mongodb objectid
存储在mongodb集合中的每个文档(document)都有一个默认的主键_id,这个主键名称是固定的,它可以是mongodb支持的任何数据类型,默认是ObjectId。在关系数据库schema设计中,主键大多是数值型的,比如常用的int和long,并且更通常的,主键的取值由数据库自增获得,这种主键数值的有序性有时也表明了某种逻辑。反观mongodb,它在设计之初就定位于分布式存储系统,所以它原生的不支持自增主键。而现实的世界是,大量应用在可预见的时空里并不需要分布式的mongodb,所以网上就出现了大量的实现mongodb自增主键方法的文章。恩,我之前也干过这种事情。
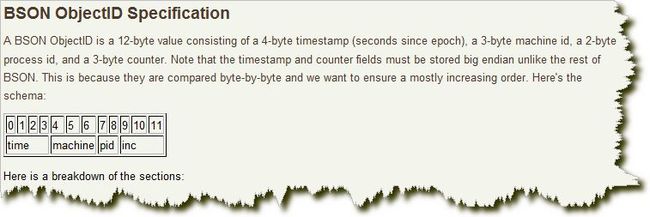
还是看看ObjectId的底细吧。ObjectId被设计成跨机器的分布式环境中全局唯一的类型,长度是12个字节。有朋友可能嘀咕了,这可比int大了两倍,比long也多了一个int,很不经济嘛,但在现在的硬件配置中,多出的这些字节很难有理由成为系统的瓶颈所在,所以尽可能放心使用之。ObjectId的12字节是如此构成的:0-3这4个字节是时间戳(timestamp)、4-6这3个字节是机器码(machine)、7-8两个字节是进程id(pid)、9-11是程序自增id(increment)。可以看下java driver中ObjectId的实现代码:
public class ObjectId implements Comparable<ObjectId> , java.io.Serializable { static final boolean D = false; /** Gets a new object id. * @return the new id */ public static ObjectId get(){ return new ObjectId(); } /** Checks if a string could be an <code>ObjectId</code>. * @return whether the string could be an object id */ public static boolean isValid( String s ){ if ( s == null ) return false; if ( s.length() < 18 ) return false; for ( int i=0; i<s.length(); i++ ){ char c = s.charAt( i ); if ( c >= '0' && c <= '9' ) continue; if ( c >= 'a' && c <= 'f' ) continue; if ( c >= 'A' && c <= 'F' ) continue; return false; } return true; } /** Turn an object into an <code>ObjectId</code>, if possible. * Strings will be converted into <code>ObjectId</code>s, if possible, and <code>ObjectId</code>s will * be cast and returned. Passing in <code>null</code> returns <code>null</code>. * @param o the object to convert * @return an <code>ObjectId</code> if it can be massaged, null otherwise */ public static ObjectId massageToObjectId( Object o ){ if ( o == null ) return null; if ( o instanceof ObjectId ) return (ObjectId)o; if ( o instanceof String ){ String s = o.toString(); if ( isValid( s ) ) return new ObjectId( s ); } return null; } public ObjectId( Date time ){ _time = _flip( (int)(time.getTime() / 1000) ); _machine = _genmachine; synchronized ( _incLock ){ _inc = _nextInc++; } _new = false; } public ObjectId( Date time , int inc ){ this( time , _genmachine , inc ); } public ObjectId( Date time , int machine , int inc ){ _time = _flip( (int)(time.getTime() / 1000) ); _machine = machine; _inc = inc; _new = false; } /** Creates a new instance from a string. * @param s the string to convert * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the string is not a valid id */ public ObjectId( String s ){ this( s , false ); } public ObjectId( String s , boolean babble ){ if ( ! isValid( s ) ) throw new IllegalArgumentException( "invalid ObjectId [" + s + "]" ); if ( babble ) s = babbleToMongod( s ); byte b[] = new byte[12]; for ( int i=0; i<b.length; i++ ){ b[b.length-(i+1)] = (byte)Integer.parseInt( s.substring( i*2 , i*2 + 2) , 16 ); } ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap( b ); _inc = bb.getInt(); _machine = bb.getInt(); _time = bb.getInt(); _new = false; } public ObjectId( byte[] b ){ if ( b.length != 12 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException( "need 12 bytes" ); reverse( b ); ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap( b ); _inc = bb.getInt(); _machine = bb.getInt(); _time = bb.getInt(); } public ObjectId( int time , int machine , int inc ){ _time = time; _machine = machine; _inc = inc; _new = false; } /** Create a new object id. */ public ObjectId(){ _time = _gentime; _machine = _genmachine; synchronized ( _incLock ){ _inc = _nextInc++; } _new = true; } public int hashCode(){ return _inc; } public boolean equals( Object o ){ if ( this == o ) return true; ObjectId other = massageToObjectId( o ); if ( other == null ) return false; return _time == other._time && _machine == other._machine && _inc == other._inc; } public String toStringBabble(){ return babbleToMongod( toStringMongod() ); } public String toStringMongod(){ byte b[] = toByteArray(); StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(24); for ( int i=0; i<b.length; i++ ){ int x = b[i] & 0xFF; String s = Integer.toHexString( x ); if ( s.length() == 1 ) buf.append( "0" ); buf.append( s ); } return buf.toString(); } public byte[] toByteArray(){ byte b[] = new byte[12]; ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap( b ); bb.putInt( _inc ); bb.putInt( _machine ); bb.putInt( _time ); reverse( b ); return b; } static void reverse( byte[] b ){ for ( int i=0; i<b.length/2; i++ ){ byte t = b[i]; b[i] = b[ b.length-(i+1) ]; b[b.length-(i+1)] = t; } } static String _pos( String s , int p ){ return s.substring( p * 2 , ( p * 2 ) + 2 ); } public static String babbleToMongod( String b ){ if ( ! isValid( b ) ) throw new IllegalArgumentException( "invalid object id: " + b ); StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder( 24 ); for ( int i=7; i>=0; i-- ) buf.append( _pos( b , i ) ); for ( int i=11; i>=8; i-- ) buf.append( _pos( b , i ) ); return buf.toString(); } public String toString(){ return toStringMongod(); } public int compareTo( ObjectId id ){ if ( id == null ) return -1; long xx = id.getTime() - getTime(); if ( xx > 0 ) return -1; else if ( xx < 0 ) return 1; int x = id._machine - _machine; if ( x != 0 ) return -x; x = id._inc - _inc; if ( x != 0 ) return -x; return 0; } public int getMachine(){ return _machine; } public long getTime(){ long z = _flip( _time ); return z * 1000; } public int getInc(){ return _inc; } public int _time(){ return _time; } public int _machine(){ return _machine; } public int _inc(){ return _inc; } public boolean isNew(){ return _new; } public void notNew(){ _new = false; } final int _time; final int _machine; final int _inc; boolean _new; static int _flip( int x ){ if ( true ){ byte b[] = new byte[4]; ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap( b ); bb.order( ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN ); bb.putInt( x ); bb.flip(); bb.order( ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN ); return bb.getInt(); } int z = 0; z |= ( x & 0xFF ) << 24; z |= ( x & 0xFF00 ) << 8; z |= ( x & 0xFF00000 ) >> 8; z |= ( x & 0xFF000000 ) >> 24; return z; } private static int _nextInc = (new java.util.Random()).nextInt(); private static final String _incLock = new String( "ObjectId._incLock" ); private static int _gentime = _flip( (int)(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000) ); static final Thread _timeFixer; private static final int _genmachine; static { try { final int machinePiece; { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); Enumeration<NetworkInterface> e = NetworkInterface.getNetworkInterfaces(); while ( e.hasMoreElements() ){ NetworkInterface ni = e.nextElement(); sb.append( ni.toString() ); } machinePiece = sb.toString().hashCode() << 16; if ( D ) System.out.println( "machine piece post: " + Integer.toHexString( machinePiece ) ); } final int processPiece = java.lang.management.ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getName().hashCode() & 0xFFFF; if ( D ) System.out.println( "process piece: " + Integer.toHexString( processPiece ) ); _genmachine = machinePiece | processPiece; if ( D ) System.out.println( "machine : " + Integer.toHexString( _genmachine ) ); } catch ( java.io.IOException ioe ){ throw new RuntimeException( ioe ); } _timeFixer = new Thread("ObjectId-TimeFixer"){ public void run(){ while ( true ){ try { Thread.sleep( 499 ); } catch ( Exception e ){} _gentime = _flip( (int)(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000) ); } } }; _timeFixer.setDaemon( true ); _timeFixer.start(); } }
对于ObjectId的组成,有一些值得说道的地方:
1、因为ObjectId以时间戳打头,所以它是近似有序的,使得_id的索引插入效率相比普通索引高很多。
2、ObjectId的前9个字节(timestamp+machine+pid)可以保证不同进程生成的ObjectId不会重复,而后3个字节increment又可以保证同一进程内生成的ObjectId不会重复,所以无需怀疑ObjectId的全局唯一性。
3、ObjectId存储是12个字节,但如果应用有需要以可读的方式表现它,就需要将它转成字符串,这需要24字节(每字节转成2字节的16进制表示),这个长度的字符串看起来就有些不让人舒服了,如果是追踪某个_id引发的bug,就需要配上copy+paste的杀招。
4、初涉ObjectId的朋友很容易犯的两个错误:1)是查询时直接使用类似db.collection.find({_id:”xx”})式的代码,结果怎么也查不到明明存在的文档,而正确的写法应该是:db.collection.find({_id:new ObjectId(“xx”)})。2)是集合间有外键关联时,也需要将外键置为ObjectId类型,而不要直接使用上24字节的string。在写与mongodb打交道的CRUD代码时,需要多留意ObjectId和string的转换代码。
5、ObjectId的产生既可以在应用程序端也可以在mongodb端,各种语言的driver都提供了程序端生成ObjectId的方法,不过大多数人徒省事直接交给mongodb做了。但从mongodb的设计哲学来说,ObjectId更应该由客户端生成,毕竟应用层比存储层更容易扩展,并会提高mongodb的插入速度。