SpEL基础
一、概述
1、概述
Spring表达式语言全称为“Spring Expression Language”,缩写为“SpEL”,类似于Struts2x中使用的OGNL表达式语言,能在运行时构建复杂表达式、存取对象图属性、对象方法调用等等,并且能与Spring功能完美整合,如能用来配置Bean定义。
表达式语言给静态Java语言增加了动态功能。
SpEL是单独模块,只依赖于core模块,不依赖于其他模块,可以单独使用。
2、能干什么
表达式语言一般是用最简单的形式完成最主要的工作,减少我们的工作量。
SpEL支持如下表达式:
1)、基本表达式:字面量表达式、关系,逻辑与算数运算表达式、字符串连接及截取表达式、三目运算及Elivis表达式、正则表达式、括号优先级表达式;
2)、类相关表达式:类类型表达式、类实例化、instanceof表达式、变量定义及引用、赋值表达式、自定义函数、对象属性存取及安全导航表达式、对象方法调用、Bean引用;
3)、集合相关表达式:内联List、内联数组、集合,字典访问、列表,字典,数组修改、集合投影、集合选择;不支持多维内联数组初始化;不支持内联字典定义;
4)、其他表达式:模板表达式。
注:SpEL表达式中的关键字是不区分大小写的。
二、SpEL基础
1、HelloWorld
首先准备支持SpEL的Jar包:“org.springframework.expression-3.0.5.RELEASE.jar”将其添加到类路径中。
SpEL在求表达式值时一般分为四步,其中第三步可选:首先构造一个解析器,其次解析器解析字符串表达式,在此构造上下文,最后根据上下文得到表达式运算后的值。
package com.iflytek.spel; import junit.framework.Assert; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext; import org.springframework.expression.Expression; import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser; import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext; /** * @author xudongwang * * @create 2013-9-3 下午11:02:46 * * @email:[email protected] * * @description SpEL测试 * */ public class SpELTest { @Test public void helloWorld() { ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("('Hello' + ' World').concat(#end)"); EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(); context.setVariable("end", "!"); Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", expression.getValue(context)); } }
接下来让我们分析下代码:
1)创建解析器:SpEL使用ExpressionParser接口表示解析器,提供SpelExpressionParser默认实现;
2)解析表达式:使用ExpressionParser的parseExpression来解析相应的表达式为Expression对象。
3)构造上下文:准备比如变量定义等等表达式需要的上下文数据。
4)求值:通过Expression接口的getValue方法根据上下文获得表达式值。
2、SpEL原理及接口
SpEL提供简单的接口从而简化用户使用,在介绍原理前让我们学习下几个概念:
1)、表达式:表达式是表达式语言的核心,所以表达式语言都是围绕表达式进行的,从我们角度来看是“干什么”;
2)、解析器:用于将字符串表达式解析为表达式对象,从我们角度来看是“谁来干”;
3)、上下文:表达式对象执行的环境,该环境可能定义变量、定义自定义函数、提供类型转换等等,从我们角度看是“在哪干”;
4)、根对象及活动上下文对象:根对象是默认的活动上下文对象,活动上下文对象表示了当前表达式操作的对象,从我们角度看是“对谁干”。
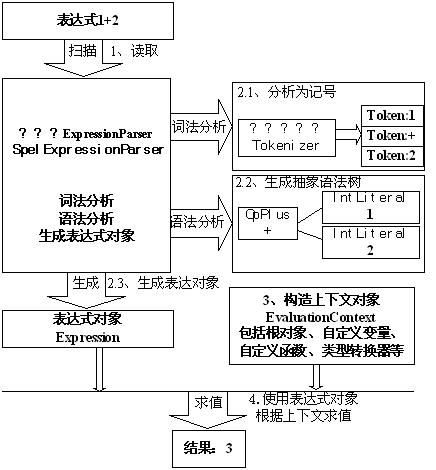
理解了这些概念后,让我们看下SpEL如何工作的呢,如图所示:
工作原理
1)、首先定义表达式:“1+2”;
2)、定义解析器ExpressionParser实现,SpEL提供默认实现SpelExpressionParser;
2.1)、SpelExpressionParser解析器内部使用Tokenizer类进行词法分析,即把字符串流分析为记号流,记号在SpEL使用Token类来表示;
2.2)、有了记号流后,解析器便可根据记号流生成内部抽象语法树;在SpEL中语法树节点由SpelNode接口实现代表:如OpPlus表示加操作节点、IntLiteral表示int型字面量节点;使用SpelNodel实现组成了抽象语法树;
2.3)、对外提供Expression接口来简化表示抽象语法树,从而隐藏内部实现细节,并提供getValue简单方法用于获取表达式值;SpEL提供默认实现为SpelExpression;
3)、定义表达式上下文对象(可选),SpEL使用EvaluationContext接口表示上下文对象,用于设置根对象、自定义变量、自定义函数、类型转换器等,SpEL提供默认实现StandardEvaluationContext;
4)、使用表达式对象根据上下文对象(可选)求值(调用表达式对象的getValue方法)获得结果。
接下来让我们看下SpEL的主要接口吧:
1)、ExpressionParser接口:
表示解析器,默认实现是org.springframework.expression.spel.standard包中的SpelExpressionParser类,使用parseExpression方法将字符串表达式转换为Expression对象,对于ParserContext接口用于定义字符串表达式是不是模板,及模板开始与结束字符:
public interface ExpressionParser {
Expression parseExpression(String expressionString);
Expression parseExpression(String expressionString, ParserContext context);
}
Demo:
@Test
public void testParserContext() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
ParserContext parserContext = new ParserContext() {
@Override
public boolean isTemplate() {
return true;
}
@Override
public String getExpressionPrefix() {
return "#{";
}
@Override
public String getExpressionSuffix() {
return "}";
}
};
String template = "#{'Hello '}#{'World!'}";
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(template, parserContext);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", expression.getValue());
}
在此我们演示的是使用ParserContext的情况,此处定义了ParserContext实现:定义表达式是模块,表达式前缀为“#{”,后缀为“}”;使用parseExpression解析时传入的模板必须以“#{”开头,以“}”结尾,如"#{'Hello '}#{'World!'}"。
默认传入的字符串表达式不是模板形式,如之前演示的Hello World。
2)EvaluationContext接口:
表示上下文环境,默认实现是org.springframework.expression.spel.support包中的StandardEvaluationContext类,使用setRootObject方法来设置根对象,使用setVariable方法来注册自定义变量,使用registerFunction来注册自定义函数等等。
3)Expression接口:
表示表达式对象,默认实现是org.springframework.expression.spel.standard包中的SpelExpression,提供getValue方法用于获取表达式值,提供setValue方法用于设置对象值
SpEL语法
一、基本表达式
1、字面量表达式
SpEL支持的字面量包括:字符串、数字类型(int、long、float、double),布尔类型、null类型
| 类型 |
示例 |
| 字符串 |
String str1 = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World!'").getValue(String.class); String str2 = parser.parseExpression("\"Hello World!\"").getValue(String.class); |
| 数字类型 |
int int1 = parser.parseExpression("1").getValue(Integer.class); long long1 = parser.parseExpression("-1L").getValue(long.class); float float1 = parser.parseExpression("1.1").getValue(Float.class); double double1 = parser.parseExpression("1.1E+2").getValue(double.class); int hex1 = parser.parseExpression("0xa").getValue(Integer.class); long hex2 = parser.parseExpression("0xaL").getValue(long.class); |
| 布尔类型 |
boolean true1 = parser.parseExpression("true").getValue(boolean.class); boolean false1 = parser.parseExpression("false").getValue(boolean.class); |
| null类型 |
Object null1 = parser.parseExpression("null").getValue(Object.class); |
2、算数运行表达式
SpEL支持加(+)、减(-)、乘(*)、除(/)、求余(%)、幂(^)运算
| 类型 |
示例 |
| 加减乘除 |
int result1 = parser.parseExpression("1+2-3*4/2").getValue(Integer.class);//-3 |
| 求余 |
int result2 = parser.parseExpression("4%3").getValue(Integer.class);//1 |
| 幂运算 |
int result3 = parser.parseExpression("2^3").getValue(Integer.class);//8 |
SpEL还提供求余(MOD)和除(DIV)而外两个运算符,与“%”和“/”等价,不区分大小写。
3、关系表达式
等于(==)、不等于(!=)、大于(>)、大于等于(>=)、小于(<)、小于等于(<=),区间(between)运算,如“parser.parseExpression("1>2").getValue(boolean.class);”将返回false;而“parser.parseExpression("1 between {1, 2}").getValue(boolean.class);”将返回true。
between运算符右边操作数必须是列表类型,且只能包含2个元素。第一个元素为开始,第二个元素为结束,区间运算是包含边界值的,即 xxx>=list.get(0) && xxx<=list.get(1)。
SpEL同样提供了等价的“EQ”、“NE”、“GT”、“GE”、“LT”、“LE”来表示等于、不等于、大于、大于等于、小于、小于等于,不区分大小写。
4、逻辑表达式
且(and)、或(or)、非(!或NOT)。
注:逻辑运算符不支持 Java中的 && 和 || 。
5、字符串连接及截取表达式
使用“+”进行字符串连接,使用“'String'[0] [index]”来截取一个字符,目前只支持截取一个,如“'Hello ' + 'World!'”得到“Hello World!”;而“'Hello World!'[0]”将返回“H”。
6、三目运算及Elivis运算表达式
三目运算符“表达式1?表达式2:表达式3”用于构造三目运算表达式,如“2>1?true:false”将返回true。
Elivis运算符“表达式1?:表达式2”从Groovy语言引入用于简化三目运算符的,当表达式1为非null时则返回表达式1,当表达式1为null时则返回表达式2,简化了三目运算符方式“表达式1? 表达式1:表达式2”,如“null?:false”将返回false,而“true?:false”将返回true。
7、正则表达式
使用“str matches regex,如“'123' matches '\\d{3}'”将返回true;
8、括号优先级表达式
使用“(表达式)”构造,括号里的具有高优先级
二、类相关表达式
1、类类型表达式
使用“T(Type)”来表示java.lang.Class实例,“Type”必须是类全限定名,“java.lang”包除外,即该包下的类可以不指定包名;使用类类型表达式还可以进行访问类静态方法及类静态字段。
对于java.lang包里的可以直接使用“T(String)”访问;其他包必须是类全限定名;可以进行静态字段访问如“T(Integer).MAX_VALUE”;也可以进行静态方法访问如“T(Integer).parseInt('1')”
2、类实例化
类实例化同样使用java关键字“new”,类名必须是全限定名,但java.lang包内的类型除外,如String、Integer。
3、instranceof表达式
SpEL支持instanceof运算符,跟Java内使用同义;如“'haha' instanceof T(String)”将返回true。
4、变量定义及引用
变量定义通过EvaluationContext接口的setVariable(variableName, value)方法定义;在表达式中使用“#variableName”引用;除了引用自定义变量,SpE还允许引用根对象及当前上下文对象,使用“#root”引用根对象,使用“#this”引用当前上下文对象;
使用“#variable”来引用在EvaluationContext定义的变量;除了可以引用自定义变量,还可以使用“#root”引用根对象,“#this”引用当前上下文对象,此处“#this”即根对象。
5、自定义函数
目前只支持类静态方法注册为自定义函数;SpEL使用StandardEvaluationContext的registerFunction方法进行注册自定义函数,其实完全可以使用setVariable代替,两者其实本质是一样的;
6、赋值表达式
SpEL即允许给自定义变量赋值,也允许给跟对象赋值,直接使用“#variableName=value”即可赋值。
使用“#root='aaaaa'”给根对象赋值,使用“"#this='aaaa'”给当前上下文对象赋值,使用“#variable=#root”给自定义变量赋值,很简单。 使用“#root='aaaaa'”给根对象赋值,使用“"#this='aaaa'”给当前上下文对象赋值,使用“#variable=#root”给自定义变量赋值,很简单。
7、对象属性存取及安全导航表达式
对象属性获取非常简单,即使用如“a.property.property”这种点缀式获取,SpEL对于属性名首字母是不区分大小写的;SpEL还引入了Groovy语言中的安全导航运算符“(对象|属性)?.属性”,用来避免但“?.”前边的表达式为null时抛出空指针异常,而是返回null;修改对象属性值则可以通过赋值表达式或Expression接口的setValue方法修改。
8、对象方法调用
对象方法调用更简单,跟Java语法一样;如“'haha'.substring(2,4)”将返回“ha”;而对于根对象可以直接调用方法;
比如根对象date方法“getYear”可以直接调用。
9、Bean引用
SpEL支持使用“@”符号来引用Bean,在引用Bean时需要使用BeanResolver接口实现来查找Bean,Spring提供BeanFactoryResolver实现;
在示例中我们首先初始化了一个IoC容器,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 实现默认会把“System.getProperties()”注册为“systemProperties”Bean,因此我们使用“@systemProperties”来引用该Bean。
三、集合相关表达式
1、内联List
从Spring3.0.4开始支持内联List,使用{表达式,……}定义内联List,如“{1,2,3}”将返回一个整型的ArrayList,而“{}”将返回空的List,对于字面量表达式列表,SpEL会使用java.util.Collections.unmodifiableList方法将列表设置为不可修改。
2、内联数组
和Java 数组定义类似,只是在定义时进行多维数组初始化。
3、集合,字典元素访问
SpEL目前支持所有集合类型和字典类型的元素访问,使用“集合[索引]”访问集合元素,使用“map[key]”访问字典元素;
注:集合元素访问是通过Iterator遍历来定位元素位置的。
4、列表,字典,数组元素修改
可以使用赋值表达式或Expression接口的setValue方法修改;
对数组修改直接对“#array[index]”赋值即可修改元素值,同理适用于集合和字典类型。
5、集合投影
在SQL中投影指从表中选择出列,而在SpEL指根据集合中的元素中通过选择来构造另一个集合,该集合和原集合具有相同数量的元素;SpEL使用“(list|map).![投影表达式]”来进行投影运算:
对于集合或数组使用如上表达式进行投影运算,其中投影表达式中“#this”代表每个集合或数组元素,可以使用比如“#this.property”来获取集合元素的属性,其中“#this”可以省略。
SpEL投影运算还支持Map投影,但Map投影最终只能得到List结果,如上所示,对于投影表达式中的“#this”将是Map.Entry,所以可以使用“value”来获取值,使用“key”来获取键。
6、集合选择
在SQL中指使用select进行选择行数据,而在SpEL指根据原集合通过条件表达式选择出满足条件的元素并构造为新的集合,SpEL使用“(list|map).?[选择表达式]”,其中选择表达式结果必须是boolean类型,如果true则选择的元素将添加到新集合中,false将不添加到新集合中。
对于集合或数组选择,如“#collection.?[#this>4]”将选择出集合元素值大于4的所有元素。选择表达式必须返回布尔类型,使用“#this”表示当前元素。
对于字典选择,如“#map.?[#this.key != 'a']”将选择键值不等于”a”的,其中选择表达式中“#this”是Map.Entry类型,而最终结果还是Map,这点和投影不同;集合选择和投影可以一起使用,如“#map.?[key != 'a'].![value+1]”将首先选择键值不等于”a”的,然后在选出的Map中再进行“value+1”的投影。
四、其他表达式--表达式模板
模板表达式就是由字面量与一个或多个表达式块组成。每个表达式块由“前缀+表达式+后缀”形式组成,如“${1+2}”即表达式块。在前边我们已经介绍了使用ParserContext接口实现来定义表达式是否是模板及前缀和后缀定义。在此就不多介绍了,如“Error ${#v0} ${#v1}”表达式表示由字面量“Error ”、模板表达式“#v0”、模板表达式“#v1”组成,其中v0和v1表示自定义变量,需要在上下文定义。
Demo:
/**
* @descrption 字面量表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:46:49
*/
@Test
public void testBasicExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 1.字符串
String str1 = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World!'").getValue(String.class);
String str2 = parser.parseExpression("\"Hello World!\"").getValue(String.class);
Assert.assertEquals(str1, str2);
int int1 = parser.parseExpression("1").getValue(Integer.class);// int类型
Assert.assertEquals(1, int1);
long long1 = parser.parseExpression("-1L").getValue(long.class);// long类型
Assert.assertEquals(-1L, long1);
float float1 = parser.parseExpression("1.1").getValue(Float.class);// float类型
Assert.assertEquals(1.1f, float1);
double double1 = parser.parseExpression("1.1E+2").getValue(double.class);// double类型
Assert.assertEquals(1.1E+2, double1);
int hex1 = parser.parseExpression("0xa").getValue(Integer.class);// 16进制int类型
Assert.assertEquals(0xa, hex1);
long hex2 = parser.parseExpression("0xaL").getValue(long.class);// 16进制long类型
Assert.assertEquals(0xaL, hex2);
boolean true1 = parser.parseExpression("true").getValue(boolean.class);// 布尔类型
Assert.assertEquals(true, true1);
boolean false1 = parser.parseExpression("false").getValue(boolean.class);// 布尔类型
Assert.assertEquals(false, false1);
Object null1 = parser.parseExpression("null").getValue(Object.class);// null类型
Assert.assertEquals(null, null1);
}
/**
* @descrption 算数运行表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:47:18
*/
@Test
public void testArithmeticExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
int result1 = parser.parseExpression("1+2-3*4/2").getValue(Integer.class);
Assert.assertEquals(-3, result1);
int result2 = parser.parseExpression("4%3").getValue(Integer.class);
Assert.assertEquals(1, result2);
int result3 = parser.parseExpression("2^3").getValue(Integer.class);
Assert.assertEquals(8, result3);
int result4 = parser.parseExpression("6 DIV 2").getValue(Integer.class);
Assert.assertEquals(3, result4);
int result5 = parser.parseExpression("4 MOD 3").getValue(Integer.class);
Assert.assertEquals(1, result5);
}
/**
* @descrption 关系表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:47:38
*/
@Test
public void testRelationalExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
boolean result1 = parser.parseExpression("1 gt 2").getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(false, result1);
boolean result2 = parser.parseExpression("1 between {1, 2}").getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result2);
}
/**
* @descrption 逻辑表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:48:00
*/
@Test
public void testLogicalExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String expression1 = "2>1 and (!true or !false)";
boolean result1 = parser.parseExpression(expression1).getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result1);
String expression2 = "2>1 and (NOT true or NOT false)";
boolean result2 = parser.parseExpression(expression2).getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result2);
}
/**
* @descrption 字符串连接及截取表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:48:33
*/
@Test
public void testStringConcatExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String expression1 = "'Hello ' + 'World!'";
String result1 = parser.parseExpression(expression1).getValue(String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", result1);
String expression2 = "'Hello World!'[0]";
String result2 = parser.parseExpression(expression2).getValue(String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("H", result2);
}
/**
* @descrption 三目运算及Elivis运算表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:49:00
*/
@Test
public void testTernaryExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String expression1 = "2>1?true:false";
boolean result1 = parser.parseExpression(expression1).getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result1);
String expression2 = "null?:false";
boolean result2 = parser.parseExpression(expression2).getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(false, result2);
String expression3 = "true?:false";
boolean result3 = parser.parseExpression(expression3).getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result3);
}
/**
* @descrption 正则表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:49:15
*/
@Test
public void testRegexExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String expression1 = "'123' matches '\\d{3}'";
boolean result1 = parser.parseExpression(expression1).getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result1);
}
/**
* @descrption 类类型表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:46:10
*/
@Test
public void testClassTypeExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// java.lang包类访问
Class<String> result1 = parser.parseExpression("T(String)").getValue(Class.class);
Assert.assertEquals(String.class, result1);
// 其他包类访问
String expression2 = "T(com.iflytek.spel.SpELTest)";
Class<String> result2 = parser.parseExpression(expression2).getValue(Class.class);
Assert.assertEquals(SpELTest.class, result2);
// 类静态字段访问
int result3 = parser.parseExpression("T(Integer).MAX_VALUE").getValue(int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.MAX_VALUE, result3);
// 类静态方法调用
int result4 = parser.parseExpression("T(Integer).parseInt('1')").getValue(int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(1, result4);
}
/**
* @descrption 类实例化
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:46:15
*/
@Test
public void testConstructorExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String result1 = parser.parseExpression("new String('haha')").getValue(String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("haha", result1);
Date result2 = parser.parseExpression("new java.util.Date()").getValue(Date.class);
Assert.assertNotNull(result2);
}
/**
* descrption instanceof表达式
*
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:51:29
*/
@Test
public void testInstanceofExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
boolean result1 = parser.parseExpression("'haha' instanceof T(String)").getValue(boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result1);
}
/**
* @descrption 变量定义及引用
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:51:57
*/
@Test
public void testVariableExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setVariable("variable", "haha");
String result1 = parser.parseExpression("#variable").getValue(context, String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("haha", result1);
context = new StandardEvaluationContext("haha");
String result2 = parser.parseExpression("#root").getValue(context, String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("haha", result2);
String result3 = parser.parseExpression("#this").getValue(context, String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("haha", result3);
}
/**
* @descrption 自定义函数
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:52:21
* @throws SecurityException
* @throws NoSuchMethodException
* @说明 此处可以看出“registerFunction”和“setVariable”都可以注册自定义函数,但是两个方法的含义不一样,推荐使用“
* registerFunction”方法注册自定义函数。
*/
@Test
public void testFunctionExpression() throws SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
Method parseInt = Integer.class.getDeclaredMethod("parseInt", String.class);
context.registerFunction("parseInt", parseInt);
context.setVariable("parseInt2", parseInt);
String expression1 = "#parseInt('3') == #parseInt2('3')";
boolean result1 = parser.parseExpression(expression1).getValue(context, boolean.class);
Assert.assertEquals(true, result1);
}
/**
* @descrption 赋值表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:53:03
*/
@Test
public void testAssignExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 1.给root对象赋值
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext("aaaa");
String result1 = parser.parseExpression("#root='aaaaa'").getValue(context, String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("aaaaa", result1);
String result2 = parser.parseExpression("#this='aaaa'").getValue(context, String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("aaaa", result2);
// 2.给自定义变量赋值
context.setVariable("#variable", "variable");
String result3 = parser.parseExpression("#variable=#root").getValue(context, String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("aaaa", result3);
}
/**
* @descrption 对象属性存取及安全导航表达式
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:53:28
*/
@Test
public void testPropertyExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 1.访问root对象属性
// 对于当前上下文对象属性及方法访问,可以直接使用属性或方法名访问,比如此处根对象date属性“year”,注意此处属性名首字母不区分大小写。
Date date = new Date();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(date);
int result1 = parser.parseExpression("Year").getValue(context, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(date.getYear(), result1);
int result2 = parser.parseExpression("year").getValue(context, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(date.getYear(), result2);
// 2.安全访问
// SpEL引入了Groovy的安全导航运算符,比如此处根对象为null,所以如果访问其属性时肯定抛出空指针异常,而采用“?.”安全访问导航运算符将不抛空指针异常,而是简单的返回null。
context.setRootObject(null);
Object result3 = parser.parseExpression("#root?.year").getValue(context, Object.class);
Assert.assertEquals(null, result3);
// 3.给root对象属性赋值
// 给对象属性赋值可以采用赋值表达式或Expression接口的setValue方法赋值,而且也可以采用点缀方式赋值。
context.setRootObject(date);
int result4 = parser.parseExpression("Year = 4").getValue(context, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(4, result4);
parser.parseExpression("Year").setValue(context, 5);
int result5 = parser.parseExpression("Year").getValue(context, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(5, result5);
}
/**
* @descrption 对象方法调用
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:54:41
*/
@Test
public void testMethodExpression() {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String result1 = parser.parseExpression("'haha'.substring(2,4)").getValue(String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("ha", result1);
Date date = new Date();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(date);
int result2 = parser.parseExpression("getYear()").getValue(context, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(date.getYear(), result2);
}
/**
* @descrption Bean引用
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:55:00
*/
@Test
public void testBeanExpression() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
ctx.refresh();
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setBeanResolver(new BeanFactoryResolver(ctx));
Properties result1 = parser.parseExpression("@systemProperties").getValue(context, Properties.class);
Assert.assertEquals(System.getProperties(), result1);
}
/**
* @descrption 内联List
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:55:36
*/
@Test
public void testInnerListExpression() {
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
List<Integer> result1 = parser.parseExpression("{1,2,3}").getValue(List.class);
Assert.assertEquals(new Integer(1), result1.get(0));
try {
result1.set(0, 2);
// 不可能执行到这,对于字面量列表不可修改
Assert.fail();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
List<Integer> result2 = parser.parseExpression("{}").getValue(List.class);
Assert.assertEquals(0, result2.size());
String expression3 = "{{1+2,2+4},{3,4+4}}";
List<List<Integer>> result3 = parser.parseExpression(expression3).getValue(List.class);
result3.get(0).set(0, 1);
Assert.assertEquals(2, result3.size());
}
/**
* @descrption 内联数组
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:55:57
*/
@Test
public void testInnerArrayExpression() {
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
int[] result1 = parser.parseExpression("new int[1]").getValue(int[].class);
Assert.assertEquals(1, result1.length);
int[] result2 = parser.parseExpression("new int[2]{1,2}").getValue(int[].class);
Assert.assertEquals(2, result2[1]);
String expression3 = "new int[1][2][3]";
int[][][] result3 = parser.parseExpression(expression3).getValue(int[][][].class);
Assert.assertEquals(3, result3[0][0].length);
String expression4 = "new int[1][2][3]{{1}{2}{3}}";
try {
int[][][] result4 = parser.parseExpression(expression4).getValue(int[][][].class);
Assert.fail();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
/**
* @descrption 集合,字典元素访问
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:56:14
*/
@Test
public void testListAndMapGetValueExpression() {
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
int result1 = parser.parseExpression("{1,2,3}[0]").getValue(int.class);
// 即list.get(0)
Assert.assertEquals(1, result1);
Collection<Integer> collection = new HashSet<Integer>();
collection.add(1);
collection.add(2);
EvaluationContext context2 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context2.setVariable("collection", collection);
int result2 = parser.parseExpression("#collection[1]").getValue(context2, int.class);
// 对于任何集合类型通过Iterator来定位元素
Assert.assertEquals(2, result2);
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("a", 1);
EvaluationContext context3 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context3.setVariable("map", map);
int result3 = parser.parseExpression("#map['a']").getValue(context3, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(1, result3);
}
/**
* @descrption 列表,字典,数组元素修改
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:56:37
*/
@Test
public void testListAndMapSetValueExpression() {
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 1.修改数组元素值
int[] array = new int[] { 1, 2 };
EvaluationContext context1 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context1.setVariable("array", array);
int result1 = parser.parseExpression("#array[1] = 3").getValue(context1, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(3, result1);
// 2.修改集合值
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<Integer>();
collection.add(1);
collection.add(2);
EvaluationContext context2 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context2.setVariable("collection", collection);
int result2 = parser.parseExpression("#collection[1] = 3").getValue(context2, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(3, result2);
parser.parseExpression("#collection[1]").setValue(context2, 4);
result2 = parser.parseExpression("#collection[1]").getValue(context2, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(4, result2);
// 3.修改map元素值
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("a", 1);
EvaluationContext context3 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context3.setVariable("map", map);
int result3 = parser.parseExpression("#map['a'] = 2").getValue(context3, int.class);
Assert.assertEquals(2, result3);
}
/**
* @descrption 集合投影
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:56:58
*/
@Test
public void testProjectionExpression() {
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 1.首先准备测试数据
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<Integer>();
collection.add(4);
collection.add(5);
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("a", 1);
map.put("b", 2);
// 2.测试集合
EvaluationContext context1 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context1.setVariable("collection", collection);
Collection<Integer> result1 = parser.parseExpression("#collection.![#this+1]").getValue(context1,
Collection.class);
Assert.assertEquals(2, result1.size());
Assert.assertEquals(new Integer(5), result1.iterator().next());
// 3.测试字典
EvaluationContext context2 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context2.setVariable("map", map);
List<Integer> result2 = parser.parseExpression("#map.![value+1]").getValue(context2, List.class);
Assert.assertEquals(2, result2.size());
}
/**
* @descrption 集合选择
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:57:25
*/
@Test
public void testSelectExpression() {
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 1.准备数据
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<Integer>();
collection.add(4);
collection.add(5);
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("a", 1);
map.put("b", 2);
// 2.集合或数组测试
EvaluationContext context1 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context1.setVariable("collection", collection);
Collection<Integer> result1 = parser.parseExpression("#collection.?[#this>4]").getValue(context1,
Collection.class);
Assert.assertEquals(1, result1.size());
Assert.assertEquals(new Integer(5), result1.iterator().next());
// 3.字典测试
EvaluationContext context2 = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context2.setVariable("map", map);
Map<String, Integer> result2 = parser.parseExpression("#map.?[#this.key != 'a']").getValue(context2, Map.class);
Assert.assertEquals(1, result2.size());
List<Integer> result3 = parser.parseExpression("#map.?[key != 'a'].![value+1]").getValue(context2, List.class);
Assert.assertEquals(new Integer(3), result3.iterator().next());
}
/**
* @descrption 表达式模板
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-3下午11:57:55
*/
@Test
public void testTemplateExpression() {
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
ParserContext parserContext = new ParserContext() {
@Override
public boolean isTemplate() {
return true;
}
@Override
public String getExpressionPrefix() {
return "${";
}
@Override
public String getExpressionSuffix() {
return "}";
}
};
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setVariable("v0", 1);
context.setVariable("v1", 2);
String result = parser.parseExpression("Error ${#v0} ${#v1}", parserContext).getValue(context, String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("Error 1 2", result);
}
@Test
public void testXmlExpression() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter5/el1.xml");
String hello1 = ctx.getBean("hello1", String.class);
String hello2 = ctx.getBean("hello2", String.class);
String hello3 = ctx.getBean("hello3", String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", hello1);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", hello2);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", hello3);
}
在Bean定义中使用SpEL
一、xml风格的配置
SpEL支持在Bean定义时注入,默认使用“#{SpEL表达式}”表示,其中“#root”根对象默认可以认为是ApplicationContext,只有ApplicationContext实现默认支持SpEL,获取根对象属性其实是获取容器中的Bean。
首先看下配置方式(el1.xml)吧:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="world" class="java.lang.String">
<constructor-arg value="#{' World!'}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="hello1" class="java.lang.String">
<constructor-arg value="#{'Hello'}#{world}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="hello2" class="java.lang.String">
<constructor-arg value="#{'Hello' + world}"/>
<!-- 不支持嵌套的 -->
<!--<constructor-arg value="#{'Hello'#{world}}"/>-->
</bean>
<bean id="hello3" class="java.lang.String">
<constructor-arg value="#{'Hello' + @world}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
模板默认以前缀“#{”开头,以后缀“}”结尾,且不允许嵌套,如“#{'Hello'#{world}}”错误,如“#{'Hello' + world}”中“world”默认解析为Bean。当然可以使用“@bean”引用了。
测试
/**
* @descrption xml风格的配置
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-4下午9:58:59
*/
@Test
public void testXmlExpression() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("el1.xml");
String hello1 = ctx.getBean("hello1", String.class);
String hello2 = ctx.getBean("hello2", String.class);
String hello3 = ctx.getBean("hello3", String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", hello1);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", hello2);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", hello3);
}
二、注解风格的配置
基于注解风格的SpEL配置也非常简单,使用@Value注解来指定SpEL表达式,该注解可以放到字段、方法及方法参数上。
测试Bean类如下,使用@Value来指定SpEL表达式:
package com.iflytek.spel; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; /** * @author xudongwang * * @create 2013-9-3 下午11:40:48 * * @email:[email protected] * * @description * */ public class SpELBean { @Value("#{'Hello' + world}") private String value; public void setValue(String value) { this.value = value; } public String getValue() { return value; } }
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="world" class="java.lang.String">
<constructor-arg value="#{' World!'}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="helloBean1" class="com.iflytek.spel.SpELBean"/>
<bean id="helloBean2" class="com.iflytek.spel.SpELBean">
<property name="value" value="haha"/>
</bean>
</beans>
配置时必须使用“<context:annotation-config/>”来开启对注解的支持。
测试
/**
* @descrption 注解风格的配置
* @author xdwang
* @create 2013-9-4下午9:59:40
*/
@Test
public void testAnnotationExpression() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("el2.xml");
SpELBean helloBean1 = ctx.getBean("helloBean1", SpELBean.class);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", helloBean1.getValue());
SpELBean helloBean2 = ctx.getBean("helloBean2", SpELBean.class);
Assert.assertEquals("haha", helloBean2.getValue());
}
其中“helloBean1 ”值是SpEL表达式的值,而“helloBean2”是通过setter注入的值,这说明setter注入将覆盖@Value的值
三、在Bean定义中SpEL的问题
如果“#{我不是SpEL表达式}”不是SpEL表达式,而是公司内部的模板,想换个前缀和后缀该如何实现呢?
那我们来看下Spring如何在IoC容器内使用BeanExpressionResolver接口实现来求值SpEL表达式,那如果我们通过某种方式获取该接口实现,然后把前缀后缀修改了不就可以了。
此处我们使用BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口提供postProcessBeanFactory回调方法,它是在IoC容器创建好但还未进行任何Bean初始化时被ApplicationContext实现调用,因此在这个阶段把SpEL前缀及后缀修改掉是安全的,具体代码如下:
package com.iflytek.spel; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.expression.StandardBeanExpressionResolver; /** * @author xudongwang * * @create 2013-9-4 下午9:57:21 * * @email:[email protected] * * @description * */ public class SpELBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { StandardBeanExpressionResolver resolver = (StandardBeanExpressionResolver) beanFactory .getBeanExpressionResolver(); resolver.setExpressionPrefix("%{"); resolver.setExpressionSuffix("}"); } }
首先通过 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory的getBeanExpressionResolver方法获取BeanExpressionResolver实现,其次强制类型转换为StandardBeanExpressionResolver,其为Spring默认实现,然后改掉前缀及后缀。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean class="com.iflytek.spel.SpELBeanFactoryPostProcessor"/>
<bean id="world" class="java.lang.String">
<constructor-arg value="%{' World!'}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="helloBean1" class="com.iflytek.spel.SpELBean"/>
<bean id="helloBean2" class="com.iflytek.spel.SpELBean">
<property name="value" value="%{'Hello' + world}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
配置文件和注解风格的几乎一样,只有SpEL表达式前缀变为“%{”了,并且注册了“com.iflytek.spel.SpELBeanFactoryPostProcessor”Bean,用于修改前缀和后缀的。
测试
@Test
public void testPrefixExpression() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("el3.xml");
SpELBean helloBean1 = ctx.getBean("helloBean1", SpELBean.class);
Assert.assertEquals("#{'Hello' + world}", helloBean1.getValue());
SpELBean helloBean2 = ctx.getBean("helloBean2", SpELBean.class);
Assert.assertEquals("Hello World!", helloBean2.getValue());
}
转自http://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/