1. 深入Struts2的配置文件
本部分主要介绍struts.xml的常用配置。
1.1. 包配置:
Struts2框架中核心组件就是Action、拦截器等,Struts2框架使用包来管理Action和拦截器等。每个包就是多个Action、多个拦截器、多个拦截器引用的集合。
在struts.xml文件中package元素用于定义包配置,每个package元素定义了一个包配置。它的常用属性有:
l name:必填属性,用来指定包的名字。
l extends:可选属性,用来指定该包继承其他包。继承其它包,可以继承其它包中的Action定义、拦截器定义等。
l namespace:可选属性,用来指定该包的命名空间。
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<!-- struts2
的
action
必须放在一个指定的包空间下定义
-->
<
package
name
=
"default"
extends
=
"struts-default"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"login"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
如上示例的配置,配置了一个名为default的包,该包下定义了一个Action。
1.2. 命名空间配置:
考虑到同一个Web应用中需要同名的Action,Struts2以命名空间的方式来管理Action,同一个命名空间不能有同名的Action。
Struts2通过为包指定namespace属性来为包下面的所有Action指定共同的命名空间。
把上示例的配置改为如下形式:
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<!-- struts2
的
action
必须放在一个指定的包空间下定义
-->
<
package
name
=
"qiujy"
extends
=
"struts-default"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"login"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"backLogin"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
如上配置了两个包:default和my,配置my包时指定了该包的命名空间为/manage。
对于包default:没有指定namespace属性。如果某个包没有指定namespace属性,即该包使用默认的命名空间,默认的命名空间总是""。
对于包my:指定了命名空间/manage,则该包下所有的Action处理的URL应该是“命名空间/Action名”。如上名为
backLogin的Action,它处理的URL为:
http://localhost:8080/userlogin_struts2
/manage/backLogin.action
Struts2的命名空间的作用等同于struts1里模块的作用。
1.3. 包含配置:
在Struts2中可以将一个配置文件分解成多个配置文件,那么我们必须在struts.xml中包含其他配置文件。
|
<
struts
>
<
include
file
=
"struts-default.xml"
/>
<
include
file
=
"struts-user.xml"
/>
<
include
file
=
"struts-book.xml"
/>
<
include
file
=
"struts-shoppingCart.xml"
/>
......
</
struts
>
|
1.4. 拦截器配置:
见后面章节介绍。
1.5. 常量配置:
Struts2框架有两个核心配置文件,其中struts.xml文件主要负责管理应用中的Action映射, 及Action处理结果和物理资源之间的映射关系。除此之外,Struts2框架还包含了一个struts.properties文件,该文件主义了Struts2框架的大量常量属性。但通常推荐也是在struts.xml文件中来配置这些常量属性。
如:后面会讲到Struts2的国际化,它的资源文件位置就用常量属性来指定:
|
<
struts
>
......
<
constant
name
=
"struts.custom.i18n.resources"
value
=
"messages"
/>
</
struts
>
|
表示指定了资源文件的放置在classes目录下,基本名是messages,则在classes目录下您就应该放置类似messages_zh_CN.properties,message_en.properties名的文件。
2. Struts2的Action
2.1. 实现Action类:
Struts2中Action是核心内容,它包含了对用户请求的处理逻辑,我们也称Action为业务控制器。
Struts2中的Action采用了低侵入式的设计,Struts2不要求Action类继承任何的Struts2的基类或实现Struts2接口。(但是,我们为了方便实现Action,大多数情况下都会继承com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport类,并重写此类里的public String execute() throws Exception方法。因为此类中实现了很多的实用接口,提供了很多默认方法,这些默认方法包括获取国际化信息的方法、数据校验的方法、默认的处理用户请求的方法等,这样可以大大的简化Action的开发。)
Struts2中通常直接使用Action来封装HTTP请求参数,因此,Action类里还应该包含与请求参数对应的属性,并且为属性提供对应的getter和setter方法。(当然,Action类中还可以封装处理结果,把处理结果信息当作一属性,提供对应的getter和setter方法)
修改第一部分的用户登录示例:把Action改成如下:
|
package
org.qiujy.web.struts2.action;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
@author
qiujy
*
@version
1.0
*/
public
class
LoginAction
extends
ActionSupport
{
private
String
userName
;
private
String
password
;
private
String
msg
;
//
结果信息属性
/**
*
@return
the
msg
*/
public
String getMsg() {
return
msg
;
}
/**
*
@param
msg
the
msg
to
set
*/
public
void
setMsg(String msg) {
this
.
msg
= msg;
}
/**
*
@return
the
userName
*/
public
String getUserName() {
return
userName
;
}
/**
*
@param
userName
the
userName
to
set
*/
public
void
setUserName(String userName) {
this
.
userName
= userName;
}
/**
*
@return
the
password
*/
public
String getPassword() {
return
password
;
}
/**
*
@param
password
the
password
to
set
*/
public
void
setPassword(String password) {
this
.
password
= password;
}
/**
*
处理用户请求的
excute()
方法
*
@return
结果导航字符串
*
@throws
Exception
*/
public
String execute()
throws
Exception{
if
(
"test"
.equals(
this
.
userName
) &&
"test"
.equals(
this
.
password
)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+
this
.
userName
;
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
}
|
往success.jsp和error.jsp页面中添加 ${msg} EL表达式来显示结果信息。则最终效果跟以前一样。
2.2. Action访问Servlet API:
Struts2中的Action并没有和任何Servlet API耦合,这样框架更具灵活性,更易测试。
但是,对于web应用的控制器而言,不访问Servlet API几乎是不可能的,例如跟踪HTTP Session状态等。Struts2框架提供了一种更轻松的方式来访问Servlet API。Struts2中提供了一个ActionContext类(当前Action的上下文对象),通过这个类可以访问Servlet API。下面是该类中提供的几个常用方法:
l public static ActionContext getContext() :获得当前Action的ActionContext实例。
l public Object get(Object key) :此方法类似于调用HttpServletRequest的getAttribute(String name)方法。
l public void put(Object key, Object value) :此方法类似于调用HttpServletRequest 的setAttribute(String name, Object o)。
l public Map getParameters() :获取所有的请求参数。类似于调用HttpServletRequest对象的getParameterMap() 方法。
l public Map getSession() :返回一个Map对象,该Map对象模拟了HttpSession实例。
l public void setSession(Map session) : 直接传入一个Map实例,将该Map实例里的key-value对转换成session的属性名-属性值对。
l public Map getApplication() :返回一个Map对象,该对象模拟了该应用的ServletContext实例。
l public void setApplication(Map application) :直接传入一个Map实例,将该Map实例里的key-value对转换成application的属性名-属性值对。
修改以上用户登录验证示例的Action类中的execute方法:
|
public
String execute()
throws
Exception{
if
(
"test"
.equals(
this
.
userName
) &&
"test"
.equals(
this
.
password
)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+
this
.
userName
;
//
获取
ActionContext
实例,通过它来访问
Servlet API
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
//
看
session
中是否已经存放了用户名,如果存放了:说明已经登录了;
//
否则说明是第一次登录成功
if
(
null
!= context.getSession().get(
"uName"
)){
msg
=
this
.
userName
+
"
:你已经登录过了
!!!"
;
}
else
{
context.getSession().put(
"uName"
,
this
.
userName
);
}
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
|
Struts2中通过ActionContext来访问Servlet API,让Action彻底从Servlet API 中分离出来,最大的好处就是可以脱离Web容器测试Action。
另外,Struts2中还提供了一个ServletActionContext类,Action只要继承自该类,就可以直接访问Servlet API。具体方法参看struts2的API文档。
3. 一个Action内包含多个请求处理方法的处理
Struts1提供了DispatchAction,从而允许一个Action内包含多个请求处理方法。Struts2也提供了类似的功能。处理方式主要有以下三种方式:
3.1. 动态方法调用:
DMI:Dynamic Method Invocation 动态方法调用。
动态方法调用是指:表单元素的action不直接等于某个Action的名字,而是以如下形式来指定对应的动作名:
|
<form method="post"
action="userOpt!login.action">
|
则用户的请求将提交到名为”userOpt”的Action实例,Action实例将调用名为”login”方法来处理请求。同时login方法的签名也是跟execute()一样,即为public String login() throws Exception。
注意:要使用动态方法调用,必须设置Struts2允许动态方法调用,通过设置struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation常量来完成,该常量属性的默认值是true。
3.1.1. 示例:
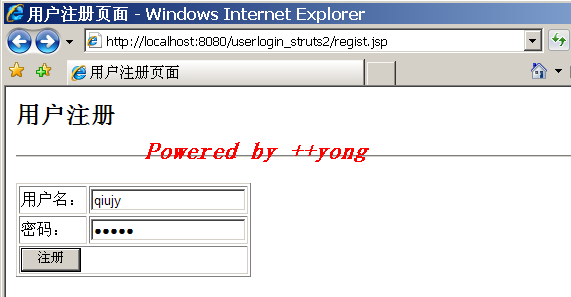
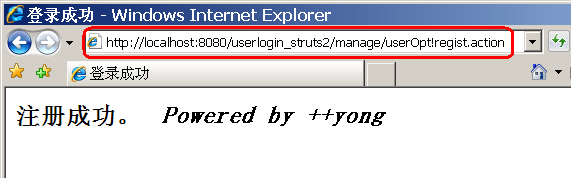
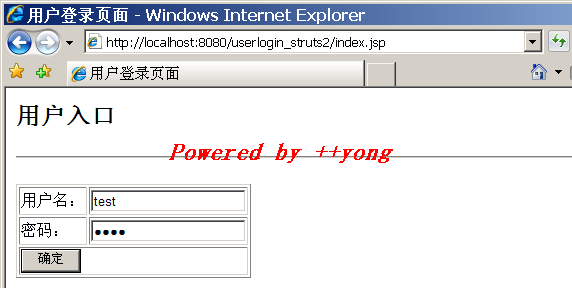
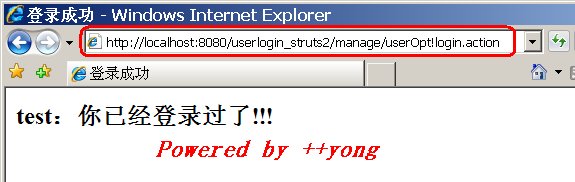
修改用户登录验证示例,多增加一个注册用户功能。
1. 修改Action类:
|
package
org.qiujy.web.struts2.action;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
@author
qiujy
*
@version
1.0
*/
public
class
LoginAction
extends
ActionSupport{
private
String
userName
;
private
String
password
;
private
String
msg
;
//
结果信息属性
/**
*
@return
the
msg
*/
public
String getMsg() {
return
msg
;
}
/**
*
@param
msg
the
msg
to
set
*/
public
void
setMsg(String msg) {
this
.
msg
= msg;
}
/**
*
@return
the
userName
*/
public
String getUserName() {
return
userName
;
}
/**
*
@param
userName
the
userName
to
set
*/
public
void
setUserName(String userName) {
this
.
userName
= userName;
}
/**
*
@return
the
password
*/
public
String getPassword() {
return
password
;
}
/**
*
@param
password
the
password
to
set
*/
public
void
setPassword(String password) {
this
.
password
= password;
}
/**
*
处理用户请求的
login()
方法
*
@return
结果导航字符串
*
@throws
Exception
*/
public
String login()
throws
Exception{
if
(
"test"
.equals(
this
.
userName
) &&
"test"
.equals(
this
.
password
)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+
this
.
userName
;
//
获取
ActionContext
实例,通过它来访问
Servlet API
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
//
看
session
中是否已经存放了用户名,如果存放了:说明已经登录了;
//
否则说明是第一次登录成功
if
(
null
!= context.getSession().get(
"uName"
)){
msg
=
this
.
userName
+
"
:你已经登录过了
!!!"
;
}
else
{
context.getSession().put(
"uName"
,
this
.
userName
);
}
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
public
String regist()
throws
Exception{
//
将用户名,密码添加到数据库中
//...
msg
=
"
注册成功。
"
;
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
}
|
2. struts.xml文件:没有什么变化,跟以前一样配置
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"userOpt"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
3. 页面:
index.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"UTF-8"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
用户登录页面
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
用户入口
</
h2
>
<
hr
>
<
form
action
=
"manage/userOpt!login.action"
method
=
"post"
>
<
table
border
=
"1"
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
用户名:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"text"
name
=
"userName"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
密码:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"password"
name
=
"password"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
colspan
=
"2"
>
<
input
type
=
"submit"
value
=
"
确定
"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
</
table
>
</
form
>
</
body
>
</
html
>
|
regist.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"UTF-8"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
用户注册页面
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
用户注册
</
h2
>
<
hr
>
<
form
action
=
"manage/userOpt!regist.action"
method
=
"post"
>
<
table
border
=
"1"
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
用户名:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"text"
name
=
"userName"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
密码:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"password"
name
=
"password"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
colspan
=
"2"
>
<
input
type
=
"submit"
value
=
"
注册
"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
</
table
>
</
form
>
</
body
>
</
html
>
|
4. 运行结果:
3.2. 为Action配置method属性:
将Action类中的每一个处理方法都定义成一个逻辑Action方法。
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<
action
name
=
"userLogin"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
method
=
"login"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
<
action
name
=
"userRegist"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
method
=
"regist"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
如上,把LoginAction中的login和regist方法都配置成逻辑Action。要调用login方法,则相应的把index.jsp中表单元素的action设置为"manage/userLogin.action";要调用regist方法,把regist.jsp中表单元素的action设置为"manage/userRegist.action"。
3.3. 使用通配符映射(wildcard mappings)方式:
在struts.xml文件中配置<action…>元素时,它的name、class、method属性都可支持通配符,这种通配符的方式是另一种形式的动态方法调用。
当我们使用通配符定义Action的name属性时,相当于用一个元素action定义了多个逻辑Action:
|
<
action
name
=
"user_*"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.UserAction"
method
=
"{1}"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
|
如上,<action name=”user_*”>定义一系列请求URL是user_*.action模式的逻辑Action。同时method属性值为一个表达式{1},表示它的值是name属性值中第一个*的值。例如:用户请求URL为user_login.action时,将调用到UserAction类的login方法;用户请求URL为user_regist.action时,将调用到UserAction类的regist方法。
4. 处理结果
Struts2的Action处理完用户请求后,将返回一个普通字符串,整个普通字符串就是一个逻辑视图名。Struts2通过配置逻辑视图名和物理视图资源之间的映射关系,一旦系统收到Action返回的某个逻辑视图名,系统就会把对应的物理视图资源呈现给浏览者。
4.1. 配置处理结果:
Struts2的Action处理用户请求结束后,返回一个普通字符串-逻辑视图名,必须在struts.xml文件中完成逻辑视图和物理视图资源的映射,才可让系统转到实际的视图资源。
Struts2通过在struts.xml文件中使用<result …/>元素来配置结果。Struts2提供了两种结果。
l 局部结果:将<result …/>作为<action …>元素的子元素配置。
l 全局结果:将<result …/>作为<global-results …>元素的子元素配置。
在package元素中配置<global-results>子元素:
|
<global-results>
<result name="error">/Error.jsp</result>
<result name="invalid.token">/Error.jsp</result>
<result name="login" type="redirect-action">Logon!input</result>
</global-results>
|
4.2. 处理结果类型:
Struts2提供了对不同种类返回结果的支持,常见的有JSP,FreeMarker,Velocity等。
Struts2支持的不同类型的返回结果为:
|
名字
|
说明
|
|
chain
|
用来处理Action链
|
|
dispatcher
|
用来转向页面,通常处理JSP
,这是默认的结果类型
|
|
freeMarker
|
处理FreeMarker模板
|
|
httpHeader
|
用来控制特殊的Http行为
|
|
redirect
|
重定向到一个URL
|
|
redirect-action
|
重定向到一个Action
|
|
stream
|
向浏览器发送InputSream对象,通常用来处理文件下载
|
|
velocity
|
处理Velocity模板
|
|
xslt
|
处理XML/XLST模板
|
|
plaintext
|
显示原始文件内容,例如文件源代码
|
|
tiles
|
结合Tile使用
|
另外第三方的Result类型还包括JasperReports Plugin,专门用来处理JasperReport类型的报表输出;Jfreechart Plugin;JSF Plugin。
4.3. 动态返回结果
有些时候,只有当Action执行完毕的时候我们才知道要返回哪个结果,这个时候我们可以在Action内部定义一个属性,这个属性用来存储Action执行完毕之后的result值,例如:
|
private String nextAction;
public String getNextAction() {
return nextAction;
}
|
在strutx.xml配置文件中,我们可以使用${nextAction}来引用到Action中的属性,通过${nextAction}表示的内容来动态的返回结果,例如:
|
<action name="fragment" class="FragmentAction">
<result name="next" type="redirect-action">${nextAction}</result>
</action>
|
上述Action的execute方法返回next的时候,还需要根据nextAction的属性来判断具体定位到哪个Action。
5. 属性驱动和模型驱动
不管属性驱动还是模型驱动,Struts2框架都是通过拦截器负责提取请求参数,并将请求数据封装到相应的Action实例的属性或专门的模型的属性。
5.1. 属性驱动:
属性驱动就是属性(property)作为贯穿MVC流程的信息携带者。简单的说,就是使用Action实例来封装请求参数和处理结果信息。前面我们做的示例都属于属性驱动模式。
5.2. 模型驱动:
模型驱动就是使用单独的javaBean作为贯穿整个MVC流程的信息携带者。也就是说,使用单独的VO(值对象)来封装请求参数和处理结果信息。
示例:继续修改用户登录验证:
1. 新增一用户域模型对象:User.java
|
package
org.qiujy.domain;
public
class
User {
private
String
userName
;
private
String
password
;
/**
*
@return
the
userName
*/
public
String getUserName() {
return
userName
;
}
/**
*
@param
userName
the
userName
to
set
*/
public
void
setUserName(String userName) {
this
.
userName
= userName;
}
/**
*
@return
the
password
*/
public
String getPassword() {
return
password
;
}
/**
*
@param
password
the
password
to
set
*/
public
void
setPassword(String password) {
this
.
password
= password;
}
}
|
2. 业务控制器:UserAction.java
|
package
org.qiujy.web.struts2.action;
import
org.qiujy.domain.User;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public
class
UserAction
extends
ActionSupport{
//
定义用于封装请求参数的模型对象
private
User
user
=
new
User();
private
String
msg
;
//
结果信息属性
/**
*
@return
the
user
*/
public
User getUser() {
return
user
;
}
/**
*
@param
user
the
user
to
set
*/
public
void
setUser(User user) {
this
.
user
= user;
}
/**
*
@return
the
msg
*/
public
String getMsg() {
return
msg
;
}
/**
*
@param
msg
the
msg
to
set
*/
public
void
setMsg(String msg) {
this
.
msg
= msg;
}
/**
*
处理用户请求的
login()
方法
*
@return
结果导航字符串
*
@throws
Exception
*/
public
String login()
throws
Exception{
String userName =
user
.getUserName();
String password =
user
.getPassword();
if
(
"test"
.equals(userName) &&
"test"
.equals(password)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+ userName;
//
获取
ActionContext
实例,通过它来访问
Servlet API
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
//
看
session
中是否已经存放了用户名,如果存放了:说明已经登录了;否则说明是第一次登录成功
if
(
null
!= context.getSession().get(
"uName"
)){
msg
= userName +
"
:你已经登录过了
!!!"
;
}
else
{
context.getSession().put(
"uName"
, userName);
}
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
public
String regist()
throws
Exception{
//
将用户名,密码添加到数据库中
//...
msg
=
"
注册成功。
"
;
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
}
|
3. 配置文件:struts.xml
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<
action
name
=
"userOpt"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.UserAction"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
4. 页面:
index.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"UTF-8"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
用户登录页面
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
用户入口
</
h2
>
<
hr
>
<
form
action
=
"manage/userOpt!login.action"
method
=
"post"
>
<
table
border
=
"1"
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
用户名:
</
td
>
<
td
>
<
input
type
=
"text"
name
=
"user.userName"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
密码:
</
td
>
<
td
>
<input type="password" name="user.password"/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
colspan
=
"2"
>
<
input
type
=
"submit"
value
=
"
确定
"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
</
table
>
</
form
>
</
body
>
</
html
>
|
其它页面略。
5. 运行效果:同以前一样。
6. 源代码:
6. Struts2的异常处理机制:
任何成熟的MVC框架都应该提供成就的异常处理机制。Strut2也不例外。Struts2提供了一种声明式的异常处理方式。Struts2也是通过配置的拦截器来实现异常处理机制的。
Struts2的异常处理机制通过在struts.xml文件中配置<exception-mapping …>元素完成的,配置该元素时,需要指定两个属性:
exception:此属性指定该异常映射所设置的异常类型。
result:此属性指定Action出现该异常时,系统转入result属性所指向的结果。
6.1. 异常映射也分为两种:
l 局部异常映射:<exception-mapping…>元素作为<action…>元素的子元素配置。
l 全局异常映射:<exception-mapping…>元素作为<global-exception-mappings>元素的子元素配置。
6.2. 输出异常信息:
使用Struts2的标签来输出异常信息:
l <s:property value="exception.message"/> : 输出异常对象本身。
l <s:property value="exceptionStack"/> : 输出异常堆栈信息。
6.3. 示例:
还是修改用户登录示例:
1) 把UserAciton.java中的regist方法改成:
|
public
String regist()
throws
Exception{
//
将用户名,密码添加到数据库中
//...
//msg = "
注册成功。
";
if
(
true
){
throw new
java.sql.SQLException(
"
没有数据库驱动程序
"
);
}
return this.SUCCESS;
}
|
2) 修改struts.xml文件:
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<!--
定义全局处理结果
-->
<
global-results
>
<!--
逻辑名为
sql
的结果,映射到
/exception.jsp
页面
-->
<
result
name
=
"sql"
>
/exception.jsp
</
result
>
</
global-results
>
<
global-exception-mappings
>
<!--
当
Action
抛出
SQLException
异常时,转入名为
sql
的结果
-->
<
exception-mapping
exception
=
"java.sql.SQLException"
result
=
"sql"
/>
</
global-exception-mappings
>
<
action
name
=
"userOpt"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.UserAction"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
3) 新增一页面:exception.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"utf-8"
%>
<%@
taglib
uri
=
"/struts-tags"
prefix
=
"s"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
异常信息
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
出现异常啦
</
h2
>
<
hr
/>
<
h3
style
=
"color:red"
>
<!--
获得异常对象
-->
<
s:property
value
=
"exception.message"
/>
</
h3
>
<
br
/>
<!--
异常堆栈信息
-->
<
s:property
value
=
"exceptionStack"
/>
</
html
>
|
4) 运行regist.jsp进行调试:
下面两篇文章也值得参考