Equinox OSGi服务器应用程序的配置步骤
本文介绍在Eclipse里如何配置一个简单的基于Eclipse Equinox OSGi实现的Web应用程序,在它的基础上可以构造更加复杂的应用,本文使用的是Eclipse 3.3.1版本,如果你的Eclipse版本在3.2.0或以上应该都可以。
一、支持静态页面和Servlet
1. 创建一个新的plugin项目, net.bjzhanghao.osgi.test,在向导第一步里选中“This plug-in is target,在下一步的“Plug-in Options”里选中“Generate an activator”。
2. 在例子项目的MANIFEST.MF里添加如下依赖项目,这些项目都是Eclipse自带的:
org.eclipse.equinox.http.servlet
org.mortbay.jetty
org.apache.commons.logging
javax.servlet
org.eclipse.equinox.http.registry
3. 在例子项目根目录下创建一个放置web文件的目录,如“web_files”,在这个目录下写一个简单的index.html文件。
4. 为项目建一个plugin.xml文件,内容如下:
< extension point ="org.eclipse.equinox.http.registry.resources" >
< resource
alias ="/web"
base-name ="/web_files" />
</ extension >
</ plugin >
注意,这时若MANIFEST.MF里提示错误,只要在Bundle-SymbolicName这一行后面加上“;singleton:=true”即可解决。
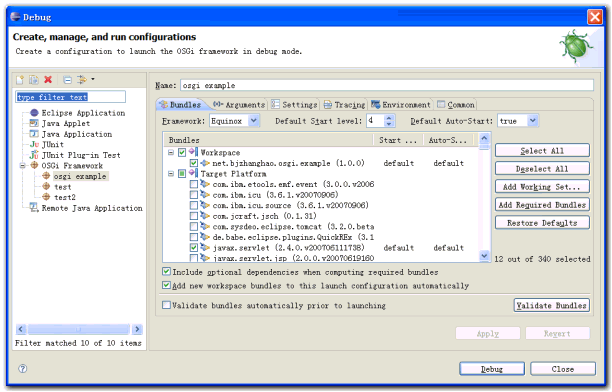
5. 现在可以启动这个应用程序了。在Eclipse菜单里选择“Run->Open Run Dialog...”,在左边的 “OSGi Framework”项下创建一个新的启动配置项,在右边先点“Deselect All”清空所有复选框,然后在Workspace下选中 自己的osgi项目,再点“Add Required Bundles”按钮,Eclipse会自动把所依赖的项目选中。 最后按“Debug”按钮启动,内嵌的jetty和我们的项目会一起被启动。6. 打开浏览器,输入“http://localhost/web/index.html”应该可以看到index.html里的内容。
以上只验证了静态页面,现在来配置一个servlet看看。
7. 在项目里创建一个继承自HttpServlet的类,覆盖doGet()方法,内容是在网页上打印一些文本。
8. 在项目的plugin.xml里添加下面的内容,这些内容指定了servlet的访问路径和实现类:
< servlet
alias ="/exampleServlet"
class ="net.bjzhanghao.osgi.example.servlet.ExampleServlet" />
</ extension >
9. 重新启动项目,在浏览器里输入“http://localhost/exampleServlet”,应该可以看到servlet的输出。
二、支持JSP页面
10. 在index.html所在目录下创建一个简单的jsp文件index.jsp
11. 打开项目的MANIFEST.MF文件,添加如下项目依赖:
org.apache.jasper ,
org.eclipse.equinox.jsp.jasper.registry ,
javax.servlet.jsp ,
org.apache.commons.el ,
org.eclipse.equinox.http.helper ,
org.eclipse.osgi ,
org.eclipse.osgi.services
其中org.eclipse.equinox.http.helper需要从cvs里下载得到(目前是在/cvsroot/eclipse下的 equinox-incubator目录里,以后可能会直接放到/cvsroot/eclipse下)。
12. 修改Activator,目的是注册一个处理扩展名为.jsp类型的servlet,感觉这一步以后应该有更简单的方法,例如通过扩展点。
private ServiceTracker httpServiceTracker;
String jspContext = " /jsps " ;
String jspFolder = " /web_files " ;
public void start(BundleContext context) throws Exception {
httpServiceTracker = new HttpServiceTracker(context);
httpServiceTracker.open();
}
public void stop(BundleContext context) throws Exception {
httpServiceTracker.open();
}
private class HttpServiceTracker extends ServiceTracker {
public HttpServiceTracker(BundleContext context) {
super (context, HttpService. class .getName(), null );
}
public Object addingService(ServiceReference reference) {
final HttpService httpService = (HttpService) context
.getService(reference);
try {
HttpContext commonContext = new BundleEntryHttpContext(context
.getBundle(), jspFolder);
httpService.registerResources(jspContext, " / " , commonContext);
Servlet adaptedJspServlet = new ContextPathServletAdaptor(
new JspServlet(context.getBundle(), jspFolder),
jspContext);
httpService.registerServlet(jspContext + " /*.jsp " ,
adaptedJspServlet, null , commonContext);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return httpService;
}
public void removedService(ServiceReference reference, Object service) {
final HttpService httpService = (HttpService) service;
httpService.unregister(jspContext);
httpService.unregister(jspContext + " /*.jsp " );
super .removedService(reference, service);
}
}
}
13. 打开Debug对话框,选中workspace里的例子osgi项目和org.eclipse.equinox.http.helper项目,再按“Add Required Bundles”按钮,然后启动程序。
14. 在浏览器里输入“http://localhost/jsps/index.jsp”,应该可以看到jsp输出。
例子项目下载(链接)。
参考链接: