRequest.ToString());
if (!IsHttpPost)
{
return byteData;
}
else
{
byte[] sendData = new byte[byteData.Length + _state.RequestInfo.PostData.Length];
Array.Copy(byteData, 0, sendData, 0, byteData.Length);
Array.Copy(_state.RequestInfo.PostData, 0, sendData, byteData.Length, _state.RequestInfo.PostData.Length);
return sendData;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 初始化State以及ResponseInfo
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">请求对象</param>
void InitRequestSockeStateObject(HttpRequestInfo info, out RequestSockeStateObject _state)
{
this.IsBusy = true;
_state = new RequestSockeStateObject()
{
RequestHandler = this,
Buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024],
HeaderBuffer = new List<byte>(),
RequestInfo = info,
ResponseInfo = new HttpResponseInfo()
};
if (info.PostData == null || info.PostData.Length < 1)
{
IsHttpPost = false;
}
else
{
IsHttpPost = true;
}
if (info.Url.ToLower().Trim().StartsWith("https"))
{
IsHttps = true;
}
else
{
IsHttps = false;
}
}
void HandException(Exception ex, RequestSockeStateObject state)
{
if (IsHttps)
{
if (state.SslStream != null)
state.SslStream.Close();
else if (state._socket != null)
{
state._socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
state._socket.Close();
}
}
else
{
state._socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
state._socket.Close();
}
if (state.RequestInfo.ActionException != null)
{
state.RequestInfo.ActionException(new HttpRequestException(state, ex));
}
state.RequestHandler.IsBusy = false;
}
static bool ValidateServerCertificate(object sender, X509Certificate certificate, X509Chain chain, SslPolicyErrors sslPolicyErrors)
{
/*
if (sslPolicyErrors == SslPolicyErrors.None)
return true;
Console.WriteLine("Certificate error: {0}", sslPolicyErrors);
return false;
*/
return true;
}
bool IsHttps { set; get; }
bool IsHttpPost { set; get; }
public bool IsBusy
{
set;
get;
}
}
}
调用代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.OleDb;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Threading;
namespace HttpRequest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LogManager.ExceptionLogFilePath = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ExceptionLogFilePath"].Trim();
ConnectionString = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ConnectionString"].Trim();
string remoteHostUrl = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["remoteHostUrl"].Trim();
string destinationBasePath = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["destinationBasePath"].Trim();
HttpRequestFactory.MaxRequestCount = Convert.ToInt32(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["MaxRequestCount"]);
HttpRequestFactory.SetHttpRequestType(typeof(SocketHttpRequest));
try
{
DateTime startTime = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine("Start Time:" + startTime.ToLongTimeString());
DownLoadFiles(remoteHostUrl, destinationBasePath, null, false);
while (true)
{
if (HttpRequestFactory.TaskCount < 1)
{
Thread.Sleep(1000 * HttpRequestFactory.MaxRequestCount);
break;
}
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
DateTime endtime = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine("End Time:" + endtime.ToLongTimeString());
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static void DownLoadFiles(string remoteHostUrl, string destinationBasePath, List<string> tables, bool download)
{
try
{
List<string> archiveTables = tables;
if (archiveTables == null || archiveTables.Count < 1)
{
string sql = "SELECT DISTINCT TableName FROM dbo.Archive_Files ORDER BY TableName";
DataTable dt = GetData(sql);
archiveTables = new List<string>();
foreach (DataRow row in dt.Rows)
{
archiveTables.Add(row["TableName"].ToString());
}
}
foreach (string tablename in archiveTables)
{
string sql = "SELECT ID,file_name_path FROM dbo.Archive_Files WHERE TableName ='" + tablename + "' AND Copyed=0 ORDER BY ID ASC";
DataTable dt = GetData(sql);
foreach (DataRow row in dt.Rows)
{
string id = row["ID"].ToString();
string file_name_path = row["file_name_path"].ToString();
file_name_path = file_name_path.Substring(2);
DownLoadFile(remoteHostUrl + file_name_path, destinationBasePath + file_name_path, id);
}
while (true)
{
if (HttpRequestFactory.TaskCount <= HttpRequestFactory.MaxRequestCount)
{
break;
}
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
string message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + ex.Message;
LogManager.LogException(message);
}
}
public static void DownLoadFile(string remoteurl, string destinationFilePath, string id)
{
try
{
if (HasIllegalCharacters(destinationFilePath, false))
{
SetFileCopyed(id, "400", "HasIllegalCharacters");
return;
}
DirectoryInfo dir = new DirectoryInfo(destinationFilePath);
FileInfo destinationFile = new FileInfo(destinationFilePath);
if (!destinationFile.Directory.Exists)
{
destinationFile.Directory.Create();
}
HttpRequestInfo request = new HttpRequestInfo(remoteurl);
request.ActionCompleted = new Action<HttpContextInfo>(x =>
{
if (x.ResponseInfo.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
using (Stream wr = File.Open(destinationFilePath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write), sr = x.ResponseInfo.ResponseContent)
{
byte[] data = new byte[1024 * 1024];
int readcount = sr.Read(data, 0, data.Length);
while (readcount > 0)
{
wr.Write(data, 0, readcount);
readcount = sr.Read(data, 0, data.Length);
}
}
SetFileCopyed(id, "200", string.Empty);
}
else
{
SetFileCopyed(id, ((int)x.ResponseInfo.StatusCode).ToString(), x.ResponseInfo.StatusDescription);
string message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + remoteurl + " : " + x.ResponseInfo.StatusDescription;
LogManager.LogException(message);
}
});
request.ActionException = new Action<HttpRequestException>(ex =>
{
Regex reg = new Regex(@"\d{3}", RegexOptions.Compiled);
string message = ex.Message;
Match m = reg.Match(message);
if (m.Success)
{
SetFileCopyed(id, m.Value, message);
}
else
{
SetFileCopyed(id, "503", message);
HttpRequestInfo newRequest = ex.HttpContextInfo.RequestInfo.Clone();
request.ActionCompleted = null;
request.ActionException = null;
HttpRequestFactory.AddRequestTask(newRequest);
}
message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + ex.HttpContextInfo.RequestInfo.Url + " : " + message;
LogManager.LogException(message);
});
HttpRequestFactory.AddRequestTask(request);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SetFileCopyed(id, "-1", ex.Message);
string message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + remoteurl + " : " + ex.Message;
LogManager.LogException(message);
}
}
internal static bool HasIllegalCharacters(string path, bool checkAdditional)
{
for (int i = 0; i < path.Length; i++)
{
int num2 = path[i];
if (((num2 == 0x22) || (num2 == 60)) || (((num2 == 0x3e) || (num2 == 0x7c)) || (num2 < 0x20)))
{
return true;
}
if (checkAdditional && ((num2 == 0x3f) || (num2 == 0x2a)))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static bool SetFileCopyed(string id, string statusCode, string error)
{
string sql = string.Format("UPDATE dbo.Archive_Files SET Copyed={0}, CopyDate=GETDATE() ", statusCode);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(error))
{
sql += string.Format(" ,CopyError='{0}' ", error);
}
sql += string.Format(" WHERE ID={0}", id);
return ExecuteCmd(sql);
}
private static bool SetFilesDeleted(List<string> ids, bool success)
{
string sql = string.Empty;
if (success)
{
sql = "UPDATE dbo.Archive_Files SET Deleted=1 , DeleteDate=GETDATE() WHERE ID in (" + string.Join(",", ids.ToArray()) + ")";
}
else
{
sql = "UPDATE dbo.Archive_Files SET Deleted=-1 WHERE ID in (" + string.Join(",", ids.ToArray()) + ")";
}
return ExecuteCmd(sql);
}
private static DataTable GetData(string sql)
{
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
try
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter(sql, con);
adapter.Fill(dt);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
string message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + ex.Message;
LogManager.LogException(message);
}
return dt;
}
private static bool ExecuteCmd(string sql)
{
int resultCount = 0;
try
{
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, connection);
connection.Open();
cmd.CommandTimeout = 2 * 60;
resultCount = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
connection.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
string message = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " : " + ex.Message;
LogManager.LogException(message);
}
return resultCount > 0;
}
static int ExecuteScalar(string sql)
{
int result = 0;
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sql, con);
cmd.CommandTimeout = 2 * 60;
con.Open();
result = Convert.ToInt32(cmd.ExecuteScalar());
con.Close();
}
return result;
}
public static string ConnectionString { set; get; }
}
}
有不对的地方还请大家拍砖!

