struts2源码分析
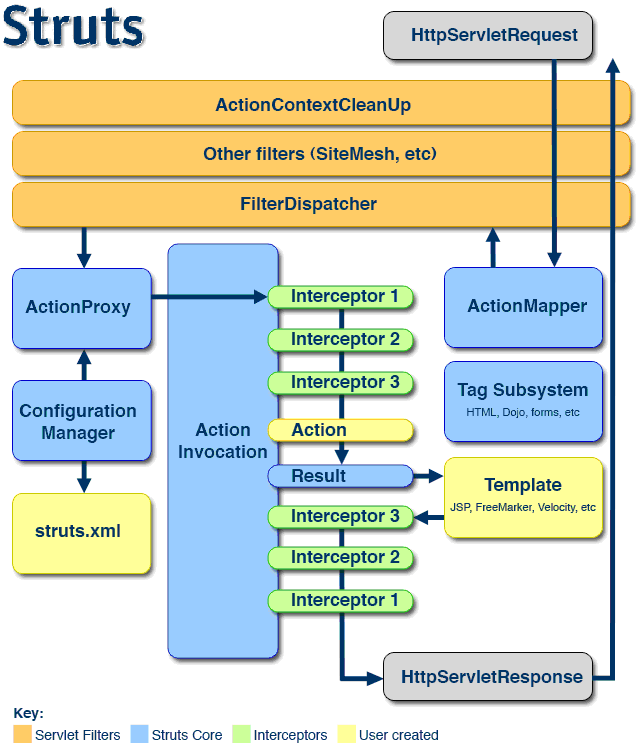
Struts2架构图
请求首先通过Filter chain,Filter主要包括ActionContextCleanUp,它主要清理当前线程的ActionContext和Dispatcher;FilterDispatcher主要通过AcionMapper来决定需要调用哪个Action。
ActionMapper取得了ActionMapping后,在Dispatcher的serviceAction方法里创建ActionProxy,ActionProxy创建ActionInvocation,然后ActionInvocation调用Interceptors,执行Action本身,创建Result并返回,当然,如果要在返回之前做些什么,可以实现PreResultListener。
Struts2部分类介绍
这部分从Struts2参考文档中翻译就可以了。
ActionMapper
ActionMapper其实是HttpServletRequest和Action调用请求的一个映射,它屏蔽了Action对于Request等java Servlet类的依赖。Struts2中它的默认实现类是DefaultActionMapper,ActionMapper很大的用处可以根据自己的需要来设计url格式,它自己也有Restful的实现,具体可以参考文档的docs\actionmapper.html。
ActionProxy&ActionInvocation
Action的一个代理,由ActionProxyFactory创建,它本身不包括Action实例,默认实现DefaultActionProxy是由ActionInvocation持有Action实例。ActionProxy作用是如何取得Action,无论是本地还是远程。而ActionInvocation的作用是如何执行Action,拦截器的功能就是在ActionInvocation中实现的。
ConfigurationProvider&Configuration
ConfigurationProvider就是Struts2中配置文件的解析器,Struts2中的配置文件主要是尤其实现类XmlConfigurationProvider及其子类StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider来解析,
Struts2请求流程
1、客户端发送请求
2、请求先通过ActionContextCleanUp-->FilterDispatcher
3、FilterDispatcher通过ActionMapper来决定这个Request需要调用哪个Action
4、如果ActionMapper决定调用某个Action,FilterDispatcher把请求的处理交给ActionProxy,这儿已经转到它的Delegate--Dispatcher来执行
5、ActionProxy根据ActionMapping和ConfigurationManager找到需要调用的Action类
6、ActionProxy创建一个ActionInvocation的实例
7、ActionInvocation调用真正的Action,当然这涉及到相关拦截器的调用
8、Action执行完毕,ActionInvocation创建Result并返回,当然,如果要在返回之前做些什么,可以实现PreResultListener。添加PreResultListener可以在Interceptor中实现,不知道其它还有什么方式?
Struts2(2.1.2)部分源码阅读
从org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher开始
//
创建Dispatcher,此类是一个Delegate,它是真正完成根据url解析,读取对应Action的地方
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
try {
this .filterConfig = filterConfig;
initLogging();
dispatcher = createDispatcher(filterConfig);
dispatcher.init();
dispatcher.getContainer().inject( this );
// 读取初始参数pakages,调用parse(),解析成类似/org/apache/struts2/static,/template的数组
String param = filterConfig.getInitParameter( " packages " );
String packages = " org.apache.struts2.static template org.apache.struts2.interceptor.debugging " ;
if (param != null ) {
packages = param + " " + packages;
}
this .pathPrefixes = parse(packages);
} finally {
ActionContext.setContext( null );
}
}
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
try {
this .filterConfig = filterConfig;
initLogging();
dispatcher = createDispatcher(filterConfig);
dispatcher.init();
dispatcher.getContainer().inject( this );
// 读取初始参数pakages,调用parse(),解析成类似/org/apache/struts2/static,/template的数组
String param = filterConfig.getInitParameter( " packages " );
String packages = " org.apache.struts2.static template org.apache.struts2.interceptor.debugging " ;
if (param != null ) {
packages = param + " " + packages;
}
this .pathPrefixes = parse(packages);
} finally {
ActionContext.setContext( null );
}
}
顺着流程我们看Disptcher的init方法。init方法里就是初始读取一些配置文件等,先看init_DefaultProperties,主要是读取properties配置文件。
private
void
init_DefaultProperties() {
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider( new DefaultPropertiesProvider());
}
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider( new DefaultPropertiesProvider());
}
打开DefaultPropertiesProvider
public
void
register(ContainerBuilder builder, LocatableProperties props)
throws ConfigurationException {
Settings defaultSettings = null ;
try {
defaultSettings = new PropertiesSettings( " org/apache/struts2/default " );
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ConfigurationException( " Could not find or error in org/apache/struts2/default.properties " , e);
}
loadSettings(props, defaultSettings);
}
// PropertiesSettings
// 读取org/apache/struts2/default.properties的配置信息,如果项目中需要覆盖,可以在classpath里的struts.properties里覆写
public PropertiesSettings(String name) {
URL settingsUrl = ClassLoaderUtils.getResource(name + " .properties " , getClass());
if (settingsUrl == null ) {
LOG.debug(name + " .properties missing " );
settings = new LocatableProperties();
return ;
}
settings = new LocatableProperties( new LocationImpl( null , settingsUrl.toString()));
// Load settings
InputStream in = null ;
try {
in = settingsUrl.openStream();
settings.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StrutsException( " Could not load " + name + " .properties: " + e, e);
} finally {
if (in != null ) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException io) {
LOG.warn( " Unable to close input stream " , io);
}
}
}
}
throws ConfigurationException {
Settings defaultSettings = null ;
try {
defaultSettings = new PropertiesSettings( " org/apache/struts2/default " );
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ConfigurationException( " Could not find or error in org/apache/struts2/default.properties " , e);
}
loadSettings(props, defaultSettings);
}
// PropertiesSettings
// 读取org/apache/struts2/default.properties的配置信息,如果项目中需要覆盖,可以在classpath里的struts.properties里覆写
public PropertiesSettings(String name) {
URL settingsUrl = ClassLoaderUtils.getResource(name + " .properties " , getClass());
if (settingsUrl == null ) {
LOG.debug(name + " .properties missing " );
settings = new LocatableProperties();
return ;
}
settings = new LocatableProperties( new LocationImpl( null , settingsUrl.toString()));
// Load settings
InputStream in = null ;
try {
in = settingsUrl.openStream();
settings.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StrutsException( " Could not load " + name + " .properties: " + e, e);
} finally {
if (in != null ) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException io) {
LOG.warn( " Unable to close input stream " , io);
}
}
}
}
再来看init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations方法,这个是读取struts-default.xml和Struts.xml的方法。
private
void
init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations() {
// 首先读取web.xml中的config初始参数值
// 如果没有配置就使用默认的"struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml",
// 这儿就可以看出为什么默认的配置文件必须取名为这三个名称了
// 如果不想使用默认的名称,直接在web.xml中配置config初始参数即可
String configPaths = initParams.get( " config " );
if (configPaths == null ) {
configPaths = DEFAULT_CONFIGURATION_PATHS;
}
String[] files = configPaths.split( " \\s*[,]\\s* " );
// 依次解析配置文件,xwork.xml单独解析
for (String file : files) {
if (file.endsWith( " .xml " )) {
if ( " xwork.xml " .equals(file)) {
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider( new XmlConfigurationProvider(file, false ));
} else {
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider( new StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider(file, false , servletContext));
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( " Invalid configuration file name " );
}
}
}
// 首先读取web.xml中的config初始参数值
// 如果没有配置就使用默认的"struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml",
// 这儿就可以看出为什么默认的配置文件必须取名为这三个名称了
// 如果不想使用默认的名称,直接在web.xml中配置config初始参数即可
String configPaths = initParams.get( " config " );
if (configPaths == null ) {
configPaths = DEFAULT_CONFIGURATION_PATHS;
}
String[] files = configPaths.split( " \\s*[,]\\s* " );
// 依次解析配置文件,xwork.xml单独解析
for (String file : files) {
if (file.endsWith( " .xml " )) {
if ( " xwork.xml " .equals(file)) {
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider( new XmlConfigurationProvider(file, false ));
} else {
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider( new StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider(file, false , servletContext));
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( " Invalid configuration file name " );
}
}
}
对于其它配置文件只用StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider,此类继承XmlConfigurationProvider,而XmlConfigurationProvider又实现ConfigurationProvider接口。类XmlConfigurationProvider负责配置文件的读取和解析,addAction()方法负责读取<action>标签,并将数据保存在ActionConfig中;addResultTypes()方法负责将<result-type>标签转化为ResultTypeConfig对象;loadInterceptors()方法负责将<interceptor>标签转化为InterceptorConfi对象;loadInterceptorStack()方法负责将<interceptor-ref>标签转化为InterceptorStackConfig对象;loadInterceptorStacks()方法负责将<interceptor-stack>标签转化成InterceptorStackConfig对象。而上面的方法最终会被addPackage()方法调用,将所读取到的数据汇集到PackageConfig对象中。来看XmlConfigurationProvider的源代码,详细的我自己也就大体浏览了一下,各位可以自己研读。
protected
PackageConfig addPackage(Element packageElement)
throws
ConfigurationException {
PackageConfig.Builder newPackage = buildPackageContext(packageElement);
if (newPackage.isNeedsRefresh()) {
return newPackage.build();
}
 .
.
addResultTypes(newPackage, packageElement);
loadInterceptors(newPackage, packageElement);
loadDefaultInterceptorRef(newPackage, packageElement);
loadDefaultClassRef(newPackage, packageElement);
loadGlobalResults(newPackage, packageElement);
loadGobalExceptionMappings(newPackage, packageElement);
NodeList actionList = packageElement.getElementsByTagName( " action " );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < actionList.getLength(); i ++ ) {
Element actionElement = (Element) actionList.item(i);
addAction(actionElement, newPackage);
}
loadDefaultActionRef(newPackage, packageElement);
PackageConfig cfg = newPackage.build();
configuration.addPackageConfig(cfg.getName(), cfg);
return cfg;
}
PackageConfig.Builder newPackage = buildPackageContext(packageElement);
if (newPackage.isNeedsRefresh()) {
return newPackage.build();
}
addResultTypes(newPackage, packageElement);
loadInterceptors(newPackage, packageElement);
loadDefaultInterceptorRef(newPackage, packageElement);
loadDefaultClassRef(newPackage, packageElement);
loadGlobalResults(newPackage, packageElement);
loadGobalExceptionMappings(newPackage, packageElement);
NodeList actionList = packageElement.getElementsByTagName( " action " );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < actionList.getLength(); i ++ ) {
Element actionElement = (Element) actionList.item(i);
addAction(actionElement, newPackage);
}
loadDefaultActionRef(newPackage, packageElement);
PackageConfig cfg = newPackage.build();
configuration.addPackageConfig(cfg.getName(), cfg);
return cfg;
}
这儿发现一个配置上的小技巧,我的xwork2.0.*是没有的,但是看源码是看到xwork2.1.*是可以的。继续看XmlConfigurationProvider的源代码:
private
List loadConfigurationFiles(String fileName, Element includeElement) {
List < Document > docs = new ArrayList < Document > ();
if ( ! includedFileNames.contains(fileName)) {

Element rootElement = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList children = rootElement.getChildNodes();
int childSize = children.getLength();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < childSize; i ++ ) {
Node childNode = children.item(i);
if (childNode instanceof Element) {
Element child = (Element) childNode;
final String nodeName = child.getNodeName();
// 解析每个action配置是,对于include文件可以使用通配符*来进行配置
// 如Struts.xml中可配置成<include file="actions_*.xml"/>
if (nodeName.equals( " include " )) {
String includeFileName = child.getAttribute( " file " );
if (includeFileName.indexOf( ' * ' ) != - 1 ) {
ClassPathFinder wildcardFinder = new ClassPathFinder();
wildcardFinder.setPattern(includeFileName);
Vector < String > wildcardMatches = wildcardFinder.findMatches();
for (String match : wildcardMatches) {
docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(match, child));
}
}
else {
docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(includeFileName, child));
}
}
}
}
docs.add(doc);
loadedFileUrls.add(url.toString());
}
}
return docs;
}
List < Document > docs = new ArrayList < Document > ();
if ( ! includedFileNames.contains(fileName)) {
Element rootElement = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList children = rootElement.getChildNodes();
int childSize = children.getLength();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < childSize; i ++ ) {
Node childNode = children.item(i);
if (childNode instanceof Element) {
Element child = (Element) childNode;
final String nodeName = child.getNodeName();
// 解析每个action配置是,对于include文件可以使用通配符*来进行配置
// 如Struts.xml中可配置成<include file="actions_*.xml"/>
if (nodeName.equals( " include " )) {
String includeFileName = child.getAttribute( " file " );
if (includeFileName.indexOf( ' * ' ) != - 1 ) {
ClassPathFinder wildcardFinder = new ClassPathFinder();
wildcardFinder.setPattern(includeFileName);
Vector < String > wildcardMatches = wildcardFinder.findMatches();
for (String match : wildcardMatches) {
docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(match, child));
}
}
else {
docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(includeFileName, child));
}
}
}
}
docs.add(doc);
loadedFileUrls.add(url.toString());
}
}
return docs;
}
init_CustomConfigurationProviders方式初始自定义的Provider,配置类全名和实现ConfigurationProvider接口,用逗号隔开即可。
private
void
init_CustomConfigurationProviders() {
String configProvs = initParams.get( " configProviders " );
if (configProvs != null ) {
String[] classes = configProvs.split( " \\s*[,]\\s* " );
for (String cname : classes) {
try {
Class cls = ClassLoaderUtils.loadClass(cname, this .getClass());
ConfigurationProvider prov = (ConfigurationProvider)cls.newInstance();
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(prov);
}

}
}
}
String configProvs = initParams.get( " configProviders " );
if (configProvs != null ) {
String[] classes = configProvs.split( " \\s*[,]\\s* " );
for (String cname : classes) {
try {
Class cls = ClassLoaderUtils.loadClass(cname, this .getClass());
ConfigurationProvider prov = (ConfigurationProvider)cls.newInstance();
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(prov);
}
}
}
}
好了,现在再回到FilterDispatcher,每次发送一个Request,FilterDispatcher都会调用doFilter方法。
public
void
doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws
IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String timerKey = " FilterDispatcher_doFilter: " ;
try {
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory. class ).createValueStack();
ActionContext ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
// 根据content type来使用不同的Request封装,可以参见Dispatcher的wrapRequest
request = prepareDispatcherAndWrapRequest(request, response);
ActionMapping mapping;
try {
// 根据url取得对应的Action的配置信息--ActionMapping,actionMapper是通过Container的inject注入的
mapping = actionMapper.getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error( " error getting ActionMapping " , ex);
dispatcher.sendError(request, response, servletContext, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex);
return ;
}
// 如果找不到对应的action配置,则直接返回。比如你输入***.jsp等等
// 这儿有个例外,就是如果path是以“/struts”开头,则到初始参数packages配置的包路径去查找对应的静态资源并输出到页面流中,当然.class文件除外。如果再没有则跳转到404
if (mapping == null ) {
// there is no action in this request, should we look for a static resource?
String resourcePath = RequestUtils.getServletPath(request);
if ( "" .equals(resourcePath) && null != request.getPathInfo()) {
resourcePath = request.getPathInfo();
}
if (serveStatic && resourcePath.startsWith( " /struts " )) {
String name = resourcePath.substring( " /struts " .length());
findStaticResource(name, request, response);
} else {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
return ;
}
// 正式开始Action的方法了
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
} finally {
try {
ActionContextCleanUp.cleanUp(req);
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
}
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String timerKey = " FilterDispatcher_doFilter: " ;
try {
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory. class ).createValueStack();
ActionContext ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
// 根据content type来使用不同的Request封装,可以参见Dispatcher的wrapRequest
request = prepareDispatcherAndWrapRequest(request, response);
ActionMapping mapping;
try {
// 根据url取得对应的Action的配置信息--ActionMapping,actionMapper是通过Container的inject注入的
mapping = actionMapper.getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error( " error getting ActionMapping " , ex);
dispatcher.sendError(request, response, servletContext, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex);
return ;
}
// 如果找不到对应的action配置,则直接返回。比如你输入***.jsp等等
// 这儿有个例外,就是如果path是以“/struts”开头,则到初始参数packages配置的包路径去查找对应的静态资源并输出到页面流中,当然.class文件除外。如果再没有则跳转到404
if (mapping == null ) {
// there is no action in this request, should we look for a static resource?
String resourcePath = RequestUtils.getServletPath(request);
if ( "" .equals(resourcePath) && null != request.getPathInfo()) {
resourcePath = request.getPathInfo();
}
if (serveStatic && resourcePath.startsWith( " /struts " )) {
String name = resourcePath.substring( " /struts " .length());
findStaticResource(name, request, response);
} else {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
return ;
}
// 正式开始Action的方法了
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
} finally {
try {
ActionContextCleanUp.cleanUp(req);
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
}