用Maven构建Java Web开发环境(Jetty容器)之二
本文接上一篇
第一部分继续来介绍。
目前为止我们还是手工命令行方式执行程序的,没有和IDE结合,其实Maven天生就对Eclipse做了集成,我们使用mvn eclipse:eclipse就得到了一个Eclipse的项目结构,在Eclipse中使用import功能就能直接导入到IDE中了。我们来看一下这个过程:
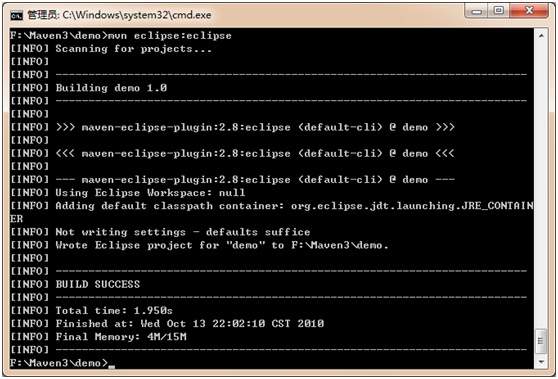
此时的demo就是Eclipse项目格式的了,出现了.project和.classpath文件。我们在Eclipse中引入这个项目,此时的Eclipse没有安装Maven插件,不能自动运行Maven命令,我们来安装Maven的Eclipse插件M2E。
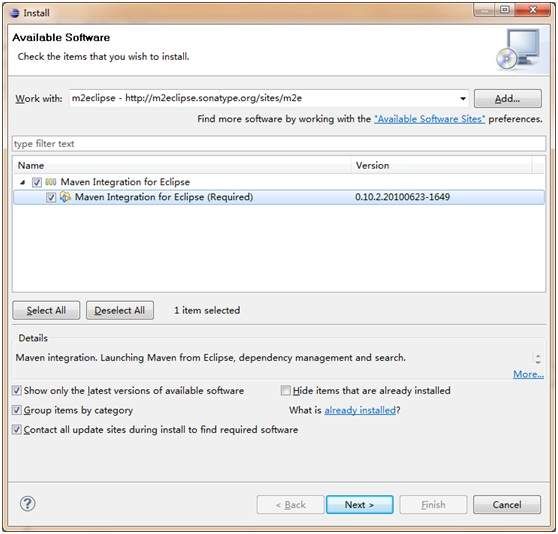
在Eclipse的Install New Software中直接选择安装即可,非常简单。下面我们来创建Web项目并导入Eclipse中,在Jetty容器中运行程序。首先执行mvn archetype:generate命令创建。
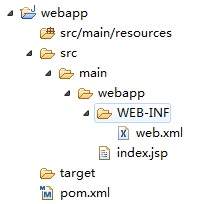
可以看到,刚创建的web项目结构包含了resources目录,而没有java代码目录,我们需要手工创建,在Eclipse中创建source folder,路径为src/main/java/src,现在我们得到如下一个项目结构,新建一个Servlet用于测试。
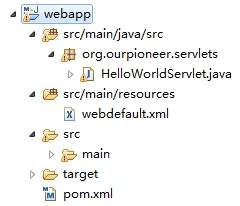
此时,项目中没有Servlet的依赖,需要添加,我们使用m2eclipse插件来直接添加依赖,如下所示:
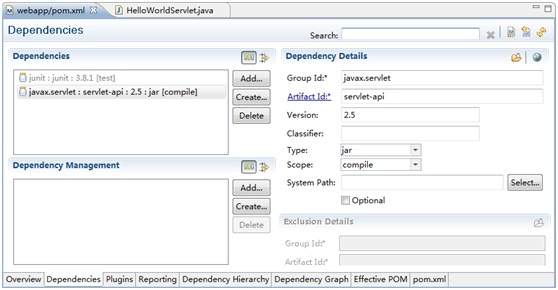
相应的XML为:
下面就可以编写Servlet了,很简单,就输出HelloWorld吧。
然后不能忘了在web.xml中配置这个Servlet,这里是Servlet 2.5的规范,不是Servlet 3,不能用注解。这也很简单。
程序都有了,剩下就是运行了,Maven既然天生和Jetty是一对儿,这里我们就使用Jetty吧,在Maven中配置Jetty,首先是webdefault.xml要准备好,它是配置Jetty的,这个可以从Jetty的包中找到,并复制到resources下,这里多说一点,默认Jetty运行时是锁定JS/CSS等静态文件的,如果想在Jetty运行时也能修改它们,要在webdefault.xml中修改如下设置:
Jetty也准备了,运行命令是jetty:run,这要在Maven中设置,那么需要在pom.xml中加入Jetty的插件的设置信息。这里直接贴出其整体构建信息。
此时,更新一下Maven依赖,它们就都自动下载到本地了,到这个过程结束,我们就可以在Eclipse中配置Debug运行了。配置很简单,如下。
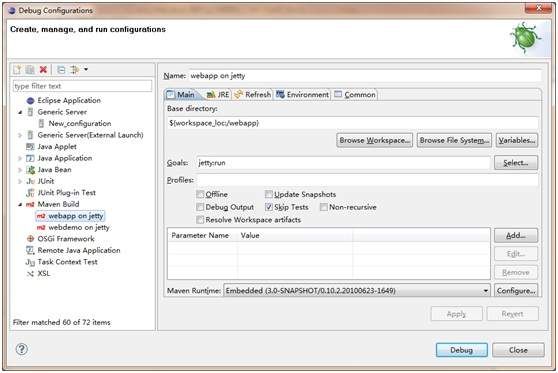
这是Debug模式运行,Run模式下是一样的,用Debug模式可以在Eclipse中断点运行程序,非常便于调试。下面我们就让它跑起来吧。运行命令是jetty:run,Base directory配置是:${workspace_loc:/应用名},启动调试,看到如下信息,Jetty就成功启动了。
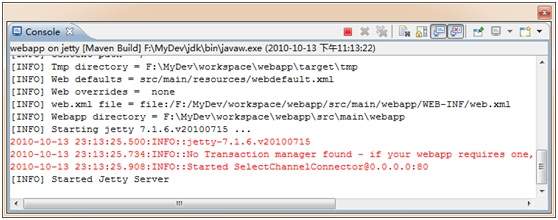
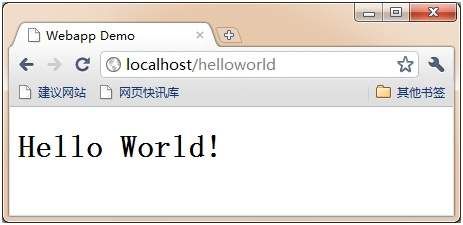
这里我们使用了80端口,配置方式在pom.xml中,上面的代码已经体现了。在浏览器中访问地址如下:http://localhost/helloworld,之后,我们就看到了效果。
本文系作者本人的实践和探索,希望对使用者有用,欢迎交流。
(全篇完)
目前为止我们还是手工命令行方式执行程序的,没有和IDE结合,其实Maven天生就对Eclipse做了集成,我们使用mvn eclipse:eclipse就得到了一个Eclipse的项目结构,在Eclipse中使用import功能就能直接导入到IDE中了。我们来看一下这个过程:

此时的demo就是Eclipse项目格式的了,出现了.project和.classpath文件。我们在Eclipse中引入这个项目,此时的Eclipse没有安装Maven插件,不能自动运行Maven命令,我们来安装Maven的Eclipse插件M2E。

在Eclipse的Install New Software中直接选择安装即可,非常简单。下面我们来创建Web项目并导入Eclipse中,在Jetty容器中运行程序。首先执行mvn archetype:generate命令创建。

可以看到,刚创建的web项目结构包含了resources目录,而没有java代码目录,我们需要手工创建,在Eclipse中创建source folder,路径为src/main/java/src,现在我们得到如下一个项目结构,新建一个Servlet用于测试。

此时,项目中没有Servlet的依赖,需要添加,我们使用m2eclipse插件来直接添加依赖,如下所示:

相应的XML为:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<type>jar</type>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
下面就可以编写Servlet了,很简单,就输出HelloWorld吧。
package org.ourpioneer.servlets;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.process(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.process(request, response);
}
private void process(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String title="Webapp Demo";
out.println("<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN\" \"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd\">");
out.println("<html xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml\">");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<meta http-equiv=\"Content-Type\" content=\"text/html;charset=utf-8\" />");
out.println("<title>" + title + "</title>");
out.println("<body>");
out.println("<h1>Hello World!</h1>");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
}
}
然后不能忘了在web.xml中配置这个Servlet,这里是Servlet 2.5的规范,不是Servlet 3,不能用注解。这也很简单。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"> <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>helloworld</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.ourpioneer.servlets.HelloWorldServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>helloworld</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/helloworld</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
程序都有了,剩下就是运行了,Maven既然天生和Jetty是一对儿,这里我们就使用Jetty吧,在Maven中配置Jetty,首先是webdefault.xml要准备好,它是配置Jetty的,这个可以从Jetty的包中找到,并复制到resources下,这里多说一点,默认Jetty运行时是锁定JS/CSS等静态文件的,如果想在Jetty运行时也能修改它们,要在webdefault.xml中修改如下设置:
<init-param>
<param-name>useFileMappedBuffer</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
Jetty也准备了,运行命令是jetty:run,这要在Maven中设置,那么需要在pom.xml中加入Jetty的插件的设置信息。这里直接贴出其整体构建信息。
<build> <finalName>webapp</finalName> <sourceDirectory>src/main/java/src</sourceDirectory> <testSourceDirectory>src/test</testSourceDirectory> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.0.2</version> <configuration> <source>1.6</source> <target>1.6</target> <encoding>utf-8</encoding> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId> <artifactId>jetty-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>7.1.6.v20100715</version> <configuration> <stopKey>stop</stopKey> <stopPort>5599</stopPort> <webAppConfig> <contextPath>/</contextPath> <defaultsDescriptor>src/main/resources/webdefault.xml</defaultsDescriptor> </webAppConfig> <scanIntervalSeconds>0</scanIntervalSeconds> <connectors> <connector implementation="org.eclipse.jetty.server.nio.SelectChannelConnector"> <port>80</port> <maxIdleTime>60000</maxIdleTime> </connector> </connectors> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.7</version> <configuration> <addVersionToProjectName>false</addVersionToProjectName> <useProjectReferences>false</useProjectReferences> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> <wtpmanifest>false</wtpmanifest> <wtpapplicationxml>true</wtpapplicationxml> <wtpversion>1.5</wtpversion> <additionalBuildcommands> <buildcommand>org.eclipse.jdt.core.javabuilder</buildcommand> <buildcommand>org.eclipse.wst.common.project.facet.core.builder</buildcommand> <buildcommand>org.eclipse.wst.validation.validationbuilder</buildcommand> </additionalBuildcommands> <additionalProjectnatures> <nature>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springnature</nature> <nature>org.maven.ide.eclipse.maven2Nature</nature> <nature>org.eclipse.wst.common.project.facet.core.nature</nature> <nature>org.eclipse.jdt.core.javanature</nature> <nature>org.eclipse.wst.common.modulecore.ModuleCoreNature</nature> </additionalProjectnatures> <classpathContainers> <classpathContainer>org.eclipse.jdt.launching.JRE_CONTAINER</classpathContainer> </classpathContainers> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.1-beta-1</version> <configuration> <warName>webapp</warName> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
此时,更新一下Maven依赖,它们就都自动下载到本地了,到这个过程结束,我们就可以在Eclipse中配置Debug运行了。配置很简单,如下。

这是Debug模式运行,Run模式下是一样的,用Debug模式可以在Eclipse中断点运行程序,非常便于调试。下面我们就让它跑起来吧。运行命令是jetty:run,Base directory配置是:${workspace_loc:/应用名},启动调试,看到如下信息,Jetty就成功启动了。

这里我们使用了80端口,配置方式在pom.xml中,上面的代码已经体现了。在浏览器中访问地址如下:http://localhost/helloworld,之后,我们就看到了效果。

本文系作者本人的实践和探索,希望对使用者有用,欢迎交流。
(全篇完)