JBPM4.4之HelloWorld示例
一般来说都是按照这样几个步骤来做的
1.新建项目
2.src下新建JBPM4 Process Definition命名为hello,会生成hello.jpdl.xml的文件
3.添加依赖库【eclipse或者MyEclipse中右键build path-->add External Archives然后添加jbpm.jar和lib下的所有jar】
4.添加JPBM必须配置文件,进入D:\jbpm-4.4\examples\src 将该目录下所有配置文件拷贝到项目src下
至此,环境已经配置完毕,下面就是在hello.jpdl.xml进行设计了,具体内容如下
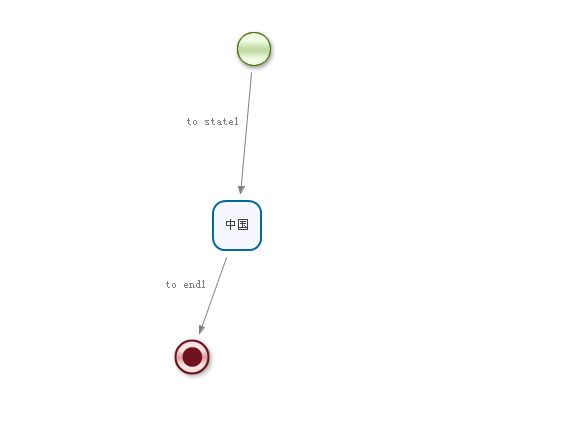
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<process name="helloworld" xmlns="http://jbpm.org/4.4/jpdl">
<start g="230,25,114,64" name="start1">
<transition g="-59,-17" name="to state1" to="中国"/>
</start>
<end g="168,333,80,51" name="end1"/>
<state g="206,194,62,63" name="中国">
<transition g="-47,-17" name="to end1" to="end1"/>
</state>
</process>
上面的文件保存之后会自动在SRC下面生成一张一样效果的图片
下面就要在利用JUNIT来进行第一个示例的各项测试喽
测试之前,首先说下流程定义和流程实例两个概念,当然是现有流程定义,后可以发起新流程了,好好理解下他们的区别
下面先上关于流程定义的测试类
package com.test;
import java.util.List;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.jbpm.api.Configuration;
import org.jbpm.api.ProcessDefinition;
import org.jbpm.api.ProcessEngine;
import org.jbpm.api.RepositoryService;
public class HelloTest extends TestCase {
//----发布流程定义
//第一步:启动流程引擎
ProcessEngine engine;
public HelloTest(){
engine=Configuration.getProcessEngine();
}
//测试发布
public void testDeploy(){
//获取流程服务
RepositoryService service=engine.getRepositoryService();
//把流程定义发布到流程引擎中
String developementId=service.createDeployment()
.addResourceFromClasspath("helloworld.jpdl.xml").deploy();
//----查看流程定义
//发布流程定义信息,查看已发布流程定义列表
List<ProcessDefinition> definitions=service.createProcessDefinitionQuery().list();//执行搜索
for (ProcessDefinition processDefinition : definitions) {
System.out.println(processDefinition.getId());
}
//----删除流程定义,这里用级联删除会比较好
service.deleteDeploymentCascade(developementId);
//查看输出后流程定义的个数
System.out.println(service.createProcessDefinitionQuery().list().size());
}
}
然后就是流程实例测试
package com.test;
import java.util.List;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.jbpm.api.Configuration;
import org.jbpm.api.ExecutionService;
import org.jbpm.api.ProcessEngine;
import org.jbpm.api.ProcessInstance;
public class ProcessInstanceTest extends TestCase {
//----发布流程定义
//第一步:启动流程引擎
ProcessEngine engine;
public ProcessInstanceTest(){
engine=Configuration.getProcessEngine();
}
protected void setUp(){
engine.getRepositoryService().createDeployment()
.addResourceFromClasspath("helloworld.jpdl.xml").deploy();
}
public void testProcessInstance(){
//这个是专门管理流程实例的
ExecutionService executionService=engine.getExecutionService();
//通过流程定义文件的名称当做KEY来获取流程实例;也就是发布新流程
ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("helloworld");
System.out.println(processInstance);
//这里输出流程实例是否结束,针对本实例来说肯定是FALSE,因为本实例中有STATE,所以会在STATE这里处理等待状态,不会结束
//也就是接下来要说的执行等待的流程,除非你调用executionService.signalExecutionById
System.out.println(processInstance.isEnded());
//这个方法将是处理等待转该的流程执行到结束,返回值热仍然是一个流程实例
processInstance=executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId());
System.out.println(processInstance.isEnded());
}
public void testDeleteProcessInstance(){
ExecutionService executionService=engine.getExecutionService();
ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("helloworld");
executionService.deleteProcessInstanceCascade(processInstance.getId());
}
public void testProcessInastanceList(){
ExecutionService executionService=engine.getExecutionService();
ProcessInstance pi=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("helloworld");
ProcessInstance pi1=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("helloworld");
List<ProcessInstance> pis=executionService.createProcessInstanceQuery().list();
for (ProcessInstance processInstance : pis) {
System.out.println(processInstance);
}
}
}