- Android应用性能优化
轻口味
Android
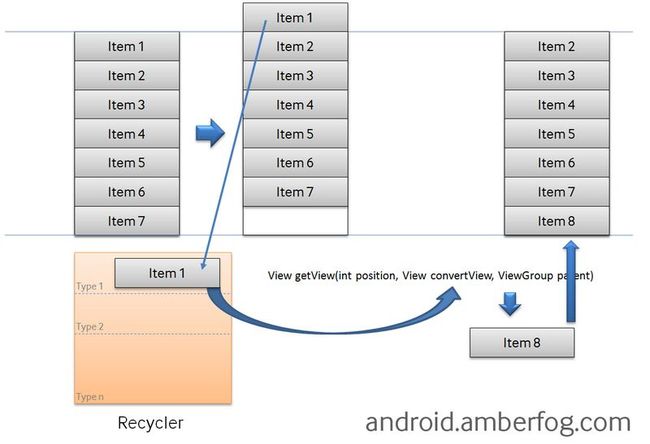
Android手机由于其本身的后台机制和硬件特点,性能上一直被诟病,所以软件开发者对软件本身的性能优化就显得尤为重要;本文将对Android开发过程中性能优化的各个方面做一个回顾与总结。Cache优化ListView缓存:ListView中有一个回收器,Item滑出界面的时候View会回收到这里,需要显示新的Item的时候,就尽量重用回收器里面的View;每次在getView函数中inflate新
- Android面试题
1b16bebb1c3c
ListView和RecyclerView区别参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/shu_lan...既然RecyclerView在很多方面能取代ListView,Google为什么没把ListView划上一条过时的横线?答案:可以沿着回收机制来回答。ListView采用的是RecyclerBin的回收机制在一些轻量级的List显示时效率更高你用过MVP和MVVM的区别参考链接:
- Flutter学习之九 ListView
MQ_Twist
极端很容易,平衡才是最难的。Flutter学习之八Container前言Flutter中的ListView的地位,就好比于iOS中的UITableView,算是最常用的可滚动组件之一,它可以沿一个方向线性排布所有子组件,并且它也支持列表项懒加载(在需要时才会创建)。默认构造函数我们看看ListView的默认构造函数定义:ListView({...//可滚动widget公共参数AxisscrollD
- Android 自定义控件基础-ListView的加载更多
琼珶和予
ListView加载更多与之前的下拉刷新实现的方式差不多,都是通过自定义控件来实现的,而且都是通过重写ListView来实现的。1.foot布局 foot布局当中有一个progressbar控件,在我们使用这个控件的时候,要注意一点:如果我们想要使用·父布局来限制progressbar的大小,如果progressbar的layout_width设置的是wrap_content的话,会发现父布
- Android学习之RecyclerView快速添加头部布局
如果可以003
Androidandroid布局
众所周知我们的ListView、GridView都可以增加头部布局;这样在遇到复杂的头部布局就不用增加视图类型了,不管是对于代码的可维护性还是整洁性;在Adapter中写又臭又长的代码,无论是自己看还是留给后来者都是痛苦的,而且你要是把代码都堆在getView中,ohno!我要分分钟切腹自尽…RecyclerView增加头部布局传统方式真的不是我懒,真的;传统方式我相信大家应该都会了,好吧我还是简
- Android 网络编程一
uniapp
Android的ListView采用MVC的方式显示,Model代表显示条目实体,View代表ListView,C代表Adapter。相比iOS中Controller和View相互融合的处境,Android中的MVC更加清新自然。Google在Android中预制了很多示例Demo,集中放在了ApiDemo中,代码可以从github上单独下载。在Mac下的地址为Library/Android/sd
- Android学习之-RecyclerView带刺的玫瑰
如果可以003
Androidandroidrecycleview
我的小鱼你醒了,还认识早晨吗?昨夜你曾经说,愿夜幕永不开启…上述小诗先逗比一下,接下来切入正题;自从RecyclerView的诞生起,人们就为她贴上了高贵的标签;她灵活华丽高度可定制,而另一边ListView确已是明日黄花;人们趋之若鹜的奔向了RecyclerView赞美她吹捧她似乎一切的一切都尽在他们的掌握中;各大技术论坛开始讲解RecyclerView是多么的好用;于是乎我也加入了使用Recy
- android 下拉刷新,androidx.swiperefreshlayout:swiperefreshlayout:1.1.0
No Promises﹉
androidandroidx
介绍`androidx.swiperefreshlayout:swiperefreshlayout:1.1.0`是Android中一个常用的组件,用于实现“下拉刷新”功能。这个组件主要用于在列表(如`RecyclerView`、`ListView`等)或其他可滚动视图上,实现用户通过下拉手势来触发内容刷新操作。1.添加依赖在项目的`build.gradle`文件中添加依赖:dependencies
- Flutter之ListView 嵌套不同的Item
涂文远
Flutterflutterandroid
效果实现代码如下home_page.dartimport'dart:convert';import'dart:ffi';import'package:flutter/material.dart';import'package:flutterwncq/constants/constants.dart'showAppUrls;import'package:flutterwncq/models/inde
- ListView通过不同列的数据实现某一列颜色变化
一个小兵仔
WPF
1、首先定义一个ListView,姓名添加模板,用StackPanel包装TextBox绑定的NAME,背景绑定状态STATUS,实现通过状态的不同,名字显示不同</GridViewColumn&
- WPF ListView 改变某行某列的属性值(背景颜色)
吃饭睡觉摸鱼上网
C#wpf
前言:WPf的listView简单的绑定数据之后,没办法访问内部的行列item属性,思考:怎样才能将listView中的某一行中的某一列进行背景颜色的切换。正常用法:如上代码所示,只需要将listView的itemssoure绑定好特定的数据,就可以进行简单的展示。cs代码如下:ListITEMS=newList();//资源绑定listView1.ItemsSource=ITEMS;其中:需要自
- Qt: QComboBox
大白萝卜不紧张
qtqt
示例1:隐藏某一个下拉选项,并不改变索引序号//QComboBox::view()方法返回的是QListView类型的指针,表示QComboBox中下拉列表的视图部分。QListView*listView=static_cast(ui->combo_box_initial_guess->view());listView->setRowHidden(1,true);//隐藏第一行listView->
- WPF 程序内存优化,主要考虑哪些技术点和业务点
海的那边-
内存优化wpf
在优化WPF程序的内存使用时,通常需要从技术点和业务点两方面进行考虑。以下是主要需要关注的方面:技术点虚拟化(Virtualization)VirtualizingStackPanel:WPF内置的虚拟化功能用于列表控件(如ListBox、ListView、DataGrid),只渲染当前可见的项目。通过设置VirtualizingStackPanel.IsVirtualizing="True"和V
- listview的addHeaderView和addFooterView的几点笔记
_沐风_
androidandroidlistview
转载自https://software.intel.com/zh-cn/blogs/2014/12/15/android-listview-addheaderview-addfooterviewaddHeaderView()方法:主要是向listView的头部添加布局addFooterView()方法:主要是向listView的底部添加布局需要注意的是添加布局的时候应该添加从父容器开始添加,而不能
- Flutter 之 ListView 控件
Goach
ListTileListView控件为我们提供了一个常用的布局ListTile,它的样式固定,使用如下:class_MyHomePageStateextendsState{Listitems=['https://cn.bing.com/th?id=OIP.xq1C2fmnSw5DEoRMC86vJwD6D6&pid=Api&rs=1','https://cn.bing.com/th?id=OIP.
- 学习Android的第十九天
Java'
Android学习android
目录AndroidExpandableListView分组列表ExpandableListView属性ExpandableListView事件ExpandableListView的Adapter范例参考文档AndroidViewFlipper翻转视图ViewFlipper属性ViewFlipper方法为ViewFlipper加入View例子:全屏幕可以滑动的引导页参考文档AndroidExpand
- 【无标题】
一支春夏、几多秋冬
QtDemoqtqmlqtquick表格分页listiew
使用qml编写,实现类似qlistview的多页切换风格,子页中还有表格以及相关toolbar的实现效果图:候补具体实现:配置:QT+=quickCONFIG+=c++11#Thefollowingdefinemakesyourcompileremitwarningsifyouuse#anyQtfeaturethathasbeenmarkeddeprecated(theexactwarnings#
- android中小说信息抓取展示
?。。!
android爬虫小说阅读
1、引言这两天打算把以前弄的一个小说阅读软件的爬虫规则更新一下,然后略微修改后准备上线使用,目前只改了一下搜索界面的规则,勉强能用,加载数据方面还需要优化一下,把这一部分发出来给大家看看,感兴趣的可以直接复制去使用。2、主要代码2.1、主界面布局2.2、ListView布局2.3、activity界面代码packagexyz.dritrtj.read.ui;importandroid.annota
- flutter列表长度不够,如何下拉刷新
为谁点墨成痴
在flutter开发中你是否遇到过这样的问题,当你使用了RefreshIndicator这个刷新控件时,列表的长度没有填满屏幕,所以无法下拉刷新,这是因为listview有一个参数physics,ListView不满的时候默认的physics会把shouldAcceptUserOffset设置为false所以你无法滑动这时如果我们需要让列表滑动,只需要将listview的physics设置为Alw
- Android ScrollView嵌套ListView显示不全问题
杰奎琳子
AndroidScrollView嵌套ListView显示不全问题未嵌套ScrollView的ListView显示正常显示全一旦嵌套了ScrollView只显示了一行item的高度,显示不全通过查看源码发现因为ScrollView和ListView的heightMeasureSpec都是MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED@OverrideprotectedvoidonMeasure(i
- 学习Android的第十五天
世俗ˊ
Android学习android
目录AndroidAdapter适配器MVC模式AdapterArrayAdapter泛型ArrayAdapter构造函数的第二个参数范例SimpleAdapter适配器范例SimpleCursorAdapter适配器范例参考文档AndroidAdapter适配器Android中的Adapter(适配器)是用于在UI组件(如ListView、RecyclerView)和数据之间建立连接的桥梁。它负
- ListView和RecycleView使用
浪矢咨询者
ListView定义list中基本项的布局方式定义list中基本项对应的类publicclassFruit{privateStringname;publicFruit(Stringname){this.name=name;}publicStringgetName(){returnname;}publicvoidsetName(Stringname){this.name=name;}}在需要添加li
- 学习Android的第十六天
世俗ˊ
Android学习android
目录Android自定义AdapterAdapter接口SpinnerAdapterListAdapterBaseAdapter自定义BaseAdapter参考文档AndroidListView列表控件ListView的属性和方法表头表尾分割线的设置列表从底部开始显示android:stackFromBottom设置点击颜色cacheColorHint隐藏滑动条Android自定义Adapter在
- Android资源文件命名与使用
丁功春
来源:阿里巴巴Android开发手册1.layout文件的命名方式Activity、Fragment、Dialog、include、的layout以module_activity开头ListView、RecyclerView、GridView的itemlayout以module_list/recycler/grid_item开头2.drawable的资源名称以小写单词+下划线的方式命名,根据分辨率
- Flutter - Listview
yyggzc521
什么是基于Sliver的延迟构建模型呢?通常可滚动组件的子组件可能会非常多、占用的总高度也会非常大;如果一次性将子组件全部构建出将会非常浪费资源!为此,Flutter中提出一个Sliver(中文为“薄片”的意思)概念,如果一个可滚动组件支持Sliver模型,那么该滚动可以将子组件分成好多个“薄片”(Sliver),只有当Sliver出现在视图中时才会去构建它,这种模型也称为“基于Sliver的延迟
- Android studio 3.1 新设计和新工具(1)
zidea
图在Androidstudio这个版本中提供支持样本数据的功能,这种功能即实用️美观。尤其是对于listView和reyclerview的开发有很大帮助。大家知道一般app都少不了对recyclerview和listview的应用。在正式开始之前,我们先看一些其他的新特性图中列出了所有工具的新特性我们在这里我在这里只简单的介绍一个新的工具如果大家感兴趣的话,可以去官方网站查看API来了解每个特性的
- Listview 局部item刷新的机制
洺优
对于一个有限性列表,最长不大于10,做flutter的同事选择了逐个控件生成,自行构建list的方式来实现。I/flutter(29896):************callApicomplete:2019-04-0815:26:58.294069I/flutter(29896):************ipsbuildView:2019-04-0815:26:58.605058I/flutter
- ListView的setOnItemClickListener失效解决方案
世道无情
1.概述这篇文章主要记录下自己在项目中的:点击ListView的setOnItemClickListener失效问题。有时候listview的adapter中包含很多控件,像Button、Checkbox、ImageButton等控件,这些子控件会首先获取焦点,导致点击item没有反应,有反应的却是这些子控件,解决方法也比较简单,给adapter的根布局添加属性即可android:descenda
- Flutter 拖拽排序组件 ReorderableListView 如何自定义拖拽触发行为
jiaming_
本文记录实现如何使用ReorderableListView实现列表项的某个子组件点击直接进行拖拽,去除默认的长按整个列表项实现拖拽的默认行为。Flutter官方提供了ReorderableListView组件用于实现列表的拖拽排序功能,但根据移动端实际使用效果发现,拖拽的触发限制在整个item的长按点击拖拽事件上,有时候需要根据产品需求,需要自定义item上的某个button点击后直接拖拽,这时,
- 点击ListView的setOnItemClickListener失效
世道无情
1.概述在开发过程中,显示listview列表数据中时,如果listview的item的控件含有textview、CheckBox、Button、ImageButton等本身带有click等事件的View,这个时候,点击ListView时,setOnItemClickListener可能会失效:2.原因与解决方案1>:原因如下:此时在item区域中,event(事件)的焦点被内部View抢占了,也
- 关于旗正规则引擎规则中的上传和下载问题
何必如此
文件下载压缩jsp文件上传
文件的上传下载都是数据流的输入输出,大致流程都是一样的。
一、文件打包下载
1.文件写入压缩包
string mainPath="D:\upload\"; 下载路径
string tmpfileName=jar.zip; &n
- 【Spark九十九】Spark Streaming的batch interval时间内的数据流转源码分析
bit1129
Stream
以如下代码为例(SocketInputDStream):
Spark Streaming从Socket读取数据的代码是在SocketReceiver的receive方法中,撇开异常情况不谈(Receiver有重连机制,restart方法,默认情况下在Receiver挂了之后,间隔两秒钟重新建立Socket连接),读取到的数据通过调用store(textRead)方法进行存储。数据
- spark master web ui 端口8080被占用解决方法
daizj
8080端口占用sparkmaster web ui
spark master web ui 默认端口为8080,当系统有其它程序也在使用该接口时,启动master时也不会报错,spark自己会改用其它端口,自动端口号加1,但为了可以控制到指定的端口,我们可以自行设置,修改方法:
1、cd SPARK_HOME/sbin
2、vi start-master.sh
3、定位到下面部分
- oracle_执行计划_谓词信息和数据获取
周凡杨
oracle执行计划
oracle_执行计划_谓词信息和数据获取(上)
一:简要说明
在查看执行计划的信息中,经常会看到两个谓词filter和access,它们的区别是什么,理解了这两个词对我们解读Oracle的执行计划信息会有所帮助。
简单说,执行计划如果显示是access,就表示这个谓词条件的值将会影响数据的访问路径(表还是索引),而filter表示谓词条件的值并不会影响数据访问路径,只起到
- spring中datasource配置
g21121
dataSource
datasource配置有很多种,我介绍的一种是采用c3p0的,它的百科地址是:
http://baike.baidu.com/view/920062.htm
<!-- spring加载资源文件 -->
<bean name="propertiesConfig"
class="org.springframework.b
- web报表工具FineReport使用中遇到的常见报错及解决办法(三)
老A不折腾
finereportFAQ报表软件
这里写点抛砖引玉,希望大家能把自己整理的问题及解决方法晾出来,Mark一下,利人利己。
出现问题先搜一下文档上有没有,再看看度娘有没有,再看看论坛有没有。有报错要看日志。下面简单罗列下常见的问题,大多文档上都有提到的。
1、repeated column width is largerthan paper width:
这个看这段话应该是很好理解的。比如做的模板页面宽度只能放
- mysql 用户管理
墙头上一根草
linuxmysqluser
1.新建用户 //登录MYSQL@>mysql -u root -p@>密码//创建用户mysql> insert into mysql.user(Host,User,Password) values(‘localhost’,'jeecn’,password(‘jeecn’));//刷新系统权限表mysql>flush privileges;这样就创建了一个名为:
- 关于使用Spring导致c3p0数据库死锁问题
aijuans
springSpring 入门Spring 实例Spring3Spring 教程
这个问题我实在是为整个 springsource 的员工蒙羞
如果大家使用 spring 控制事务,使用 Open Session In View 模式,
com.mchange.v2.resourcepool.TimeoutException: A client timed out while waiting to acquire a resource from com.mchange.
- 百度词库联想
annan211
百度
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>RunJS</title&g
- int数据与byte之间的相互转换实现代码
百合不是茶
位移int转bytebyte转int基本数据类型的实现
在BMP文件和文件压缩时需要用到的int与byte转换,现将理解的贴出来;
主要是要理解;位移等概念 http://baihe747.iteye.com/blog/2078029
int转byte;
byte转int;
/**
* 字节转成int,int转成字节
* @author Administrator
*
- 简单模拟实现数据库连接池
bijian1013
javathreadjava多线程简单模拟实现数据库连接池
简单模拟实现数据库连接池
实例1:
package com.bijian.thread;
public class DB {
//private static final int MAX_COUNT = 10;
private static final DB instance = new DB();
private int count = 0;
private i
- 一种基于Weblogic容器的鉴权设计
bijian1013
javaweblogic
服务器对请求的鉴权可以在请求头中加Authorization之类的key,将用户名、密码保存到此key对应的value中,当然对于用户名、密码这种高机密的信息,应该对其进行加砂加密等,最简单的方法如下:
String vuser_id = "weblogic";
String vuse
- 【RPC框架Hessian二】Hessian 对象序列化和反序列化
bit1129
hessian
任何一个对象从一个JVM传输到另一个JVM,都要经过序列化为二进制数据(或者字符串等其他格式,比如JSON),然后在反序列化为Java对象,这最后都是通过二进制的数据在不同的JVM之间传输(一般是通过Socket和二进制的数据传输),本文定义一个比较符合工作中。
1. 定义三个POJO
Person类
package com.tom.hes
- 【Hadoop十四】Hadoop提供的脚本的功能
bit1129
hadoop
1. hadoop-daemon.sh
1.1 启动HDFS
./hadoop-daemon.sh start namenode
./hadoop-daemon.sh start datanode
通过这种逐步启动的方式,比start-all.sh方式少了一个SecondaryNameNode进程,这不影响Hadoop的使用,其实在 Hadoop2.0中,SecondaryNa
- 中国互联网走在“灰度”上
ronin47
管理 灰度
中国互联网走在“灰度”上(转)
文/孕峰
第一次听说灰度这个词,是任正非说新型管理者所需要的素质。第二次听说是来自马化腾。似乎其他人包括马云也用不同的语言说过类似的意思。
灰度这个词所包含的意义和视野是广远的。要理解这个词,可能同样要用“灰度”的心态。灰度的反面,是规规矩矩,清清楚楚,泾渭分明,严谨条理,是决不妥协,不转弯,认死理。黑白分明不是灰度,像彩虹那样
- java-51-输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字。
bylijinnan
java
public class PrintMatrixClockwisely {
/**
* Q51.输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字。
例如:如果输入如下矩阵:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9
- mongoDB 用户管理
开窍的石头
mongoDB用户管理
1:添加用户
第一次设置用户需要进入admin数据库下设置超级用户(use admin)
db.addUsr({user:'useName',pwd:'111111',roles:[readWrite,dbAdmin]});
第一个参数用户的名字
第二个参数
- [游戏与生活]玩暗黑破坏神3的一些问题
comsci
生活
暗黑破坏神3是有史以来最让人激动的游戏。。。。但是有几个问题需要我们注意
玩这个游戏的时间,每天不要超过一个小时,且每次玩游戏最好在白天
结束游戏之后,最好在太阳下面来晒一下身上的暗黑气息,让自己恢复人的生气
&nb
- java 二维数组如何存入数据库
cuiyadll
java
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using System.IO;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1
{
- 本地事务和全局事务Local Transaction and Global Transaction(JTA)
darrenzhu
javaspringlocalglobaltransaction
Configuring Spring and JTA without full Java EE
http://spring.io/blog/2011/08/15/configuring-spring-and-jta-without-full-java-ee/
Spring doc -Transaction Management
http://docs.spring.io/spri
- Linux命令之alias - 设置命令的别名,让 Linux 命令更简练
dcj3sjt126com
linuxalias
用途说明
设置命令的别名。在linux系统中如果命令太长又不符合用户的习惯,那么我们可以为它指定一个别名。虽然可以为命令建立“链接”解决长文件名的问 题,但对于带命令行参数的命令,链接就无能为力了。而指定别名则可以解决此类所有问题【1】。常用别名来简化ssh登录【见示例三】,使长命令变短,使常 用的长命令行变短,强制执行命令时询问等。
常用参数
格式:alias
格式:ali
- yii2 restful web服务[格式响应]
dcj3sjt126com
PHPyii2
响应格式
当处理一个 RESTful API 请求时, 一个应用程序通常需要如下步骤 来处理响应格式:
确定可能影响响应格式的各种因素, 例如媒介类型, 语言, 版本, 等等。 这个过程也被称为 content negotiation。
资源对象转换为数组, 如在 Resources 部分中所描述的。 通过 [[yii\rest\Serializer]]
- MongoDB索引调优(2)——[十]
eksliang
mongodbMongoDB索引优化
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2178555 一、概述
上一篇文档中也说明了,MongoDB的索引几乎与关系型数据库的索引一模一样,优化关系型数据库的技巧通用适合MongoDB,所有这里只讲MongoDB需要注意的地方 二、索引内嵌文档
可以在嵌套文档的键上建立索引,方式与正常
- 当滑动到顶部和底部时,实现Item的分离效果的ListView
gundumw100
android
拉动ListView,Item之间的间距会变大,释放后恢复原样;
package cn.tangdada.tangbang.widget;
import android.annotation.TargetApi;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import andr
- 程序员用HTML5制作的爱心树表白动画
ini
JavaScriptjqueryWebhtml5css
体验效果:http://keleyi.com/keleyi/phtml/html5/31.htmHTML代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" >
<ti
- 预装windows 8 系统GPT模式的ThinkPad T440改装64位 windows 7旗舰版
kakajw
ThinkPad预装改装windows 7windows 8
该教程具有普遍参考性,特别适用于联想的机器,其他品牌机器的处理过程也大同小异。
该教程是个人多次尝试和总结的结果,实用性强,推荐给需要的人!
缘由
小弟最近入手笔记本ThinkPad T440,但是特别不能习惯笔记本出厂预装的Windows 8系统,而且厂商自作聪明地预装了一堆没用的应用软件,消耗不少的系统资源(本本的内存为4G,系统启动完成时,物理内存占用比
- Nginx学习笔记
mcj8089
nginx
一、安装nginx 1、在nginx官方网站下载一个包,下载地址是:
http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.4.2.tar.gz
2、WinSCP(ftp上传工
- mongodb 聚合查询每天论坛链接点击次数
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境mongodb纵观千象
/* 18 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5596414cbe4d73a327e50274"),
"msgType" : "text",
"sendTime" : ISODate("2015-07-03T08:01:16.000Z"
- java术语(PO/POJO/VO/BO/DAO/DTO)
Luob.
DAOPOJODTOpoVO BO
PO(persistant object) 持久对象
在o/r 映射的时候出现的概念,如果没有o/r映射,就没有这个概念存在了.通常对应数据模型(数据库),本身还有部分业务逻辑的处理.可以看成是与数据库中的表相映射的java对象.最简单的PO就是对应数据库中某个表中的一条记录,多个记录可以用PO的集合.PO中应该不包含任何对数据库的操作.
VO(value object) 值对象
通
- 算法复杂度
Wuaner
Algorithm
Time Complexity & Big-O:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/487258/plain-english-explanation-of-big-o
http://bigocheatsheet.com/
http://www.sitepoint.com/time-complexity-algorithms/