Util.concurrent工具包概述
Util.concurrent工具包概述
Doug Lea
State University of New York at Oswego
http://gee.cs.oswego.edu
翻译:
Cocia Lin([email protected] )
Huihoo.org
原文
http://gee.cs.oswego.edu/dl/cpjslides/util.pdf
要点
-- 目标和结构
-- 主要的接口和实现
Sync : 获得 / 释放 (acquire/release) 协议
Channel : 放置 / 取走 (put/take) 协议
Executor : 执行 Runnable 任务
-- 每一个部分都有一些关联的接口和支持类
-- 简单的涉及其他的类和特性
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
目标
-- 一些简单的接口
- 但是覆盖大部分程序员需要小心处理代码的问题
-- 高质量实现
- 正确的,保守的,有效率的,可移植的
-- 可能作为将来标准的基础
- 获取经验和收集反馈信息

Sync
-- acquire/release 协议的主要接口
- 用来定制锁,资源管理,其他的同步用途
- 高层抽象接口
- 没有区分不同的加锁用法
-- 实现
- Mutex, ReentrantLock, Latch, CountDown,Semaphore, WaiterPreferenceSemaphore, FIFOSemaphore, PrioritySemaphore
<!-- [if !supportLists]-->n <!-- [endif]-->还有,有几个简单的实现,例如 ObservableSync, LayeredSync
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
独占锁
try {
lock.acquire();
try {
action();
}
finally {
lock.release();
}
}
catch (InterruptedException ie) { ... }
-- Java 同步块不适用的时候使用它
- 超时,回退 (back-off)
- 确保可中断
- 大量迅速锁定
- 创建 Posix 风格应用 (condvar)
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
独占例子
class ParticleUsingMutex {
int x; int y;
final Random rng = new Random();
final Mutex mutex = new Mutex();
public void move() {
try {
mutex.acquire();
try { x += rng.nextInt(2)-1; y += rng.nextInt(2)-1; }
finally { mutex.release(); }
}
catch (InterruptedException ie) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); }
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
int lx, ly;
try {
mutex.acquire();
try { lx = x; ly = y; }
finally { mutex.release(); }
}
catch (InterruptedException ie) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); return; }
g.drawRect(lx, ly, 10, 10);
}
}
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
回退 (Backoff) 例子
class CellUsingBackoff {
private long val;
private final Mutex mutex = new Mutex();
void swapVal(CellUsingBackoff other)
throws InterruptedException {
if (this == other) return; // alias check
for (;;) {
mutex.acquire();
try {
I f ( other.mutex.attempt(0) ) {
try {
long t = val;
val = other.val;
other.val = t;
return;
}
finally { other.mutex.release(); }
}
}
finally { mutex.release(); };
Thread.sleep(100); // heuristic retry interval
}
}
}
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
读写锁
interface ReadWriteLock {
Sync readLock();
Sync writeLock();
}
-- 管理一对锁
- 和普通的锁一样的使用习惯
-- 对集合类很有用
- 半自动的方式实现 SyncSet, SyncMap, ...
-- 实现者使用不同的锁策略
- WriterPreference, ReentrantWriterPreference,
ReaderPreference, FIFO
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
ReadWriteLock 例子
-- 示范在读写锁中执行任何 Runnable 的包装类
class WithRWLock {
final ReadWriteLock rw;
public WithRWLock(ReadWriteLock l) { rw = l; }
public void performRead(Runnable readCommand)
throws InterruptedException {
rw.readLock().acquire();
try { readCommand.run(); }
finally { rw.readlock().release(); }
}
public void performWrite(...) // similar
}
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
闭锁 (Latch)
-- 闭锁是开始时设置为 false, 但一旦被设置为 true ,他将永远保持 true 状态
- 初始化标志
- 流结束定位
- 线程中断
- 事件出发指示器
-- CountDown 和他有点类似,不同的是, CountDown 需要一定数量的触发设置,而不是一次
-- 非常简单,但是广泛使用的类
- 替换容易犯错的开发代码
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
Latch Example 闭锁例子
class Worker implements Runnable {
Latch startSignal;
Worker(Latch l) { startSignal = l; }
public void run() {
startSignal.acquire();
// ... doWork();
}
}
class Driver { // ...
void main() {
Latch ss = new Latch();
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) // make threads
new Thread(new Worker( ss )).start();
doSomethingElse(); // don’t let run yet
ss.release(); // now let all threads proceed
}
}
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
信号 (Semaphores)
-- 服务于数量有限的占有者
- 使用许可数量构造对象 ( 通常是 0)
- 如果需要一个许可才能获取,等待,然后取走一个许可
- 释放的时候将许可添加回来
-- 但是真正的许可并没有转移 (But no actual permits change hands.)
- 信号量仅仅保留当前的计数值
-- 应用程序
- 锁:一个信号量可以被用作互斥体 (mutex)
- 一个独立的等待缓存或者资源控制的操作
- 设计系统是想忽略底层的系统信号
-- (phores ‘remember’ past signals) 记住已经消失的信号量
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
信号量例子
class Pool {
ArrayList items = new ArrayList();
HashSet busy = new HashSet();
final Semaphore available;
public Pool(int n) {
available = new Semaphore(n);
// ... somehow initialize n items ...;
}
public Object getItem() throws InterruptedException {
available.acquire();
return doGet();
}
public void returnItem(Object x) {
if (doReturn(x)) available.release();
}
synchronized Object doGet() {
Object x = items.remove(items.size()-1);
busy.add(x); // put in set to check returns
return x;
}
synchronized boolean doReturn(Object x) {
return busy.remove(x); // true if was present
}
}
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
屏障 (Barrier)
-- 多部分同步接口
- 每一部分都必须等待其他的分不撞倒屏障
-- CyclicBarrier 类
- CountDown 的一个可以重新设置的版本
- 对于反复划分算法很有用 (iterative partitioning algorithms)
-- Rendezvous 类
- 一个每部分都能够和其他部分交换信息的屏障
- 行为类似同时的在一个同步通道上 put 和 take
- 对于资源交换协议很有用 (resource-exchange protocols)
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
通道 (Channel)
-- 为缓冲,队列等服务的主接口
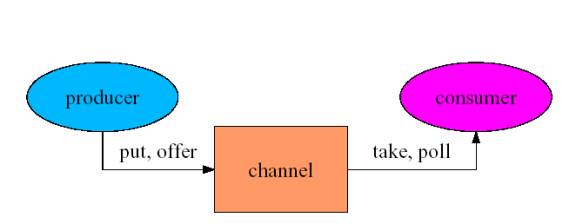
-- 具体实现
- LinkedQueue, BoundedLinkedQueue,BoundedBuffer, BoundedPriorityQueue,SynchronousChannel, Slot
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
通道属性
-- 被定义为 Puttable 和 Takable 的子接口
- 允许安装生产者 / 消费者模式执行
-- 支持可超时的操作 offer 和 poll
- 当超时值是 0 时,可能会被阻塞
- 所有的方法能够抛出 InterruptedException 异常
-- 没有接口需要 size 方法
- 但是一些实现定义了这个方法
- BoundedChannel 有 capacity 方法
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
通道例子
class Service { // ...
final Channel msgQ = new LinkedQueue();
public void serve() throws InterruptedException {
String status = doService();
msgQ.put(status);
}
public Service() { // start background thread
Runnable logger = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
for(;;)
System.out.println( msqQ.take() );
}
catch(InterruptedException ie) {} }
};
new Thread(logger).start();
}
}
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
<!-- [if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!-- [endif]-->
运行器 (Executor)
-- 类似线程的类的主接口 font-size: 18pt; fon