目录贴: 跟我学Shiro目录贴
在一些场景中,比如某个领导因为一些原因不能进行登录网站进行一些操作,他想把他网站上的工作委托给他的秘书,但是他不想把帐号/密码告诉他秘书,只是想把工作委托给他;此时和我们可以使用Shiro的RunAs功能,即允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问。
本章代码基于《第十六章 综合实例》,请先了解相关数据模型及基本流程后再学习本章。
表及数据SQL
请运行shiro-example-chapter21/sql/ shiro-schema.sql 表结构
请运行shiro-example-chapter21/sql/ shiro-schema.sql 数据
实体
具体请参考com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter21包下的实体。
public class UserRunAs implements Serializable {
private Long fromUserId;//授予身份帐号
private Long toUserId;//被授予身份帐号
}
该实体定义了授予身份帐号(A)与被授予身份帐号(B)的关系,意思是B帐号将可以假装为A帐号的身份进行访问。
DAO
具体请参考com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter21.dao包下的DAO接口及实现。
Service
具体请参考com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter21.service包下的Service接口及实现。
public interface UserRunAsService {
public void grantRunAs(Long fromUserId, Long toUserId);
public void revokeRunAs(Long fromUserId, Long toUserId);
public boolean exists(Long fromUserId, Long toUserId);
public List<Long> findFromUserIds(Long toUserId);
public List<Long> findToUserIds(Long fromUserId);
}
提供授予身份、回收身份、关系存在判断及查找API。
Web控制器RunAsController
该控制器完成:授予身份/回收身份/切换身份功能。
展示当前用户能切换到身份列表,及授予给其他人的身份列表:
@RequestMapping
public String runasList(@CurrentUser User loginUser, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("fromUserIds",
userRunAsService.findFromUserIds(loginUser.getId()));
model.addAttribute("toUserIds", userRunAsService.findToUserIds(loginUser.getId()));
List<User> allUsers = userService.findAll();
allUsers.remove(loginUser);
model.addAttribute("allUsers", allUsers);
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
model.addAttribute("isRunas", subject.isRunAs());
if(subject.isRunAs()) {
String previousUsername =
(String)subject.getPreviousPrincipals().getPrimaryPrincipal();
model.addAttribute("previousUsername", previousUsername);
}
return "runas";
}
1、Subject.isRunAs():表示当前用户是否是RunAs用户,即已经切换身份了;
2、Subject.getPreviousPrincipals():得到切换身份之前的身份,一个用户可以切换很多次身份,之前的身份使用栈数据结构来存储;
授予身份
把当前用户身份授予给另一个用户,这样另一个用户可以切换身份到该用户。
@RequestMapping("/grant/{toUserId}")
public String grant(
@CurrentUser User loginUser,
@PathVariable("toUserId") Long toUserId,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
if(loginUser.getId().equals(toUserId)) {
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("msg", "自己不能切换到自己的身份");
return "redirect:/runas";
}
userRunAsService.grantRunAs(loginUser.getId(), toUserId);
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("msg", "操作成功");
return "redirect:/runas";
}
1、自己不能授予身份给自己;
2、调用UserRunAsService. grantRunAs把当前登录用户的身份授予给相应的用户;
回收身份
把授予给某个用户的身份回收回来。
@RequestMapping("/revoke/{toUserId}")
public String revoke(
@CurrentUser User loginUser,
@PathVariable("toUserId") Long toUserId,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
userRunAsService.revokeRunAs(loginUser.getId(), toUserId);
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("msg", "操作成功");
return "redirect:/runas";
}
切换身份
@RequestMapping("/switchTo/{switchToUserId}")
public String switchTo(
@CurrentUser User loginUser,
@PathVariable("switchToUserId") Long switchToUserId,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
User switchToUser = userService.findOne(switchToUserId);
if(loginUser.equals(switchToUser)) {
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("msg", "自己不能切换到自己的身份");
return "redirect:/runas";
}
if(switchToUser == null || !userRunAsService.exists(switchToUserId, loginUser.getId())) {
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("msg", "对方没有授予您身份,不能切换");
return "redirect:/runas";
}
subject.runAs(new SimplePrincipalCollection(switchToUser.getUsername(), ""));
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("msg", "操作成功");
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("needRefresh", "true");
return "redirect:/runas";
}
1、首先根据switchToUserId查找到要切换到的身份;
2、然后通过UserRunAsService. exists()判断当前登录用户是否可以切换到该身份;
3、通过Subject.runAs()切换到该身份;
切换到上一个身份
@RequestMapping("/switchBack")
public String switchBack(RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if(subject.isRunAs()) {
subject.releaseRunAs();
}
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("msg", "操作成功");
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("needRefresh", "true");
return "redirect:/runas";
}
1、通过Subject.releaseRunAs()切换会上一个身份;
此处注意的是我们可以切换多次身份,如A切换到B,然后再切换到C;那么需要调用两次Subject. releaseRunAs()才能切换会A;即内部使用栈数据结构存储着切换过的用户;Subject. getPreviousPrincipals()得到上一次切换到的身份,比如当前是C;那么调用该API将得到B的身份。
其他代码和配置和《第十六章 综合实例》一样,请参考该章。
测试
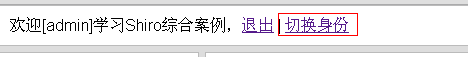
1、首先访问http://localhost:8080/chapter21/,输入admin/123456进行登录;会看到如下界面:
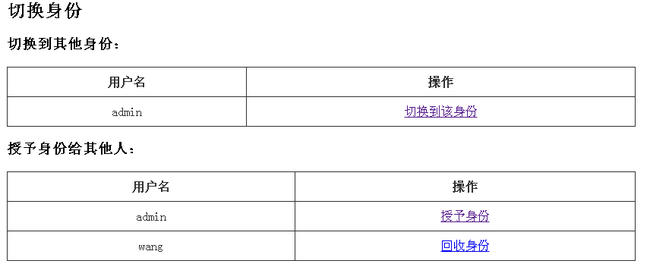
2、点击切换身份按钮,跳到如下界面:
在该界面可以授权身份给其他人(点击授权身份可以把自己的身份授权给其他人/点击回收身份可以把之前授予的身份撤回)、或切换到其他身份(即假装为其他身份运行);
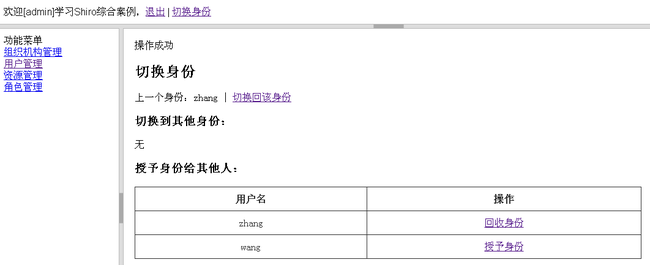
3、点击切换到该身份按钮,切换到相应的身份运行,如:
此时zhang用户切换到admin身份;如果点击切换回该身份,会把当前身份切换会zhang。
示例源代码:https://github.com/zhangkaitao/shiro-example;可加群 231889722 探讨Spring/Shiro技术。