1.首先理解下浅克隆和深克隆的含义吧:
浅克隆:简单说就是对当前要克隆的对象的复制,但是不会复制当前对象对其他对象的引用,即引用还是指向之前被引用对象的地址。
深克隆:就是把要克隆对象以及他所有引用对象全部复制一份。
2.浅克隆的代码演示:通过这段代码你就会明白浅克隆到底是什么意思了。
class Teacher{
public String name;
public int age;
public Teacher(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public int age;
public Teacher teacher;
public Student(String name,int age,Teacher t){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.teacher = t;
}
@Override
public Student clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student s= (Student)super.clone();
return s;
}
}
public class TestClone {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Job",50);
Student stu1 = new Student("Kobe",24,teacher);
Student stu2 = stu1.clone();
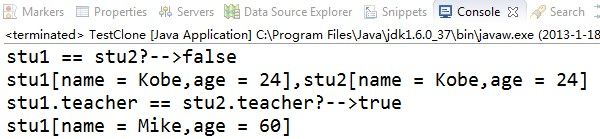
System.out.println("stu1 == stu2?-->" + (stu1 == stu2));
System.out.println("stu1[name = "+ stu1.name + ",age = " + stu1.age
+ "],stu2[name = " + stu2.name + ",age = " + stu2.age + "]");
System.out.println("stu1.teacher == stu2.teacher?-->"
+ (stu1.teacher == stu2.teacher));
/**
* 此处改变stu2引用对象的值,会改变stu1引用对象的值
*
*/
stu2.teacher.name = "Mike";
stu2.teacher.age = 60;
System.out.println("stu1[name = " + stu1.teacher.name
+ ",age = " + stu1.teacher.age + "]");
}
}
由上段代码的结果可以看出:stu1和stu2的内存地址不同,只是形成了值得拷贝,Student对象中的Teacher对象的引用没有改变。一旦改变stu2引用Teacher的值,stu1所引用的Teacher的值也会改变,其实他俩指向的是同一内存地址,这就是所谓的浅克隆。
顺便说一下Object基类中clone()方法的含义:Object中的clone()方法可以识别出我们要复制的是哪一个对象,然后会为此对象分配内存空间,并进行对象的复制,将原始对象的内容一一复制到新对象的存储空间中。
引用下官网API的一段话:
The method clone for class Object performs a specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does not implement the interface Cloneable, then a CloneNotSupportedException is thrown. Note that all arrays are considered to implement the interface Cloneable. Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
3.深克隆代码的演示:
先来一段代码:
class Teacher implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public int age;
public Teacher(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public int age;
public Teacher teacher;
public Student(String name,int age,Teacher t){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.teacher = t;
}
@Override
public Student clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student s= (Student)super.clone();
s.teacher = (Teacher)teacher.clone();
return s;
}
}
public class TestClone {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Job",50);
Student stu1 = new Student("Kobe",24,teacher);
Student stu2 = stu1.clone();
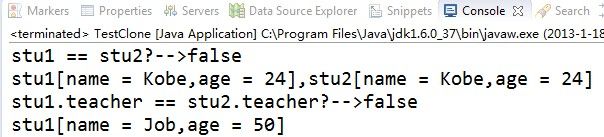
System.out.println("stu1 == stu2?-->" + (stu1 == stu2));
System.out.println("stu1[name = "+ stu1.name + ",age = " + stu1.age
+ "],stu2[name = " + stu2.name + ",age = " + stu2.age + "]");
System.out.println("stu1.teacher == stu2.teacher?-->"
+ (stu1.teacher == stu2.teacher));
/**
* 此处改变stu2引用对象的值,不会改变stu1引用对象的值,因为在Student的clone()方法中已经对引用Teacher进行了复制。
*
*/
stu2.teacher.name = "Mike";
stu2.teacher.age = 60;
System.out.println("stu1[name = " + stu1.teacher.name
+ ",age = " + stu1.teacher.age + "]");
}
}
从结果可以看出改变stu2引用对象属性的值,stu1中的引用对象属性值并没有改变,这在要拷贝对象中引用对象内部没有其他引用的时候是成立的,如果Teacher中有其他对象的引用,则这样又会产生浅克隆的现象,这样并不能叫做深克隆,除非一层层的拷贝下去,所以网上很多举例解释是错误的。
还有一种是通过串行化来进行深拷贝,也就是流的过程。把对象写入流--->串行化,从流中读出对象--->并行化,对象本身还是存在于JVM中,流也是对对象的一种拷贝。代码如下:
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
class Teacher implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public String name;
public int age;
public Teacher(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
class Student implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public String name;
public int age;
public Teacher teacher;
public Student(String name,int age,Teacher t){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.teacher = t;
}
public Object deepClone()throws Exception{
ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);//从流里读出来
ByteArrayInputStream bis=new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(bis);
return(ois.readObject());
}
}
public class TestClone {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Job",50);
Student stu1 = new Student("Kobe",24,teacher);
Student stu2 = (Student)stu1.deepClone();
System.out.println("stu1 == stu2?-->" + (stu1 == stu2));
System.out.println("stu1[name = "+ stu1.name + ",age = " + stu1.age
+ "],stu2[name = " + stu2.name + ",age = " + stu2.age + "]");
System.out.println("stu1.teacher == stu2.teacher?-->"
+ (stu1.teacher == stu2.teacher));
/**
* 此处改变stu2引用对象的值,不会改变stu1引用对象的值
*
*/
stu2.teacher.name = "Mike";
stu2.teacher.age = 60;
System.out.println("stu1[name = " + stu1.teacher.name
+ ",age = " + stu1.teacher.age + "]");
}
}
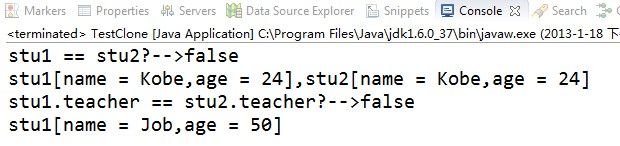
从结果可以看出改变stu2引用对象属性的值,stu1中的引用对象属性值并没有改变,这种方法也可以实现深拷贝(前提是所有引用对象都必须可序列化,否则,就需要仔细考察那些不可串行化的对象可否设成transient,从而将之排除在复制过程之外)
ok,深浅克隆到此结束,可以下班回家了,吼吼