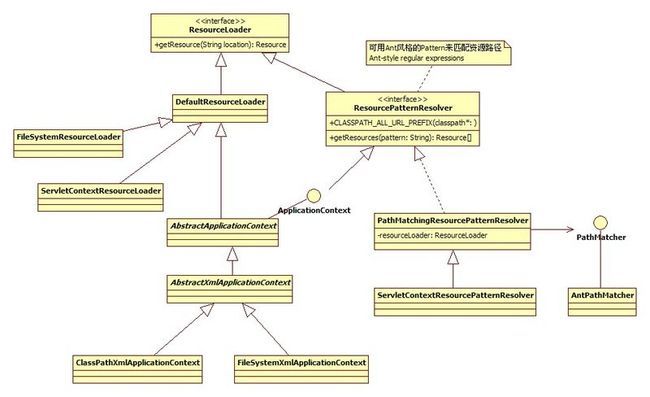
DefaultResourceLoader:
ResourceLoader接口的默认实现,通过参数资源路径的前缀获得相应的Resource.
1、若以"classpath:"开头,则获得classPathResource
2、若location符合URL格式,如http:,ftp:,file:,jar等,则获得URLResource
3、1,2都不符合,表示无前缀或其他,则尝试getResourceByPath()方法获得Resource(默认:ClassPathContextResource)。子类通过getResourceByPath方法获得不同的Resource。如FileSystemXMLApplicationContext
DefaultResourceLoader代码:
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
//1.若以"classpath:"开头,则表示使用classPathResource加载
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
//2.尝试是否符合URL格式,如http:,ftp:,file等
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
//3.不符合URL格式,则采用自定义形式加载。方法可子类覆盖,默认ClassPathContextResource
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
/**
* Return a Resource handle for the resource at the given path.
* <p>The default implementation supports class path locations. This should
* be appropriate for standalone implementations but can be overridden,
* e.g. for implementations targeted at a Servlet container.
* @param path the path to the resource
* @return the corresponding Resource handle
* @see ClassPathResource
* @see org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext#getResourceByPath
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext#getResourceByPath
*/
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
资源路径同Resource转换规则:(选择不同加载策略规则)

从DefaultResourceLoader.getResource(String location)可看出,未指定前缀时,通过getResourceByPath()获得Resource。不同ApplicationContext不同实现。
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 覆盖getResourceByPath()方法,获得FileSystemResource
/**
* Resolve resource paths as file system paths.
* <p>Note: Even if a given path starts with a slash, it will get
* interpreted as relative to the current VM working directory.
* This is consistent with the semantics in a Servlet container.
* @param path path to the resource
* @return Resource handle
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext#getResourceByPath
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemResource(path);
}
XmlWebApplicationContext:
/**
* This implementation supports file paths beneath the root of the ServletContext.
* @see ServletContextResource
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, path);
}
ResourceLoader策略模式应用
ResourceLoaderAware接口
void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader);实现该接口的类部署到application context中时,context会识别为ResourceLoaderAware,application context 会调用 setResourceLoader方法,把自身作为参数传入该方法。(因为ApplicationContext 实现了ResourceLoader接口)
自动装配@Autowired xml:autowire="byType" 代替接口实现
ApplicationContext中资源路径通配符
ant风格路径表达式:
* 匹配0或者任意数量的字符
? 匹配任何单字符
** 匹配0或者更多的目录
属性:
最长匹配原则(has more characters)
说明,URL请求/app/dir/file.jsp,现在存在两个路径匹配模式/**/*.jsp和/app/dir/*.jsp,那么会根据模式/app/dir/*.jsp来匹配
a) 资源路径前缀classpath: 同 classpath*: 区别
http://blog.csdn.net/zl3450341/article/details/9306983
1、classpath 只返回第一个匹配Resource,classpath* 返回所有匹配Resource
2、classpath*:直接跟通配符路径,则无法找到jar中的资源
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
try {
/**
* 21
URL [file:/E:/xxx/target/classes/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF]
URL [jar:file:/E:/xxx/lib/jboss-jmx.jar!/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF]
URL [jar:file:/E:/xxx/lib/jboss-system.jar!/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF]
*/
Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources("classpath*:/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF");
/*only
file [E:\xxxx\target\classes\META-INF\MANIFEST.MF]
*/
//Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources("classpath*:/META-INF*/MANIFEST*.MF");
System.out.println(resources.length);
for(Resource res:resources){
System.out.println(res);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
b)
Spring 资源访问剖析和策略模式应用