简要解析class文件,理解class结构
class文件的结构如下。u1,u2,u3,u4分别表示多少字节。java文件,读4字节,可以得到magic,这是一个数,如果读到该数,说明读的是class文件。再读2字节,会读到小版本号。 依次继续。 可以读到魔数,小版本号,大版本号,常量池中常量个数,常量池信息,类的访问标识符,当前类在常量池的索引,父类在常量池的索引,接口个数,接口的索引,属性个数,属性信息,方法个数,方法信息,类的attribute个数,类的attribute.
其中常量池的结构如下:
constant_pool cp_info
–CONSTANT_Utf8 1 UTF-8编码的Unicode字符串
–CONSTANT_Integer 3 int类型的字面值
–CONSTANT_Float 4 float类型的字面值
–CONSTANT_Long 5 long类型的字面值
–CONSTANT_Double 6 double类型的字面值
–CONSTANT_Class 7 对一个类或接口的符号引用
–CONSTANT_String 8 String类型字面值的引用
–CONSTANT_Fieldref 9 对一个字段的符号引用
–CONSTANT_Methodref 10 对一个类中方法的符号引用
–CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref 11 对一个接口中方法的符号引用
–CONSTANT_NameAndType 12 对一个字段或方法的部分符号引用
先读一个字节,是常量结构的tag, tag的值和上面的表对应,就能知道该常量是什么类型,进而进一步解析。需要注意的是,第0个常量是系统保留的,并没有正真的常量,我们从索引为1的开始解析。另外double和long常量超出了常量项的保存能力,所以当索引为i的常量解析为double或者long的时候,接下来要解析索引为i+2的常量,而不是i+1的常量。
常量的机构见代码。
解析出常量之后需要将常量池保存下来,接下来解析其他信息时要用。
接下来是类的访问标识符,是通过将16位各个位上置为1来表示是否有修饰符的。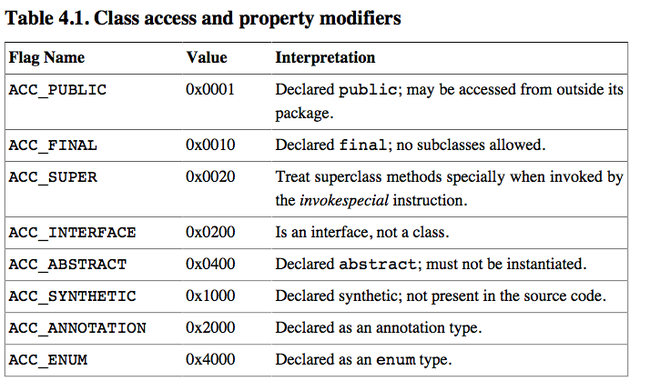
待会解析到方法和属性的时候,也会有访问修饰符的解析,方法类似,但规则稍有不同。
接下来解析当前的类。我们读到的2字节,实际上是指向常量池的索引。根据索引去常量池里需找,会发现常量项的类型是CONSTANT_Class,而这个结构又指向了常量池里的另一个常量CONSTANT_UTF8, 这是一个类似java/lang/Object的utf8序列。当我们解析方法名,字段名,方法描述等信息的时候,过程和这个是类似的。
接下来用同样的方法可以解析出父类,所实现的接口等信息。
之后开始解析属性和方法,都是先读出有多少属性及方法,依次解析。看看属性和方法的结构
他们结构类似。其中attribute_info是最复杂的信息。 attribute_info是一类复杂的信息,比如方法内的代码,异常处理代码的偏移量、是否被废弃(deprecated),对应源代码的行数,源文件名、局部变量表等等有用的信息。attribute_info不是只有方法和属性结构有,类本身也会有。每一种attribute_info都有自己的格式,attribute_info结构可以嵌套,解析起来比较麻烦,我这里就省略了。。。如果都解析出来,可以做反编译了。
在属性和方法的结构中access_flags是访问标识符,和class的有点像,但是解析的时候是不一样的。name_index是指向常量池的索引。descriptor_index也指向常量池,是对类和方法的描述。描述为了节省空间,都是简写的
通过一些代码,我们就可以解析class文件,得到一些类的信息,这里不解析attribute_info.
public class ClassAnalyser {
private static Cons_info[] cons = null;
//public static String myClass = "D:Worker.class";
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataInputStream input = null;
try {
input = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(myClass)));
// 获取文件大小
FileSize(new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(myClass))));
// 解析数据
analyze(input);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("解析失败!");
} finally {
try {
input.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
public static void FileSize(DataInputStream input) throws IOException {
int length = 0; // 长度,字节,B
double kblength = 0.0D; // 长度,千字节,KB
while (input.read() != -1)
++length;
kblength = length / 1024.0D;
System.out.println("文件大小(字节):" + length + "\n文件大小(KB):" + kblength);
input.close();
}
public static void analyze(DataInputStream input) throws IOException {
// 读取魔数
int magic = u4(input);
if (magic == 0xCAFEBABE) // -
System.out.println("魔数 = 0xCAFEBABE -----标准class文件");
else {
System.out.println("无效的魔数,不是.class文件");
return;
}
// 读取版本号
int minor_ver = u2(input);
int major_ver = u2(input);
System.out.println("版本号 :大版本- " + major_ver + " 小版本-" + minor_ver);
// 读取常量池表中表项的个数
short cons_count = u2(input);
System.out.println("常量池大小 = " + cons_count);
cons = new Cons_info[cons_count];
// 读取每个常量
//第一个系统保留,不读
for (int i = 1; i < cons_count; ++i){
i = analyzeConstant(input, i);
}
short access_flags = u2(input);
analyzeAccessFlag(access_flags);
// 读取类或者接口
short this_class_index = u2(input);
short super_class_index = u2(input);
System.out.println("当前类的索引为:" + this_class_index);
System.out.println("类名为:"+cons[cons[this_class_index].n16].utf8);
System.out.println("父类的索引为:" + super_class_index);
System.out.println("类名为:"+cons[cons[super_class_index].n16].utf8);
short inteCes_count = u2(input);
System.out.println("实现的接口数量为:" + inteCes_count);
for (int i = 1; i <= inteCes_count; i++) {
short inteCe_index = u2(input);
System.out.println("接口第 " + i + "个的索引为:"+ inteCe_index);
System.out.println("接口名为:"+cons[cons[inteCe_index].n16].utf8);
}
short fields_count = u2(input);
System.out.println("属性的个数为:"+fields_count+"个");
for(int i=0;i<fields_count;i++){
readField(input,i);
}
short method_count = u2(input);
System.out.println("方法的个数为:"+method_count+"个");
for(int i=0;i<method_count;i++){
readMethod(input,i);
}
}
/**
* 读方法
* @param input
* @param i
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void readMethod(DataInputStream input, int i) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----------------------方法"+i);
short access = u2(input);
analyzeAccessFlagMethod(access);
short name_index = u2(input);
System.out.println("方法名为:"+cons[name_index].utf8);
short desc_index = u2(input);
System.out.println("描述符为:"+cons[desc_index].utf8);
short attr_count = u2(input);
for(int j=0;j<attr_count;j++){
readAttribute(input,j);
}
}
/**
* 读属性
* @param input
* @param i
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void readField(DataInputStream input, int i) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----------------------属性"+i);
short access = u2(input);
analyzeAccessFlagField(access);
short name_index = u2(input);
System.out.println("属性名为:"+cons[name_index].utf8);
short desc_index = u2(input);
System.out.println("描述符为:"+cons[desc_index].utf8);
short attr_count = u2(input);
for(int j=0;j<attr_count;j++){
readAttribute(input,j);
}
}
/**
* 读attribute 暂时不做任何事情
* @param input
* @param j
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void readAttribute(DataInputStream input,int j) throws IOException{
u2(input);
int length = u4(input);
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
input.readFully(bytes);
}
public static byte u1(DataInputStream input) throws IOException {
return input.readByte();
}
public static Short u2(DataInputStream input) throws IOException {
return input.readShort();
}
public static int u4(DataInputStream input) throws IOException {
return input.readInt();
}
public static long u8(DataInputStream input) throws IOException {
return input.readLong();
}
/**
* 类访问权限
* @param i
*/
private static void analyzeAccessFlag(short i){
System.out.println("类的访问权限:");
String desc = toBinary(i);
if('1' == desc.charAt(15)){
System.out.print("Public ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(14)){
System.out.print("final ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(13)){
System.out.print("ACC_super ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(12)){
System.out.print("interface ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(11)){
System.out.print("Abstract ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(10)){
System.out.print("synthetic ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(9)){
System.out.print("annotation ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(8)){
System.out.print("enum ");
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 属性访问权限
* @param i
*/
private static void analyzeAccessFlagField(short i){
String desc = toBinary(i);
if('1' == desc.charAt(15)){
System.out.print("public ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(14)){
System.out.print("private ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(13)){
System.out.print("potected ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(12)){
System.out.print("static ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(11)){
System.out.print("final ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(10)){
System.out.print("volatile ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(9)){
System.out.print("transient ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(8)){
System.out.print("synthetic ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(7)){
System.out.print("enum ");
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 方法权限
* @param i
*/
private static void analyzeAccessFlagMethod(short i){
String desc = toBinary(i);
if('1' == desc.charAt(15)){
System.out.print("public ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(14)){
System.out.print("private ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(13)){
System.out.print("potected ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(12)){
System.out.print("static ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(11)){
System.out.print("final ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(10)){
System.out.print("sychronized ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(9)){
System.out.print("bridge ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(8)){
System.out.print("varargs ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(7)){
System.out.print("native ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(6)){
System.out.print("abstract ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(5)){
System.out.print("strictfp ");
}
if('1' == desc.charAt(4)){
System.out.print("synthetic ");
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 解析常量
* @param input
* @param index
* @throws IOException
*/
public static int analyzeConstant(DataInputStream input, int index)
throws IOException {
// 用于读:
// byte n8;
short n16 = 0;
short n162 = 0;
int n32 = 0;
long n64 = 0l;
float f = 0f;
double d = 0d;
byte[] buffer;
byte tag = input.readByte(); // 读取数据类型标签
System.out.println("第"+index+"个常量");
switch (tag) {
case 1: // utf-8 string
System.out.println("常量类型=utf8");
n16 = u2(input);
System.out.println(" length = " + n16);
buffer = new byte[n16];
input.readFully(buffer); // 数组读满才返回
System.out.println(" value = " + new String(buffer));
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n16,0,0,0,0,new String(buffer));
break;
case 3: // integer
System.out.println("常量类型=Integer");
n32 = u4(input);
System.out.println(" value = " + n32);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n16,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
case 4: // float
System.out.println("常量类型=Float");
f = u4(input);
System.out.println(" value = " + f);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n16,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
case 5: // long
System.out.println("常量类型=Long");
//n64 = u8(input);
n64 = input.readLong();
System.out.println(" value = " + n64);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n16,n32,n64,f,d,"");
index ++;
break;
case 6: // double
System.out.println("常量类型=Double");
//d = u8(input);
d = input.readDouble();
System.out.println(" value = " + d);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n16,n32,n64,f,d,"");
index ++;
break;
case 7: //Class_info
System.out.println("常量类型=Class"); // 类或者接口的 索引
n16 = u2(input);
System.out.println(" 索引 = " + n16 );
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n16,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
case 8: // String_info
System.out.println("常量类型=String"); // 字符串索引
n16 = u2(input);
System.out.println(" 索引 = " + n16);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n16,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
case 9://Fieldref_info
System.out.println("常量类型=字段引用");
n16 = u2(input);
System.out.println("类名索引 = "+n16);
n162 = u2(input);
System.out.println("名称和类型 = "+n162);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n162,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
case 10: //Methodref_info
System.out.println("常量类型=类中方法引用");
n16 = u2(input);
System.out.println(" 索引 = " + n16);
n162 = u2(input);
System.out.println("名称和类型 = " + n162);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n162,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
case 11: //InterfaceMethodref_info
System.out.println("常量类型=接口中的方法引用");
n16 = u2(input);
System.out.println(" 索引 = " + n16 );
n162 = u2(input);
System.out.println("名称和类型 = " + n162 );
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n162,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
case 12: //NameAndType_info
System.out.println("常量类型=字段和方法的名称以及类型的符号引用 ");
n16 = u2(input);
System.out.println(" 索引 = " + n16 );
n162 = u2(input);
System.out.println(" 描述符 = " + n162);
cons[index] = new Cons_info(n16,n162,n32,n64,f,d,"");
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("unknown constant pool flag: " + tag);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
return index;
}
/**
* 补足16位
* @param i
* @return
*/
private static String toBinary(short i){
String a = Integer.toBinaryString(i);
while(a.length()<16){
a = "0"+a;
}
return a;
}
}
/**
* 常量
*/
class Cons_info{
short n16;
short n162;
int n32;
long n64;
float f;
double d;
String utf8;
public Cons_info(short n16, short n162, int n32, long n64, float f,
double d, String utf8) {
super();
this.n16 = n16;
this.n162 = n162;
this.n32 = n32;
this.n64 = n64;
this.f = f;
this.d = d;
this.utf8 = utf8;
}
}


