Android TabActivity Essentials
以Tab的形式显示,在各个平台上都很常见,这个UI 元素的应用很广泛。
TabActivity的用法示例在APIDemo里面都能找到。这里不介绍了,本文主要讲下它的原理和扩展
TabActivity是个比较有意思的东西。TabActivity是继承自ActivityGroup的,Android里面很少涉及ActivityGroup的介绍,借此也可以研究下ActivityGroup.
1. 首先看TabActivity分上下两个部分

下面看Code,可以看到
TabActivity有几个关键的东西
TabActivity -- ActivityGroup
TabHost -- FrameLayout
TabWidget -- LinearLayout
TabActivity ---- TabHost ---- TabWidget+mTabContent(FrameLayout)
TabActivity里面有一个TabHost
TabHost里面有TabWidget+mTabContent
TabWidget就是上面的部分
mTabContent就是下面的部分
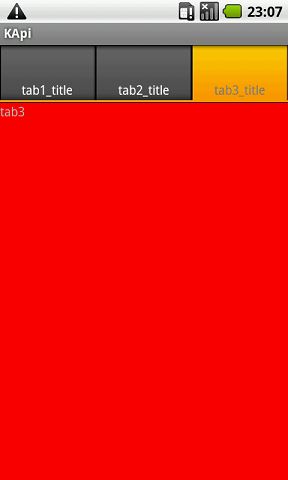
2. 先举一个简单的例子,就是显示上面那幅图的例子。每一个Tab就是一个Text
发现TabHost要讲的东西实在太多。
重点讲下TabWidget和mTabContent吧。
大家都知道TabActivity的显示很灵活。
上面的TabWidget可以是1. String 2. String + Icon 3. 自定义的View
下面的mTabContent可以是1.用resId指定的View(如示例) 2.用TabContentFactory动态生成的View 3.还可以显示指定intent叫起的Activity
它是为什么这么灵活呢?
就是因为在TabHost里用Strategy Pattern-策略模式来实现这两个东西的显示。
如下
这里还要提到另外一个东西。
private List<TabSpec> mTabSpecs = new ArrayList<TabSpec>(2);
存着TabSpec就是在addTab()时传入的东西,一个就是一个Tab。
TabSpec里面就有上面的两个Strategy.
在显示的时候,就会从这个List中取TabSpec,然后根据不同的策略来显示内容。
留下一个小问题。
有没有注意当我们去按当前选中的Tab的时候,TabWidget下面的一个长条也会跟选中的Tab一起高亮,好像它们是连在一起的(如下图),这是怎么回事呢?
TabActivity的用法示例在APIDemo里面都能找到。这里不介绍了,本文主要讲下它的原理和扩展
TabActivity是个比较有意思的东西。TabActivity是继承自ActivityGroup的,Android里面很少涉及ActivityGroup的介绍,借此也可以研究下ActivityGroup.
1. 首先看TabActivity分上下两个部分

下面看Code,可以看到
TabActivity有几个关键的东西
TabActivity -- ActivityGroup
TabHost -- FrameLayout
TabWidget -- LinearLayout
TabActivity ---- TabHost ---- TabWidget+mTabContent(FrameLayout)
TabActivity里面有一个TabHost
TabHost里面有TabWidget+mTabContent
TabWidget就是上面的部分
mTabContent就是下面的部分
2. 先举一个简单的例子,就是显示上面那幅图的例子。每一个Tab就是一个Text
public class Tabs1 extends TabActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TabHost mTabHost = getTabHost();
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabs1,
mTabHost.getTabContentView(), true);
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("tab1_tag").setIndicator(
"tab1_title").setContent(R.id.tab1)
);
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("tab2_tag").setIndicator(
"tab2_title").setContent(R.id.tab2)
);
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("tab3_tag").setIndicator(
"tab3_title").setContent(R.id.tab3)
);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tab1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_1" android:background="@color/solid_blue" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tab2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_2" android:background="@color/solid_green" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tab3" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_3" android:background="@color/solid_red" /> </FrameLayout>
发现TabHost要讲的东西实在太多。
重点讲下TabWidget和mTabContent吧。
大家都知道TabActivity的显示很灵活。
上面的TabWidget可以是1. String 2. String + Icon 3. 自定义的View
下面的mTabContent可以是1.用resId指定的View(如示例) 2.用TabContentFactory动态生成的View 3.还可以显示指定intent叫起的Activity
它是为什么这么灵活呢?
就是因为在TabHost里用Strategy Pattern-策略模式来实现这两个东西的显示。
如下
/**
* Specifies what you do to create a tab indicator.
*/
private static interface IndicatorStrategy {
/**
* Return the view for the indicator.
*/
View createIndicatorView();
}
/**
* Specifies what you do to manage the tab content.
*/
private static interface ContentStrategy {
/**
* Return the content view. The view should may be cached locally.
*/
View getContentView();
/**
* Perhaps do something when the tab associated with this content has
* been closed (i.e make it invisible, or remove it).
*/
void tabClosed();
}
这里还要提到另外一个东西。
private List<TabSpec> mTabSpecs = new ArrayList<TabSpec>(2);
存着TabSpec就是在addTab()时传入的东西,一个就是一个Tab。
TabSpec里面就有上面的两个Strategy.
在显示的时候,就会从这个List中取TabSpec,然后根据不同的策略来显示内容。
留下一个小问题。
有没有注意当我们去按当前选中的Tab的时候,TabWidget下面的一个长条也会跟选中的Tab一起高亮,好像它们是连在一起的(如下图),这是怎么回事呢?
