<script type="text/javascript">function StorePage(){d=document;t=d.selection?(d.selection.type!='None'?d.selection.createRange().text:''):(d.getSelection?d.getSelection():'');void(keyit=window.open('http://www.365key.com/storeit.aspx?t='+escape(d.title)+'&u='+escape(d.location.href)+'&c='+escape(t),'keyit','scrollbars=no,width=475,height=575,left=75,top=20,status=no,resizable=yes'));keyit.focus();}</script>
六、 创建Action类:BookAction
有Struts 1.x经验的朋友都知道Action是Struts的核心内容,当然Struts 2.0也不例外。不过,Struts 1.x与Struts 2.0的Action模型很大的区别。
|
Struts 1.x |
Stuts 2.0 |
| 接口 |
必须继承org.apache.struts.action.Action或者其子类 |
无须继承任何类型或实现任何接口 |
| 表单数据 |
表单数据封装在FormBean中 |
表单数据包含在Action中,通过Getter和Setter获取 |
1、建立BookAction类
 packagecom.sterning.books.web.actions;
packagecom.sterning.books.web.actions;

 importjava.util.Collection;
importjava.util.Collection;

 importcom.sterning.books.model.Books;
importcom.sterning.books.model.Books;
 importcom.sterning.books.services.iface.IBooksService;
importcom.sterning.books.services.iface.IBooksService;
 importcom.sterning.commons.AbstractAction;
importcom.sterning.commons.AbstractAction;
 importcom.sterning.commons.Pager;
importcom.sterning.commons.Pager;
 importcom.sterning.commons.PagerService;
importcom.sterning.commons.PagerService;


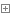 public
class
BooksAction
extends
AbstractAction
public
class
BooksAction
extends
AbstractAction
 {
{

 privateIBooksServicebooksService;
privateIBooksServicebooksService;
 privatePagerServicepagerService;
privatePagerServicepagerService;

 privateBooksbook;
privateBooksbook;
 privatePagerpager;
privatePagerpager;

 protectedCollectionavailableItems;
protectedCollectionavailableItems;
 protectedStringcurrentPage;
protectedStringcurrentPage;
 protectedStringpagerMethod;
protectedStringpagerMethod;
 protectedStringtotalRows;
protectedStringtotalRows;
 protectedStringbookId;
protectedStringbookId;
 protectedStringqueryName;
protectedStringqueryName;
 protectedStringqueryValue;
protectedStringqueryValue;
 protectedStringsearchName;
protectedStringsearchName;
 protectedStringsearchValue;
protectedStringsearchValue;
 protectedStringqueryMap;
protectedStringqueryMap;


 publicStringlist()throwsException
publicStringlist()throwsException {
{

 if(queryMap==null||queryMap.equals(""))
if(queryMap==null||queryMap.equals("")) {
{


 }else
}else {
{
 String[]str=queryMap.split("~");
String[]str=queryMap.split("~");
 this.setQueryName(str[0]);
this.setQueryName(str[0]);
 this.setQueryValue(str[1]);
this.setQueryValue(str[1]);
 }
}

 System.out.println("asd"+this.getQueryValue());
System.out.println("asd"+this.getQueryValue());
 inttotalRow=booksService.getRows(this.getQueryName(),this.getQueryValue());
inttotalRow=booksService.getRows(this.getQueryName(),this.getQueryValue());
 pager=pagerService.getPager(this.getCurrentPage(),this.getPagerMethod(),totalRow);
pager=pagerService.getPager(this.getCurrentPage(),this.getPagerMethod(),totalRow);
 this.setCurrentPage(String.valueOf(pager.getCurrentPage()));
this.setCurrentPage(String.valueOf(pager.getCurrentPage()));
 this.setTotalRows(String.valueOf(totalRow));
this.setTotalRows(String.valueOf(totalRow));
 availableItems=booksService.getBooks(this.getQueryName(),this.getQueryValue(),pager.getPageSize(),pager.getStartRow());
availableItems=booksService.getBooks(this.getQueryName(),this.getQueryValue(),pager.getPageSize(),pager.getStartRow());

 this.setQueryName(this.getQueryName());
this.setQueryName(this.getQueryName());
 this.setQueryValue(this.getQueryValue());
this.setQueryValue(this.getQueryValue());

 this.setSearchName(this.getQueryName());
this.setSearchName(this.getQueryName());
 this.setSearchValue(this.getQueryValue());
this.setSearchValue(this.getQueryValue());

 returnSUCCESS;
returnSUCCESS;
 }
}


 publicStringload()throwsException
publicStringload()throwsException {
{
 if(bookId!=null)
if(bookId!=null)
 book=booksService.getBook(bookId);
book=booksService.getBook(bookId);
 else
else
 bookId=booksService.getMaxID();
bookId=booksService.getMaxID();
 returnSUCCESS;
returnSUCCESS;
 }
}


 publicStringsave()throwsException
publicStringsave()throwsException {
{

 if(this.getBook().getBookPrice().equals(""))
if(this.getBook().getBookPrice().equals("")) {
{
 this.getBook().setBookPrice("0.0");
this.getBook().setBookPrice("0.0");
 }
}

 Stringid=this.getBook().getBookId();
Stringid=this.getBook().getBookId();
 Booksbook=booksService.getBook(id);
Booksbook=booksService.getBook(id);



 if(book==null)
if(book==null)
 booksService.addBook(this.getBook());
booksService.addBook(this.getBook());
 else
else
 booksService.updateBook(this.getBook());
booksService.updateBook(this.getBook());

 this.setQueryName(this.getQueryName());
this.setQueryName(this.getQueryName());
 this.setQueryValue(this.getQueryValue());
this.setQueryValue(this.getQueryValue());


 if(this.getQueryName()==null||this.getQueryValue()==null||this.getQueryName().equals("")||this.getQueryValue().equals(""))
if(this.getQueryName()==null||this.getQueryValue()==null||this.getQueryName().equals("")||this.getQueryValue().equals("")) {
{


 }else
}else {
{
 queryMap=this.getQueryName()+"~"+this.getQueryValue();
queryMap=this.getQueryName()+"~"+this.getQueryValue();
 }
}

 returnSUCCESS;
returnSUCCESS;
 }
}


 publicStringdelete()throwsException
publicStringdelete()throwsException {
{
 booksService.deleteBook(this.getBookId());
booksService.deleteBook(this.getBookId());


 if(this.getQueryName()==null||this.getQueryValue()==null||this.getQueryName().equals("")||this.getQueryValue().equals(""))
if(this.getQueryName()==null||this.getQueryValue()==null||this.getQueryName().equals("")||this.getQueryValue().equals("")) {
{


 }else
}else {
{
 queryMap=this.getQueryName()+"~"+this.getQueryValue();
queryMap=this.getQueryName()+"~"+this.getQueryValue();
 }
}
 returnSUCCESS;
returnSUCCESS;
 }
}


 publicBooksgetBook()
publicBooksgetBook() {
{
 returnbook;
returnbook;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetBook(Booksbook)
publicvoidsetBook(Booksbook) {
{
 this.book=book;
this.book=book;
 }
}


 publicIBooksServicegetBooksService()
publicIBooksServicegetBooksService() {
{
 returnbooksService;
returnbooksService;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetBooksService(IBooksServicebooksService)
publicvoidsetBooksService(IBooksServicebooksService) {
{
 this.booksService=booksService;
this.booksService=booksService;
 }
}


 publicCollectiongetAvailableItems()
publicCollectiongetAvailableItems() {
{
 returnavailableItems;
returnavailableItems;
 }
}


 publicStringgetCurrentPage()
publicStringgetCurrentPage() {
{
 returncurrentPage;
returncurrentPage;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetCurrentPage(StringcurrentPage)
publicvoidsetCurrentPage(StringcurrentPage) {
{
 this.currentPage=currentPage;
this.currentPage=currentPage;
 }
}


 publicStringgetPagerMethod()
publicStringgetPagerMethod() {
{
 returnpagerMethod;
returnpagerMethod;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetPagerMethod(StringpagerMethod)
publicvoidsetPagerMethod(StringpagerMethod) {
{
 this.pagerMethod=pagerMethod;
this.pagerMethod=pagerMethod;
 }
}


 publicPagergetPager()
publicPagergetPager() {
{
 returnpager;
returnpager;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetPager(Pagerpager)
publicvoidsetPager(Pagerpager) {
{
 this.pager=pager;
this.pager=pager;
 }
}


 publicStringgetTotalRows()
publicStringgetTotalRows() {
{
 returntotalRows;
returntotalRows;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetTotalRows(StringtotalRows)
publicvoidsetTotalRows(StringtotalRows) {
{
 this.totalRows=totalRows;
this.totalRows=totalRows;
 }
}


 publicStringgetBookId()
publicStringgetBookId() {
{
 returnbookId;
returnbookId;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetBookId(StringbookId)
publicvoidsetBookId(StringbookId) {
{
 this.bookId=bookId;
this.bookId=bookId;
 }
}


 publicStringgetQueryName()
publicStringgetQueryName() {
{
 returnqueryName;
returnqueryName;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetQueryName(StringqueryName)
publicvoidsetQueryName(StringqueryName) {
{
 this.queryName=queryName;
this.queryName=queryName;
 }
}


 publicStringgetQueryValue()
publicStringgetQueryValue() {
{
 returnqueryValue;
returnqueryValue;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetQueryValue(StringqueryValue)
publicvoidsetQueryValue(StringqueryValue) {
{
 this.queryValue=queryValue;
this.queryValue=queryValue;
 }
}


 publicStringgetSearchName()
publicStringgetSearchName() {
{
 returnsearchName;
returnsearchName;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetSearchName(StringsearchName)
publicvoidsetSearchName(StringsearchName) {
{
 this.searchName=searchName;
this.searchName=searchName;
 }
}


 publicStringgetSearchValue()
publicStringgetSearchValue() {
{
 returnsearchValue;
returnsearchValue;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetSearchValue(StringsearchValue)
publicvoidsetSearchValue(StringsearchValue) {
{
 this.searchValue=searchValue;
this.searchValue=searchValue;
 }
}


 publicStringgetQueryMap()
publicStringgetQueryMap() {
{
 returnqueryMap;
returnqueryMap;
 }
}


 publicvoidsetQueryMap(StringqueryMap)
publicvoidsetQueryMap(StringqueryMap) {
{
 this.queryMap=queryMap;
this.queryMap=queryMap;
 }
}


 publicPagerServicegetPagerService()
publicPagerServicegetPagerService() {
{
 returnpagerService;
returnpagerService;
 }
}



 publicvoidsetPagerService(PagerServicepagerService)
publicvoidsetPagerService(PagerServicepagerService) {
{
 this.pagerService=pagerService;
this.pagerService=pagerService;
 }
}
 }
}

com.sterning.books.web.actions.BookAction.java
(1)、默认情况下,当请求bookAction.action发生时(这个会在后面的Spring配置文件中见到的),Struts运行时(Runtime)根据struts.xml里的Action映射集(Mapping),实例化com.sterning.books.web.actions.BookAction类,并调用其execute方法。当然,我们可以通过以下两种方法改变这种默认调用。这个功能(Feature)有点类似Struts 1.x中的LookupDispathAction。
在classes/sturts.xml中新建Action,并指明其调用的方法;
访问Action时,在Action名后加上“!xxx”(xxx为方法名)。
(2)、细心的朋友应该可能会发现com.sterning.books.web.actions.BookAction.java中Action方法(execute)返回都是SUCCESS。这个属性变量我并没有定义,所以大家应该会猜到它在ActionSupport或其父类中定义。没错,SUCCESS在接口com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action中定义,另外同时定义的还有ERROR, INPUT, LOGIN, NONE。
此外,我在配置Action时都没有为result定义名字(name),所以它们默认都为success。值得一提的是Struts 2.0中的result不仅仅是Struts 1.x中forward的别名,它可以实现除forward外的很激动人心的功能,如将Action输出到FreeMaker模板、Velocity模板、JasperReports和使用XSL转换等。这些都过result里的type(类型)属性(Attribute)定义的。另外,您还可以自定义result类型。
(3)、使用Struts 2.0,表单数据的输入将变得非常方便,和普通的POJO一样在Action编写Getter和Setter,然后在JSP的UI标志的name与其对应,在提交表单到Action时,我们就可以取得其值。
(4)、Struts 2.0更厉害的是支持更高级的POJO访问,如this.getBook().getBookPrice()。private Books book所引用的是一个关于书的对象类,它可以做为一个属性而出现在BookActoin.java类中。这样对我们开发多层系统尤其有用。它可以使系统结构更清晰。
(5)、有朋友可能会这样问:“如果我要取得Servlet API中的一些对象,如request、response或session等,应该怎么做?这里的execute不像Struts 1.x的那样在参数中引入。”开发Web应用程序当然免不了跟这些对象打交道。在Strutx 2.0中可以有两种方式获得这些对象:非IoC(控制反转Inversion of Control)方式和IoC方式。
非IoC方式
要获得上述对象,关键是Struts 2.0中com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext类。我们可以通过它的静态方法getContext()获取当前Action的上下文对象。另外,org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext作为辅助类(Helper Class),可以帮助您快捷地获得这几个对象。
HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = ServletActionContext.getResponse();
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
如果你只是想访问session的属性(Attribute),你也可以通过ActionContext.getContext().getSession()获取或添加session范围(Scoped)的对象。
IoC方式
要使用IoC方式,我们首先要告诉IoC容器(Container)想取得某个对象的意愿,通过实现相应的接口做到这点。如实现SessionAware, ServletRequestAware, ServletResponseAware接口,从而得到上面的对象。
1、对BookAction类的Save方法进行验证
正如《Writing Secure Code》文中所写的名言All input is evil:“所有的输入都是罪恶的”,所以我们应该对所有的外部输入进行校验。而表单是应用程序最简单的入口,对其传进来的数据,我们必须进行校验。Struts2的校验框架十分简单方便,只在如下两步:
在Xxx-validation.xml文件中的<message>元素中加入key属性;
在相应的jsp文件中的<s:form>标志中加入validate="true"属性,就可以在用Javascript在客户端校验数据。
其验证文件为:BooksAction-save-validation.xml
 <?
xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"
?>
<?
xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"
?>
 <!
DOCTYPEvalidatorsPUBLIC"-//OpenSymphonyGroup//XWorkValidator1.0//EN""http://www.opensymphony.com/xwork/xwork-validator-1.0.dtd"
>
<!
DOCTYPEvalidatorsPUBLIC"-//OpenSymphonyGroup//XWorkValidator1.0//EN""http://www.opensymphony.com/xwork/xwork-validator-1.0.dtd"
>
 <
validators
>
<
validators
>
 <!--
Field-ValidatorSyntax
-->
<!--
Field-ValidatorSyntax
-->
 <
field
name
="book.bookName"
>
<
field
name
="book.bookName"
>
 <
field-validator
type
="requiredstring"
>
<
field-validator
type
="requiredstring"
>
 <
message
key
="book.bookName.required"
/>
<
message
key
="book.bookName.required"
/>
 </
field-validator
>
</
field-validator
>
 </
field
>
</
field
>
 <
field
name
="book.bookAuthor"
>
<
field
name
="book.bookAuthor"
>
 <
field-validator
type
="requiredstring"
>
<
field-validator
type
="requiredstring"
>
 <
message
key
="book.bookAuthor.required"
/>
<
message
key
="book.bookAuthor.required"
/>
 </
field-validator
>
</
field-validator
>
 </
field
>
</
field
>
 <
field
name
="book.bookPublish"
>
<
field
name
="book.bookPublish"
>
 <
field-validator
type
="requiredstring"
>
<
field-validator
type
="requiredstring"
>
 <
message
key
="book.bookPublish.required"
/>
<
message
key
="book.bookPublish.required"
/>
 </
field-validator
>
</
field-validator
>
 </
field
>
</
field
>
 </
validators
>
</
validators
>

com.sterning.books.web.actions.BooksAction-save-validation.xml
1、对BookAction类的Save方法进行验证的资源文件
注意配置文件的名字应该是:配置文件(类名-validation.xml)的格式。BooksAction类的验证资源文件为:BooksAction.properties
 book=Books
book=Books
 book.bookName.required=/u8bf7/u8f93/u5165/u4e66/u540d
book.bookName.required=/u8bf7/u8f93/u5165/u4e66/u540d
 book.bookAuthor.required=/u8bf7/u8f93/u5165/u4f5c/u8005
book.bookAuthor.required=/u8bf7/u8f93/u5165/u4f5c/u8005
 book.bookPublish.required=/u8bf7/u8f93/u5165/u51fa/u7248/u793e
book.bookPublish.required=/u8bf7/u8f93/u5165/u51fa/u7248/u793e
 format.date={0,date,yyyy-MM-dd}
format.date={0,date,yyyy-MM-dd}

com.sterning.books.web.actions.BooksAction.properties
资源文件的查找顺序是有一定规则的。之所以说Struts 2.0的国际化更灵活是因为它可以根据不同需要配置和获取资源(properties)文件。在Struts 2.0中有下面几种方法:
(1)、使用全局的资源文件。这适用于遍布于整个应用程序的国际化字符串,它们在不同的包(package)中被引用,如一些比较共用的出错提示;
(2)、使用包范围内的资源文件。做法是在包的根目录下新建名的package.properties和package_xx_XX.properties文件。这就适用于在包中不同类访问的资源;
(3)、使用Action范围的资源文件。做法为Action的包下新建文件名(除文件扩展名外)与Action类名同样的资源文件。它只能在该Action中访问。如此一来,我们就可以在不同的Action里使用相同的properties名表示不同的值。例如,在ActonOne中title为“动作一”,而同样用title在ActionTwo表示“动作二”,节省一些命名工夫;
(4)、使用<s:i18n>标志访问特定路径的properties文件。在使用这一方法时,请注意<s:i18n>标志的范围。在<s:i18n name="xxxxx">到</s:i18n>之间,所有的国际化字符串都会在名为xxxxx资源文件查找,如果找不到,Struts 2.0就会输出默认值(国际化字符串的名字)。
例如:某个ChildAction中调用了getText("user.title"),Struts 2.0的将会执行以下的操作:
查找ChildAction_xx_XX.properties文件或ChildAction.properties;
查找ChildAction实现的接口,查找与接口同名的资源文件MyInterface.properties;
查找ChildAction的父类ParentAction的properties文件,文件名为ParentAction.properties;
判断当前ChildAction是否实现接口ModelDriven。如果是,调用getModel()获得对象,查找与其同名的资源文件;
查找当前包下的package.properties文件;
查找当前包的父包,直到最顶层包;
在值栈(Value Stack)中,查找名为user的属性,转到user类型同名的资源文件,查找键为title的资源;
查找在struts.properties配置的默认的资源文件,参考例1;
输出user.title。
未完待续 。。。。。。