cpu基本概念
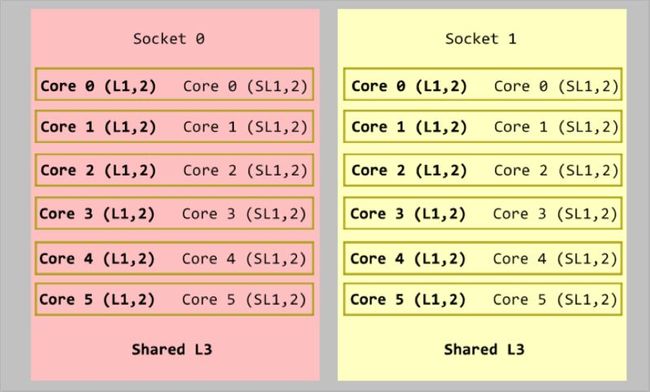
在多核心的CPU中,我们在一个封装(socket或者processor)里放入多核(core)。
在超线程(Hyper-threading, HT)中,对于一个物理存在的核心,操作系统会当成两个虚拟的逻辑核心来使用,二个逻辑核心共享L1和L2缓存。
绿色和蓝色标识一个socket
以Sandy Bridge (SNB)家族的Intel Xeon E5-2430为例:
核心(Cores)数量:六核心
线程(Threads)数量:12
架构:Sandy Bridge
Socket类型:1356
L1缓存:192KB(code), 192KB(data)
L2缓存:1.5MB
L3缓存:15MB.
架构中,缓存方面,一级、二级、三级容量分别为4×32KB、4×256K、8MB,延迟分别只有3个周期、9个周期、25个周期,而且三级缓存采用每循环256位的环形架构。[1]
黄色框内表示:HT的两个逻辑核心,共用L1和L2.
红底表示socket 0, 黄色表示socket 1.
查看cpu参数
这部分介绍如何在linux下从/proc/cpuinfo中得到cpu参数.
| cpu信息 |
/proc/cpuinfo中参数 |
示例中取值 |
| socket编号 |
physical id |
0,1 |
| socket中逻辑核心编号 |
processor |
0,1,2,……,23 |
| socket中逻辑核心数目 |
siblings |
12 |
| socket中物理核心编号 |
core id |
0,1,2,3,4,5 |
| socket中物理核心数目 |
cpu cores |
6 |
| Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers ID[2] |
apicid |
0,1,……,11 32,33,……43 |
| L3 cache |
cache size |
|
下面的例子是 intel xeon 5420的processor 0的cpuinfo参数
processor : 0
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 45
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2430 0 @ 2.20GHz
stepping : 7
cpu MHz : 2194.573
cache size : 15360 KB
physical id : 0
siblings : 12
core id : 0
cpu cores : 6
apicid : 0
initial apicid : 0
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 13
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts rep_good xtopology nonstop_tsc aperfmperf pni pclmulqdq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx smx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr pdcm dca sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic popcnt aes xsave avx lahf_lm arat epb xsaveopt pln pts dts tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid
bogomips : 4389.14
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 46 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
apicid可以用来判断processor是在哪个物理核心(core)的哪个逻辑核心(logical CPU)上。
logical_CPU_number_within_core = APIC_ID & ( (1 << logical_CPU_bits) -1)
core_number_within_chip = (APIC_ID >> logical_CPU_bits) & ( (1 << core_bits) -1)
chip_ID = APIC_ID & ~( (1 << (logical_CPU_bits+core_bits) ) -1)
详细的cache信息
ls /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cache/
index0 index1 index2 index3
4个目录
index0:1级数据cache
index1:1级指令cache
index2:2级cache
index3:3级cache ,对应cpuinfo里的cache
查看线程run在哪个processor
可以使用top命令查看一个进程的各个线程分别run在哪个processor上
同样,为了避免输入数字pid,我使用如下命令启动top:
top -p$(pidof test |sed -e ‘s/ /,/g’)
在默认配置下不显示线程信息,需要进入Top后按“shift+H”,打开线程显示。
另外,如果没有P列,还需要按“f”,按“j”,添加,这一列显示的数字就是这个线程上次run的processor id。
关于top的使用,请读者自行man top
参考文献:
1. Intel 32nm Sandy Bridge已流片 架构解析,
http://news.mydrivers.com/1/138/138855.htm
2. http://www.experts-exchange.com/OS/Unix/Q_27076862.html
3. http://www.searchtb.com/2012/12/玩转cpu-topology.html
4. http://huoding.com/2012/11/08/198
5.