布局管理(一)
5.1、ExtJS的布局管理器及其继承关系
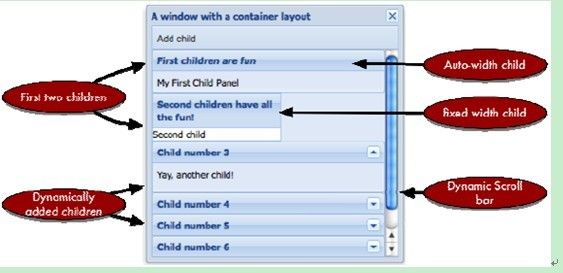
从图中可以看出:Ext.layout.ContainerLayout是ExtJS所有布局类的根,它也是容器组件的缺省布局类:在容器中一个接一个地安排组件的显示,通常也称它为流式布局。一个使用Ext.layout.ContainerLayout布局的简单例子:
var childPnl1 = {
frame : true,
height : 50,
html : 'My First Child Panel',
title : 'First children are fun'
}
var childPnl2 = {
xtype : 'panel',
width : 150,
html : 'Second child',
title : 'Second children have all the fun!'
}
var myWin = new Ext.Window({
height : 300,
width : 300,
title : 'A window with a container layout',
autoScroll : true,
items : [
childPnl1,
childPnl2
],
tbar : [
{
text : 'Add child',
handler : function() {
var numItems = myWin.items.getCount() + 1;
myWin.add({
title : 'Child number ' + numItems,
height : 60,
frame : true,
collapsible : true,
collapsed : true,
html : 'Yay, another child!'
});
myWin.doLayout();
}
}
]
});
myWin.show();
运行结果:
在对ExtJS的容器进行布局时,使用Ext.Container的”layout”属性指定布局管理,使用Ext.Container的”layoutConfig”属性来对布局管理器的特定属性进行配置。各个布局管理器可以被配置的属性在ExtJS的API的各个布局管理器的Config Options中。
5.2、Ext.layout.AnchorLayout布局
Ext.layout.AnchorLayout与流式布局类似,只是在使用Ext.layout.AnchorLayout布局时可以在容器的items属性所指定的各个组件中使用:
anchor: “width, height”
来指定各个组件相对于容器的宽度和高度:%及整数类型的值均可以,其中”%”就是子组件相对于容器的百分比,而”整数值”就是子组件的大小等于容器的大小加上这个整数值。同时,对于使用Ext.layout.AnchorLayout进行布局管理的容器来说,可以在容器的配置属性中使用:
anchorSize: {width:宽度, height:高度},
来指定容器的布局宽度和布局高度,注意,这里的” 布局宽度和布局高度”与容器实际的宽度和高度无关。一个使用Ext.layout.AnchorLayout进行布局的例子:
var myWin = new Ext.Window({
height : 300,
width : 300,
layout : 'anchor',
autoScroll : true,
border : false,
anchorSize : {width:400, height:300},
items : [
{
title : 'Panel1',
anchor : '100%, 25%',
frame : true
},
{
title : 'Panel2',
anchor : ‘100%, 50%',
frame : true
},
{
title : 'Panel3',
anchor : '50%, 25%',
frame : true
}
]
});
myWin.show();
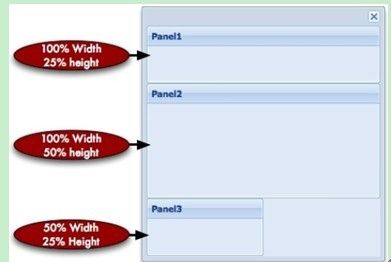
运行结果:
5.4、Ext.layout.FormLayout布局
FormLayout是AnchorLayout的子类,因此,AnchorLayout中相关配置属性,例如anchor、anchorSize同样适用于FormLayout。
使用FormLayout进行布局管理的容器可以在容器配置中使用如下这些FormLayout相关配置属性来对容器进行配置:
- hideLabels
- labelAlign
- labelPad
- labelSeparator
- labelWidth
这些配置属性的含义不言而喻。同时,对于采用FormLayout进行布局管理的容器,该容器中的组件则可以使用如下的FormLayout相关的属性进行配置:
- anchor
- clearCls
- fieldLabel
- hideLabel
- itemCls
- labelSeparator
- labelStyle
这些配置属性的含义不言而喻的。一个采用FormLayout布局的例子:
var myWin = new Ext.Window({
height : 220,
width : 230,
bodyStyle : 'padding: 5px',
layout : 'form',
labelWidth : 50,
defaultType : 'field',
items : [
{
fieldLabel : 'Name',
anchor : '-4'
},
{
fieldLabel : 'Age',
width : 25
},
{
xtype : 'combo',
fieldLabel : 'Location',
anchor : '-4',
store : [ 'Here', 'There', 'Anywhere' ]
},
{
xtype : 'textarea',
fieldLabel : 'Bio',
anchor : '-4, -135'
},
{
xtype : 'panel',
fieldLabel : ' ',
labelSeparator : '',
frame : true,
title : 'Instructions',
html : 'Please fill in the form',
anchor : '-4',
}
]
});
myWin.show();
运行结果:
5.5、Ext.layout.AbsoluteLayout布局
采用绝对位置和大小对组件进行布局。在容器的组件中可以使用”x、y”属性来指明组件在容器中的位置,及可以使用”width、height”属性来指明组件的大小,如此而已。一个例子:
var myWin = new Ext.Window({
height : 300,
width : 300,
layout : 'absolute',
autoScroll : true,
id : 'myWin',
border : false,
items : [
{
title : 'Panel1',
x : 50,
y : 50,
height : 100,
width : 100,
html : 'x: 50, y:100',
frame : true
},
{
title : 'Panel2',
x : 90,
y : 120,
height : 75,
width : 77,
html : 'x: 90, y: 120',
frame : true
}
]
});
myWin.show();
5.6、Ext.layout.FitLayout布局
容器的items中只有一个组件,并且这个组件将占据容器的全部显示空间,这就是就是fit布局。fit布局没有为容器或组件添加任何其他的配置属性。一个fit布局的例子:
var myWin = new Ext.Window({
height : 200,
width : 200,
layout : 'fit',
autoScroll : true,
border : false,
items : [
{
title : 'Panel1',
html : 'I fit in my parent!',
frame : true
}
]
});
myWin.show();
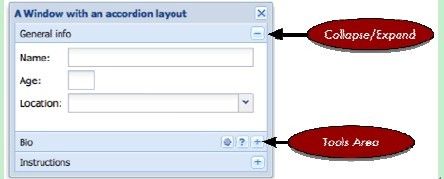
5.7、Ext.layout.AccordionLayout布局
AccordionLayout是FitLayout的直接子类。AccordionLayout布局以垂直堆叠的方式显示组件,并且,在任何一个时刻,只有一个item是展开的。一个AccordionLayout布局的例子:
var myWin = new Ext.Window({
height : 200,
width : 300,
border : false,
title : 'A Window with an accordion layout',
layout : 'accordion',
layoutConfig : {
animate : true
},
items : [
{
xtype : 'form',
title : 'General info',
bodyStyle : 'padding: 5px',
defaultType : 'field',
labelWidth : 50,
items : [
{
fieldLabel : 'Name',
anchor : '-10',
},
{
xtype : 'numberfield',
fieldLabel : 'Age',
width : 30
},
{
xtype : 'combo',
fieldLabel : 'Location',
anchor : '-10',
store : [ 'Here', 'There', 'Anywhere' ]
}
]
},
{
xtype : 'panel',
autoEl : {},
title : 'Bio',
layout : 'fit',
items : {
xtype : 'textarea',
value : 'Tell us about yourself'
}
},
{
title : 'Instructions',
html : 'Please enter information.',
tools : [
{id : 'gear'}, {id:'help'}
]
}
]
});
myWin.show();
运行实例: