google-perftools+kcachegrind profiler your program
- void function(){
- //TODO
- //...
- ProfilerStart("CPUProfile");
- //TODO
- //...
- ProfilerStop();
- }
| 命令 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| ctrl+c | 暂停程序的运行 |
| c | 继续程序的运行 |
| b | 添加函数断点(参数可以是源代码中的行号或者一个函数名) |
| p | 打印某个量的值或者执行一个函数调用 |
for example:
gdb YOUR_PROGRAM // 启动 gdb 并选择你的程序为 gdb 的启动目标
(gdb)b main1.c:num // 对应于耗时模块的起始点
(gdb)b main1.c:num // 对应于耗时模块的终止点
(gdb)r // 运行
(gdb)p ProfilerStart("MyProfile")
(gdb)c // 继续程序运行
(gdb)p ProfilerStop()
这两个函数可以在任意两个点之间开始和结束,只要你的程序能捕捉到更多的点,随意添加都不会有太大的为题。
四,分析结果
1, pprof --text ./your_execute_file ./MyProfile
Using local file ./bin/nbd_google_pertools_n.
Using local file asyn_profile_2.
Removing _L_unlock_16 from all stack traces.
Total: 30 samples
2 6.7% 6.7% 2 6.7% *__GI___libc_malloc
1 3.3% 10.0% 1 3.3% *__GI___libc_free
1 3.3% 13.3% 1 3.3% _List_impl
1 3.3% 16.7% 1 3.3% _Vector_impl
1 3.3% 20.0% 1 3.3% __fdatasync_nocancel
1 3.3% 23.3% 1 3.3% __gnu_cxx::new_allocator::construct
1 3.3% 26.7% 1 3.3% __gnu_cxx::new_allocator::destroy
1 3.3% 30.0% 1 3.3% __mutex_alloc (inline)
1 3.3% 33.3% 1 3.3% __pthread_mutex_lock
1 3.3% 36.7% 1 3.3% boost::detail::shared_count::swap
1 3.3% 40.0% 1 3.3% boost::shared_ptr::operator->
1 3.3% 43.3% 1 3.3% boost::unordered_detail::hash_table::find
1 3.3% 46.7% 2 6.7% exec_implement::print_implement
1 3.3% 50.0% 1 3.3% execution_base::begin_incoming_ins_call
1 3.3% 53.3% 1 3.3% memcpy
......................................
具体每一项的意思你可以去查下tutorial
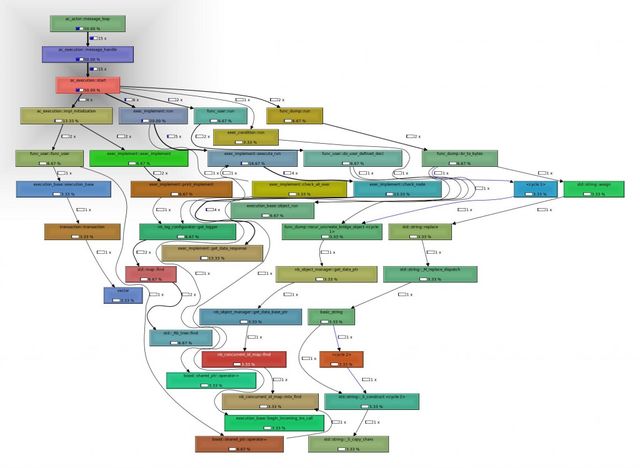
2, pprof --callgrind ./your_execute_file ./MyProfile >you_prifiler.callgrind
kcachegrind you_profiler.callgrind
注意事项:
由于perftools使用的是SIGPROF信号的handler来获取stack信息的,你的程序不能屏蔽signal,否则会出现以下情况:PROFILE: interrupts/evictions/bytes = 0/0/64,文件自然就不会有任何内容,因为我当初遇到过这样的问题,望各位不要重蹈覆辙。