LinkedIn公司实现的实时搜索引擎Zoie
一、总体架构
Zoie是linkedin公司基于Lucene实现的实时搜索引擎系统,按照其官方wiki的描述为:
http://snaprojects.jira.com/wiki/display/ZOIE/Overview
Zoie is a realtime indexing and search system, and as such needs to have relatively close coupling between the logically distinct Indexing and Searching subsystems: as soon as a document made available to be indexed, it must be immediately searchable.
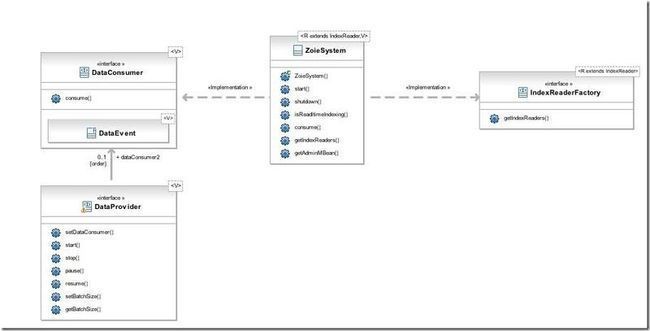
The ZoieSystem is the primary component of Zoie, that incorporates both Indexing (via implementing DataConsumer<V>) and Search (via implementingIndexReaderFactory<ZoieIndexReader<R extends IndexReader>>).
Zoie是一个实时的搜索引擎系统,其需要逻辑上独立的索引和搜索子系统相对紧密的结合在一起,从而使得一篇文档一经索引,就能够立刻被搜索的到。
ZoieSystem是Zoie的重要组成部分,其一方面通过实现DataConsumer接口而完成了索引功能,一方面通过实现IndexReaderFactory<ZoieIndexReader<R extends IndexReader>>而完成了搜索功能,并将二者紧密的结合在一起。
下面就是ZoieSystem的总体架构图:
- 对于索引系统来讲,ZoieSystem是一个DataConsumer,也即是一个消费者,其有函数consume用于消费DataEvent对象而完成索引功能。
- 既然其是消费者,则向其提供数据的就应该是生产者DataProvider,要想使用Zoie建立实时搜索系统,必须提供自己的生产者。
- 对于搜索系统来讲,ZoieSystem是一个IndexReaderFactory,也即是一个能够得到读取索引的IndexReader的工厂,其有函数getIndexReaders得到所有的IndexReader列表,从而可以完成对索引数据读取的功能。
- 熟悉Lucene的读者应该很清楚,要想对Lucene的索引进行搜索,则首先要得到IndexReader,然后根据IndexReader生成IndexSearcher,从而可以进行搜索,收集结果,打分,排序等过程。既然IndexReader可以通过Zoie的工厂得到,用户需要实现自己的搜索逻辑方可。
二、配置一个ZoieSystem
ZoieSystem是可以使用spring进行配置的,一个典型的配置如下:
|
<!--An instance of a DataProvider: FileDataProvider recurses through a given directory and provides the DataConsumer indexing requests built from the gathered files. In the example, this provider needs to be started manually, and it is done via jmx. 一个DataProvider的实例: FileDataProvider递归的访问一个指定的路径,将得到的文件构造成索引请求提供给DataConsumer。 在本例中,此生产者需要通过jmx进行手动启动。 --> <bean id="dataprovider" class="proj.zoie.impl.indexing.FileDataProvider"> <constructor-arg value="file:${source.directory}"/> <property name="dataConsumer" ref="indexingSystem" /> </bean> <!-- an instance of an IndexableInterpreter: FileIndexableInterpreter converts a text file into a lucene document, for example purposes only 一个IndexableInterpreter的实例: 在本例中,FileIndexableInterpreter将一个文本文件转换成为一个Lucene的Document对象。 从上面的介绍中我们知道,DataProvider作为一个生产者生产了DataEvent对象供消费者DataConsumer进行消费,然而由于Zoie最终是基于Lucene的,Lucene是不能够索引DataEvent对象的,这就需要有人负责将DataEvent转换成为Lucene的Document对象,根据应用的需要控制添加那些Field,添加什么样的Field等,此工作由翻译器Interpreter完成。 --> <bean id="fileInterpreter" class="proj.zoie.impl.indexing.FileIndexableInterpreter" /> <!-- A decorator for an IndexReader instance: The default decorator is just a pass through, the input IndexReader is returned. 一个IndexReader的装饰者: 默认的装饰者什么都不做,将原IndexReader返回。 注意这里使用的是一个重要的设计模式,装饰者模式。被包装的IndexReader是直接打开Lucene索引的IndexReader,IndexReaderFactory在得到这些IndexReader后,都会经过此类封装一下,再返回给用户。基本的Lucene的IndexReader打开,会加载和初始化一些基本的东西,然而有时候,用户需要在IndexReader打开的时候,同时加载一些自己的东西,此类给了用户这样一个机会,用户只要实现自己的装饰者就可以了。在和Zoie同一个项目Bobo(实现Facet搜索,使用过Solr的同学可能会比较熟悉)中,实现了BoboIndexReaderDecorator,其作用就是在IndexReader打开的时候,将Facet信息加载到内存中形成某种数据结构,从而在收集Facet的时候快速的使用。 --> <bean id="idxDecorator" class="proj.zoie.impl.indexing.DefaultIndexReaderDecorator" /> <!-- A zoie system declaration, passed as a DataConsumer to the DataProvider declared above 一个ZoieSystem的声明,在上面的DataProvider的声明中,其是作为一个DataConsumer传入的。 --> <bean id="indexingSystem" class="proj.zoie.impl.indexing.ZoieSystem" init-method="start" destroy-method="shutdown"> <!-- disk index directory 索引文件夹--> <constructor-arg index="0" value="file:${index.directory}"/> <!-- sets the interpreter 设置翻译器--> <constructor-arg index="1" ref="fileInterpreter" /> <!-- sets the decorator 设置装饰器--> <constructor-arg index="2"> <ref bean="idxDecorator"/> </constructor-arg> <!-- set the Analyzer, if null is passed, Lucene's StandardAnalyzer is used 设置分词器,如果为null,则使用默认的Lucene的StandardAnalyzer --> <constructor-arg index="3"> <null/> </constructor-arg> <!-- sets the Similarity, if null is passed, Lucene's DefaultSimilarity is used 设置相似性评分器,如果为null,则使用Lucene默认的DefaultSimilarity --> <constructor-arg index="4"> <null/> </constructor-arg> <!-- the following parameters indicate how often to triggered batched indexing, whichever the first of the following two event happens will triggered indexing 下面的两个参数表示触发批量索引的频率,任意一个满足条件则触发索引。 --> <!-- Batch size: how many items to put on the queue before indexing is triggered 批量大小:即队列中放入多少项方才触发索引 --> <constructor-arg index="5" value="1000" /> <!-- Batch delay, how long to wait before indxing is triggered 批量延时:即等待多长时间方才触发索引 --> <constructor-arg index="6" value="300000" /> <!-- flag turning on/off real time indexing 是否开启实时索引的标志位 --> <constructor-arg index="7" value="true" /> </bean>
<!-- a search service 一个搜索服务 --> <bean id="mySearchService" class="com.mycompany.search.SearchService"> <!-- IndexReader factory that produces index readers to build Searchers from ZoieSystem作为IndexReaderFactory向搜索服务提供IndexReader列表,使其可以构造Searcher。 --> <constructor-arg ref="indexingSystem" /> </bean> |
看完了ZoieSystem的配置以后,我们首先来看看ZoieSystem的构造函数是如何使用这些参数进行初始化的:
(1) 其根据制定的索引文件夹${index.directory}生成一个DefaultDirectoryManager _dirMgr,用于管理索引文件夹及索引的版本号IndexSignature。
(2) 生成一个SearchIndexManager _searchIdxMgr,它是实现实时搜索的关键类,包含如下的成员变量:
- 第一步中生成的DefaultDirectoryManager
- spring配置文件中传进来的IndexReader的装饰器IndexReaderDecorator _indexReaderDecorator
- DefaultDocIDMapperFactory _docIDMapperFactory用来维护Zoie的文档ID同Lucene的文档ID号之间的对应关系
- DiskSearchIndex _diskIndex用于操作硬盘上的索引,此时便得到一个指向硬盘索引的IndexReader
- Status _diskIndexerStatus当前索引的状态,共两种状态Sleeping和Working,所谓的Sleeping就是新添加的文档仅仅进入内存索引,所谓的Working即其中一个内存索引正在和硬盘上的索引进行合并,下一节实时机制的时候,我们会详细讨论
- Mem _mem结构,是利用两个内存索引,一个硬盘索引配合实现实时索引的关键,详细的机制,我们下一节会讨论。Mem结构包含以下部分:
- RAMSearchIndex<R> _memIndexA用于操作内存索引A
- RAMSearchIndex<R> _memIndexB用于操作内存索引B
- RAMSearchIndex<R> _currentWritable根据索引所处的状态,有时候A是用于添加新文档的内存索引,有时候B是用于添加新文档的索引
- RAMSearchIndex<R> _currentReadOnly同上一个相反,这是当前不会被添加新文档的内存索引,从下面的讨论中我们可以知道,此内存索引此时正在和硬盘上的索引进行合并。
- ZoieIndexReader<R> _diskIndexReader硬盘索引的IndexReader
(3) 将参数赋值成员变量ZoieIndexableInterpreter _interpreter,Analyzer _analyzer,Similarity _similarity
(4) 创建DiskLuceneIndexDataLoader _diskLoader对象,用于索引到硬盘索引
(5) 如果实时索引_realtimeIndexing设置为true,则创建RealtimeIndexDataLoader _rtdc,第四步中的_diskLoader作为其成员变量。将其设置为ZoieSystem的父类AsyncDataConsumer的成员变量setDataConsumer(_rtdc)
三、Zoie实现实时搜索的原理
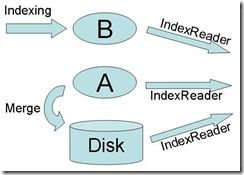
3.1、利用两个内存索引一个硬盘索引实现实时搜索的原理
(1) 当系统启动的时候,索引处在Sleeping状态,这时Mem结构中,只有索引A,索引B为null,索引A为_currentWritable,_currentReadOnly为null,_diskIndexReader为硬盘索引的IndexReader。由于内存中索引的IndexReader是每添加完文档后立刻更新的,而且速度很快,而硬盘上的索引一旦打开,在下次合并之前,一直使用,可以保证新添加的文档能够马上被搜索到。
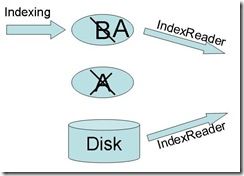
(2) 当A中的文档数量达到一定的数量的时候,需要同硬盘上的索引进行合并,因此要进入Working状态。合并是一个相对比较长的过程,这时候会创建内存索引B,在合并过程中新添加的文档全部索引到B中。此时的Mem结构中,有内存索引A,内存索引B,索引A为currentReadOnly,索引B为currentWritable,diskIndexReader为硬盘索引的IndexReader。此时要获得ZoieSystem的IndexReader,则三个IndexReader全都返回,由于索引B的IndexReader是添加文档后立刻更新的,因而能够保证新添加的文档能够马上被搜索到,这个时候虽然索引A已经在同硬盘索引进行合并,然而由于硬盘索引的IndexReader还没有重新打开,因而索引A中的数据不会被重复搜到。
(3) 当索引A中的数据已经完全合并到硬盘上之后,则要重新打开硬盘索引的IndexReader,打开完毕后,创建一个新的Mem结构,原来的索引B作为索引A,为currentWritable,原来的索引A被抛弃,设为null,currentReadOnly也设为null,diskIndexReader为新打开的硬盘索引的IndexReader。然后通过无缝切换用新的Mem结构替代旧的Mem结构,然后索引进入Sleeping状态。
3.2、有关文档的更新问题
上面一节中,我们可以看到,对于新添加的文档的实时搜索问题相对简单,然而当遇到文档更新的时候,就相对复杂了。
如何实时的删除已经索引在硬盘上的文档是一个很大的问题,为此Zoie实现了ZoieSegmentReader:
- 成员变量_decoratedReader是ZoieSegmentReader把Lucene的IndexReader被用户指定的装饰器装饰后又封装了一层。
- long[] _uidArray是从Lucene的文档ID到Zoie的文档ID的一个对应,Lucene的文档ID是下标,Zoie的文档ID是对应项的值。
- IntRBTreeSet _delDocIdSet表示在此索引中删除的Lucene的文档ID
- 在索引中,Zoie的文档ID是作为一个特殊的Term("_ID", "_UID")的倒排表中每个Lucene的文档号的Payload信息保存的,保存为如下格式,其fillDocumentID函数就是将Zoie的文档ID放入Payload中。
- 当要从此ZoieSegmentReader中删除文档的时候,调用markDeletes函数,将要删除的文档的Zoie文档号通过DocIDMapper转换为Lucene的文档号,将Lucene的文档号加入_delDocIdSet
- 熟悉Lucene的读者应该知道,IndexReader是通过TermDocs接口从索引中取得倒排表的,Zoie也实现了自己的ZoieSegmentTermDocs,其有一个DocIdSetIterator作为成员变量,是在生成的时候由ZoieSegmentReader将自己的_delDocIdSet的遍历器传给它的,每当取下一个文档号的时候,其会将DocIdSetIterator中有的文档号过滤掉。对于TermPositions也是同样实现了ZoieSegmentTermPositions
- ZoieSegmentReader使得较慢的从硬盘索引中删除文档的操作变为较快的在内存中的标记操作,并且不用重新打开IndexReader删除就能够被看到,还保证了更新的完整性(更新的操作是一个删除,外加一个添加,新添加的文档最初是在内存索引中,则删除操作也应该在内存中被标记,否则一旦系统crash,会出现新添加的丢了,老的版本也被删除了的情况,即便有重做机制也难以实现).
有了ZoieSegmentReader,下面我们来看文档更新情况下的实时搜索机制。
(1) 最初系统启动的时候,是在Sleeping状态下的,这个时候,内存索引为空,硬盘索引上有文档A,B,C。
(2) 在Sleeping状态下,更新文档B,则新的文档B进入内存索引,而硬盘索引中B被标记删除。
(3) 当内存中索引足够大的时候,索引会进入Working状态,进入合并过程。合并过程会首先将硬盘索引中被标记删除的文档先真实的删除,然后再将内存索引向硬盘索引进行合并。此时如果有新的更新进入,比如更新文档A,则将在另外一个内存索引和硬盘索引中都标记删除,然后将新文档添加到内存索引中。
(4) 当合并完毕后,硬盘索引会标记删除原来在内存索引中标记删除的文档,被合并的索引以及其标记删除的文档全部丢弃,索引进入Working状态。
四、Zoie的索引过程
4.1、将文档添加到内存索引
(1) Zoie的索引过程由DataProvider中调用ZoieSystem的consume函数开始,其实是调用AsyncDataConsumer的consume(Collection<DataEvent<V>> data)函数,其仅仅将DataEvent放在LinkedList<DataEvent<V>> _batch中。
(2) AsyncDataConsumer有一个背后的线程ConsumerThread _consumerThread,其会调用_consumer.consume(currentBatch),由ZoieSystem的构造函数中第(5)步我们知道,此处的_consumer为RealtimeIndexDataLoader _rtdc。
(3) RealtimeIndexDataLoader.consume函数分一下几个步骤:
- 调用_interpreter的convertAndInterpret函数,将所有的DataEvent转换为ZoieIndexable,放入链表ArrayList<DataEvent<ZoieIndexable>> indexableList。ZoieIndexable其中封装了Lucene的Document
- RealtimeIndexDataLoader在创建的时候,除了传进去的DiskLuceneIndexDataLoader作为成员变量_luceneDataLoader,还会创建成员变量RAMLuceneIndexDataLoader _ramConsumer用于索引到内存索引。在上一步做完后,调用_ramConsumer.consume(indexableList)将这些ZoieIndexable索引到内存中。
(4) RAMLuceneIndexDataLoader的consume函数会调用LuceneIndexDataLoader的consume函数,其包含以下步骤:
- 得到RAMSearchIndex idx
- Zoie对所有的文档都做更新操作,将文档ID放入LongOpenHashSet delSet,将封装Lucene的Document的IndexingReq放入List<IndexingReq> docList中
- 对于每一篇文档,使用ZoieSegmentReader.fillDocumentID(doc, uid)向Payload中添加Zoie的文档ID
- 更新内存索引idx.updateIndex(delSet, docList, _analyzer,_similarity),其中先用IndexReader删除,再用IndexWriter进行添加
- 当然要被删除的文档除了在内存索引中删除掉之外,还要在另外一个内存索引和硬盘索引中过滤掉。因而调用RAMLuceneIndexDataLoader的propagateDeletes(LongSet delDocs)函数:
- 首先得到另一个内存索引,这个时候应该是ReadOnly并正在和硬盘索引合并的索引:RAMSearchIndex<R> readOnlyMemoryIdx = _idxMgr.getCurrentReadOnlyMemoryIndex()
- 在ReadOnly的内存索引中标记删除,从而搜索的时候可以将其过滤掉,readOnlyMemoryIdx.markDeletes(delDocs)
- 然后得到硬盘索引,DiskSearchIndex<R> diskIdx = _idxMgr.getDiskIndex()
- 在硬盘索引中标记删除,diskIdx.markDeletes(delDocs),从而在搜索中可以将其过滤掉
4.2、将内存索引合并到硬盘索引
RealtimeIndexDataLoader的父类是BatchedIndexDataLoader,其有一个背后的线程LoaderThread,其会调用processBatch函数。
RealtimeIndexDataLoader的processBatch函数过程如下:
(1) 当内存索引中的文档数量超过配置的batch size或者时间超过设置的_delay的时候,就进行内存索引到硬盘索引的合并。
(2) 设置索引的状态从Sleeping到Working,_idxMgr.setDiskIndexerStatus(SearchIndexManager.Status.Working)
- 重新构造Mem<R> _mem结构
- 原来在Sleeping状态下用于添加新文档的memIndexA变成_currentReadOnly的
- 创建在Working状态下用于添加新文档的memIndexB为_currentWritable
- 在合并阶段,硬盘索引的IndexReader还是老的IndexReader
- 从代码我们也可以看出,内存索引A和B交换了位置:Mem<R> mem = new Mem<R>(memIndexA, memIndexB, memIndexB, memIndexA, oldMem.get_diskIndexReader());
(3) 得到需要合并的内存索引readOnlyMemIndex = _idxMgr.getCurrentReadOnlyMemoryIndex()
(4) 将内存索引合并到硬盘索引:_luceneDataLoader.loadFromIndex(readOnlyMemIndex),DiskLuceneIndexDataLoader的loadFromIndex函数做以下事情
- 得到DiskSearchIndex<R> idx = getSearchIndex()
- idx.loadFromIndex(ramIndex),其中首先用IndexReader删除被标记的文档,然后调用IndexWriter的addIndexesNoOptimize函数将内存索引合并到硬盘
- 刷新硬盘索引的IndexReader,idx.refresh()
- idx.markDeletes(ramIndex.getDelDocs())继承内存索引中被标记删除的文档
(5) 设置索引的状态从Working到Sleeping,_idxMgr.setDiskIndexerStatus(Status.Sleep)
- 重新构造Mem<R> _mem结构
- 将在Working状态下的memIndexB付给memIndexA以及currentWritable,而memIndexB设为null,也即把B当做A,没有B
- Mem<R> mem = new Mem<R>(oldMem.get_memIndexB(), null, oldMem.get_memIndexB(), null, diskIndexReader)
- lockAndSwapMem将Mem结构进行无缝切换
五、Zoie的搜索过程
在使用Zoie进行搜索的时候,要调用ZoieSystem的getIndexReaders()函数,其调用了_searchIdxMgr.getIndexReaders()。
SearchIndexManager的getIndexReaders函数,分别得到RAMSearchIndex<R> memIndexA的IndexReader,RAMSearchIndex<R> memIndexB的IndexReader,以及硬盘索引的IndexReader。在Sleeping状态下得到两个IndexReader,在Working状态下得到三个IndexReader。