问题1:一对一单向和一对一双向有什么区别呀?单向和双向在数据库中的表现都一样吗?没错,在数据库里面一对一单向和一对一双向其实没区别,在后面学的一对多,多对多都一样,数据库没什么区别,但是它的区别主要在外面java程序里面有区别(eg,(hibernate-One2one-test)如果我们双向的,我们可以通过Wife找到Husband,如果我们是单向我们就不能通过Wife找到Husband;所谓单向双向的映射的意思是:在同样的数据库的基础之上,你要实现单向的编程模型你该怎么映射,如果你要实现双向的变成模型你该怎么映射
1.一对一单向外键关联
A) Annotation: @OneToOne @JoinColunm
B) xml: <many-to-one name="studentcard" column="studentId" unique="true"/>
情景:每个人都有一张身份证,一张身份证当然属于一个人。
工程的目录结构以及所需要的jar包如下:
package com.bjsxt.hibernate;
import java.util.Date;
public class People {
private int id;
private String name; //姓名
private int age; //年龄
private Date birthday; //出生日期
private boolean sex;//性别 true: 男, false:女
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public boolean isSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
②IdentityCard类的编写如下:
package com.bjsxt.hibernate;
public class IdentityCard {
private int id;
private String identityNO; //身份证号
//一对一单向外键关联,只需要在IdentityCard进行配置
private People people; //一个身份证肯定只属于某一个人
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getIdentityNO() {
return identityNO;
}
public void setIdentityNO(String identityNO) {
this.identityNO = identityNO;
}
public People getPeople() {
return people;
}
public void setPeople(People people) {
this.people = people;
}
}
③People.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.bjsxt.hibernate.People" dynamic-update="true">
<id name="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name"></property>
<property name="age" />
<property name="birthday" type="date"/>
<property name="sex" type="yes_no" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
④IdentityCard.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.bjsxt.hibernate.IdentityCard">
<id name="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="identityNO"/>
<!-- unique 说明 fk_people_id具有唯一性 -->
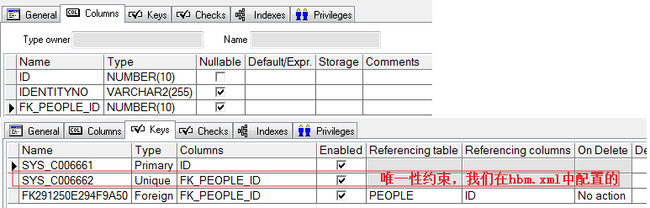
<many-to-one name="people" column="fk_people_id" unique="true"></many-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
⑤使用hibernate的SchemaExport来自动创建表
package com.bjsxt.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaExport;
import org.junit.Test;
public class HibernateORMappingTest {
@Test
public void testSchemaExport() {
new SchemaExport(new Configuration().configure()).create(true, true);
}
}
⑥执行HibernateORMappingTest 生成的表结构如下
IdentityCard的表结构如下: