fstream与 C 风格(例如fread 和 fwrite )两种读写文件方法的效率比较
我觉得作者写的挺好,评论也写的很对。
目前我的项目就是在VS2008+Qt+win7上开发的。我上次总结的QFile和C语言对文件操作的性能比较.--读取double型二进制数据文件也说明了这个问题。
在windows平台下,MSVC编译器的环境下,对大文件的数据读写操作。采用C语言的形式(例如fread 和 fwrite )确实比C++/QT的串行序列化读写文件,速度快上好几倍。可以参考这两篇文章。
1、QFile和C语言对文件操作的性能比较.--读取double型二进制数据文件
2、fstream与 C 风格(例如fread 和 fwrite )两种读写文件方法的效率比较
转载:
为了探录c++ 风格的fstream与 C 风格(例如fread 和 fwrite )两种读写文件的方法的效率,我特意做了两个实验。
我的机器是Windows XP, Visual Studio 2008
1. 测试写文件速度
程序设计思路: 将TEST_SIZE个字符用两种方式写入文件,记录两种方式的耗时。
实验代码:
[cpp] view plaincopy
- void test_write()
- {
- const int TEST_SIZE = 10000000 ;
- const char* c_plus_write_file = "H://c_plus_write_file.txt";
- const char* c_write_file = "H://c_write_file.txt";
- cout<<"Test size :" << TEST_SIZE <<endl;
- //c++ style writing file
- ofstream of(c_plus_write_file);
- assert(of);
- time_t start, end;
- start = clock();
- for(int i=0; i < TEST_SIZE; ++i)
- {
- char tmp[1];
- tmp[0] = char(i);
- of << tmp[0];
- }
- end = clock();
- of.close();
- cout<<"C++ style: "<<end - start <<" ms"<<endl;
- //c style writing file
- FILE* fp = fopen(c_write_file, "w");
- start = clock();
- for(int i=0; i < TEST_SIZE; ++i)
- {
- char tmp[1];
- tmp[0] = char(i);
- fwrite( tmp, 1, 1, fp);
- }
- end = clock();
- fclose(fp);
- cout<<"C style: "<<end - start <<" ms"<<endl;
- cin.get();
- }
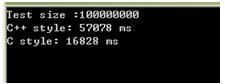
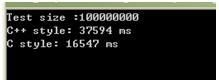
实验结果:
图1
图2
图3
**从图1、2、3,可以看出, ofstream 的 << 运算符 所耗时 是fwrite()的近三倍
把of<<的代码改成了: of.write(tmp,1); 后结果:
实验代码:
- void test_write()
- {
- const int TEST_SIZE = 1000000 ;
- const char* c_plus_write_file = "H://c_plus_write_file.txt";
- const char* c_write_file = "H://c_write_file.txt";
- cout<<"Test size :" << TEST_SIZE <<endl;
- //c++ style writing file
- ofstream of(c_plus_write_file);
- assert(of);
- time_t start, end;
- start = clock();
- for(int i=0; i < TEST_SIZE; ++i)
- {
- char tmp[1];
- tmp[0] = char(i);
- of.write(tmp,1);
- }
- end = clock();
- of.close();
- cout<<"C++ style: "<<end - start <<" ms"<<endl;
- //c style writing file
- FILE* fp = fopen(c_write_file, "w");
- start = clock();
- for(int i=0; i < TEST_SIZE; ++i)
- {
- char tmp[1];
- tmp[0] = char(i);
- fwrite( tmp, 1, 1, fp);
- }
- end = clock();
- fclose(fp);
- cout<<"C style: "<<end - start <<" ms"<<endl;
- cin.get();
- }
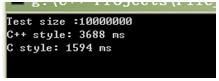
实验结果:
图4
图5
图6
对比图4 和 图1、 图5 和 图2、图6 和 图3, 可以看到 << 运算符没有 ofstream.write(), 快, 但两者还是没有 fwrite() 快
结论: 效率 fwrite() > ofstream.operator<<() > ofstream.write()
3. 下面做读文件的比较:
程序设计思路: 用两种方法去读一个近100M的文本,记录时间。
实验代码:
- void test_read()
- {
- const char* read_file = "H://read4.txt";
- const int BUF_SIZE = 1024 ;
- char buf[BUF_SIZE];
- //c++ style writing file
- ifstream ifs(read_file,ios::binary);
- assert(ifs);
- time_t start, end;
- start = clock();
- while(!ifs.eof())
- {
- ifs.read(buf,BUF_SIZE);
- }
- end = clock();
- ifs.close();
- cout<<"C++ style: "<<end - start <<" ms"<<endl;
- //c style writing file
- FILE* fp = fopen(read_file, "rb");
- start = clock();
- int len = 0;
- do
- {
- len = fread(buf,1,BUF_SIZE,fp);
- //cout<<len<<endl;
- }while(len != 0);
- end = clock();
- fclose(fp);
- cout<<"C style: "<<end - start <<" ms"<<endl;
- cin.get();
- }
实验结果:
图7
结论: 读取一个 100M 的文件, fread() 的效率 是 ifstream.read()的将近十倍! (此结论惊人!)

看看我用你的代码在MinGW的g++上的测试结果:
Test text-style writing:
Test size :10000000
C++ style: 718 ms
C style: 1594 ms
Test binary-style writing:
Test size :1000000
C++ style: 63 ms
C style: 156 ms
Test reading:
C++ style: 1047 ms
C style: 609 ms
结果是输出时C++风格比C风格还快,就算是输入C++风格也只花了C风格不到一半的时间。看看你我结果的对比能说明什么(硬件不同所以绝对数值没有可比性,只有同一平台上的对比才有意义)?
只能说明M$VC的C++ I/O是多么的Disabled(翻译成无能还是残疾随你便),奉劝你不要只在M$VC平台上发现了什么就以偏概全地说A比B快云云,就算在M$WIN上,编译器也多的是。多测几个再看看吧,相信你会有新的发现。