Spring安全权限管理(Spring Security)
1.Spring Security简要介绍
Spring Security以前叫做acegi,是后来才成为Spring的一个子项目,也是目前最为流行的一个安全权限管理框架,它与Spring紧密结合在一起。
Spring Security关注的重点是在企业应用安全层为您提供服务,你将发现业务问题领域存在着各式各样的需求。银行系统跟电子商务应用就有很大的不同。电子商务系统与企业销售自动化工具又有很大不同。这些客户化需求让应用安全显得有趣,富有挑战性而且物有所值。Spring Security为基于J2EE的企业应用软件提供了一套全面的安全解决方案。
2.为Spring Security配置过滤器和其他参数
要使用Spring Security,首先就是在web.xml中为它配置过滤器, 其次因为我的spring配置文件是放在WEB-INF下的,因此还要配置上下文的参数,最后添加spring的监听器:
- <?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <web-appversion="2.5"xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaeehttp://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
- <!--配置上下文参数,指定spring配置文件的位置-->
- <context-param>
- <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
- <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-*.xml</param-value>
- </context-param>
- <!--springsecurity必须的过滤器,保证在访问所有的页面时都必须通过认证-->
- <filter>
- <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
- <filter-class>
- org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy
- </filter-class>
- </filter>
- <filter-mapping>
- <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
- <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
- </filter-mapping>
- <listener>
- <listener-class>
- org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
- </listener-class>
- </listener>
- <welcome-file-list>
- <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
- </welcome-file-list>
- <login-config>
- <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method>
- </login-config>
- </web-app>
3.配置security(spring-security.xml)
- <?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <!--这里必须使用security的命名空间,提供了beans这个假名-->
- <beans:beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
- xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/securityhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-2.0.4.xsd">
- <!--SpringSecurity采用就近原则,有多个约束时,从上至下只要找到第一条满足就返回,因此因该将最严格的约束放在最前面,而将最宽松的约束放在最后面.auto-config属性可以让springsecurity为我们自动配置几种常用的权限控制机制,包括form,anonymous,rememberMe等。当然你也可以手工配置。-->
- <httpauto-config="true">
- <!--我们利用intercept-url来判断用户需要具有何种权限才能访问对应的url资源,可以在pattern中指定一个特定的url资源,也可以使用通配符指定一组类似的url资源。例子中定义的两个intercepter-url,第一个用来控制对/security/**的访问,第二个使用了通配符/**,说明它将控制对系统中所有url资源的访问。-->
- <intercept-urlpattern="/security/**"access="ROLE_ADMIN"/>
- <intercept-urlpattern="/**"access="ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_USER"/>
- <intercept-urlpattern="/login.jsp*"filters="none"/>
- <logoutlogout-url="/logout.jsp"
- logout-success-url="/j_spring_security_check"/>
- </http>
- <!--使用内存权限管理的配置信息,在tomcat启动时,会加载这个文件并一直保存在内存中,知道应用程序重启,所以也叫内存权限管理
- <authentication-provider>
- <user-service>
- <username="admin"password="tomcat"authorities="ROLE_ADMIN"/>
- <username="liky"password="redhat"authorities="ROLE_USER"/>
- </user-service>
- </authentication-provider>
- -->
- <!--使用数据库作为权限管理的来源,data-source-ref指定了数据源,所指定的数据源必须包含users,authorities表,并符合security的定义规范-->
- <authentication-provider>
- <jdbc-user-servicedata-source-ref="dataSource"/>
- </authentication-provider>
- </beans:beans>
4.数据源的配置(spring-common.xml)
- <?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
- <!--定义数据源-->
- <beanid="dataSource"
- class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
- <propertyname="driverClassName"
- value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">
- </property>
- <propertyname="url"value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/csu"></property>
- <propertyname="username"value="root"></property>
- <propertyname="password"value="redhat"></property>
- <propertyname="maxActive"value="100"></property>
- <propertyname="maxIdle"value="30"></property>
- <propertyname="maxWait"value="300"></property>
- <propertyname="defaultAutoCommit"value="true"></property>
- </bean>
- </beans>
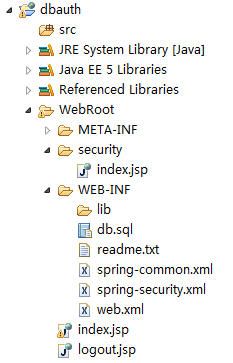
5.项目的目录结构
6. 数据库脚本
- /--注意这里的脚本是MYSQL的,因此在你演示这个实例的时候,要加入MySQL的驱动包--/
- createtableusers
- (
- usernamevarchar(50)primarykey,
- passwordvarchar(50),
- enabledtinyint(1)
- );
- createtableauthorities
- (
- idintauto_incrementprimarykey,
- usernamevarchar(50),
- authorityvarchar(50),
- constraintfk_authorities_usersforeignkey(username)referencesusers(username)
- );
- createuniqueindexix_auth_usernameonauthorities(username,authority);
7.部署和配置的要点说明
这是一个Spring Security的数据库认证实例,要注意以下几点:
(1)请自行加入Spring必须的包,Spring security的包和MySQL的驱动包,当然你也可以换成其他的数据库,但是你要相应的修改spring-common.xml中的dataSource部分
(2)数据库中的两个表users,authorites必须完全按照脚本所示来定义,也就是说表的名字不能修改.
(3)users表必须包含username,password,enabled字段,这三个字段是绝对不能少的,也不能修改类型.另外enabled一定要为1才能登录
(4)authorities表必须包含username字段,这个字段引用users的username作为外键,authority字段就是角色的名字,角色名字必须满足ROLE_XXX的格式(例如:ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_USER,ROLE_MAMAGER)
(5)如果一个用户有多个角色,不要将多个角色放在一起用逗号隔开.而是每个角色定义一条记录(例如:abu有ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_USER两个角色,那么应该定义两条记录: 一条为abu, ROLE_USER,另一条为abu, ROLE_ADMIN.而不是只有一条:abu, ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_USER)
(6)你可以给authorities表添加一个id字段作为主键.
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/csuliky/article/details/4277413
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangliang0115/archive/2012/04/02/2429584.html