jdk动态代理的情况下 前后置advice的调用过程分析 part1
这次要分析的是JdkDynamicAopProxy 中的invoke方法 因为AOP中 在target方法调用的前后 以及 异常时 调用各种advice的逻辑都在这个方法里
所以主要分析这个方法.
这个方法主要分两个步骤
1.获取到Interceptor链
2.执行方法调用
其中获取到Interceptor链是通过从advisor里面获取到advice的引用 用MethodInterceptor的实现类包装起来,存放在一个数组里
前置通知 用的是MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor类 后置通知用的是AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor类
执行方法调用则是调用了org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation 里面的proceed方法
递归的去处理每一个Interceptor 很巧妙的实现了前置advice在target方法之前执行 后置advice在target方法之后执行
下面就来分析一下这个过程 我可能有删减一些代码
我们的分析从JdkDynamicAopProxy 类的invoke方法方法开始
至于advice对象和advisor对象以及pointcut对象的生成 是Ioc的内容 具体这些对象的引用又是如何设置到AdvisedSupport类对象里面去的
下次再做分析 这些都不是很核心的逻辑
org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy 是AopProxy的一个实现类
用于获取AOP代理后的对象
invoke方法 就是代理后执行的方法
/**
* Implementation of <code>InvocationHandler.invoke</code>.
* <p>Callers will see exactly the exception thrown by the target,
* unless a hook method throws an exception.
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation invocation;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
//获取Interceptor链 这是比较核心的一步
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);
}
else {
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
//执行Interceptor链 这里是一个递归的过程
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
return retVal;
}
}
主要分析标黄的两行代码
1.获取Interceptor chain 用于在方法执行之前 或者之后执行
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
2.方法调用
retVal = invocation.proceed();
先看获取Interceptor chain
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
进入到org.springframework.aop.framework.AdvisedSupport类中 这个类AOP的一个根配置管理类 存储了AOP创建代理对象和执行interceptors所需的各种属性
比如
interfaces 创建代理对象所要实现的接口,
targetSource 持有真实对象引用的一个包装类 也是创建代理对象要用到的,
methodCache 一个list 存放了每个方法对应的interceptor链,
advisors 所有的advisor的一个集合
等等...
首先进入getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice方法
/**
* Determine a list of {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor} objects
* for the given method, based on this configuration.
* @param method the proxied method
* @param targetClass the target class
* @return List of MethodInterceptors (may also include InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatchers)
*/
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, Class targetClass) {
根据方法对象 生成cachekey 然后在缓存methodCache里面获取 如果能够获取到当前执行的这个方法对于的advisor chain 那么直接返回
MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached == null) {
如果获取不到 那么就要重新创建
cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
this, method, targetClass);
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
}
return cached;
}
下面进入到org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAdvisorChainFactory
这是一个工厂类 专门生成advice chain
这里传进来的config参数 就是上面讲到的 AdvisedSupport实例
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config, Method method, Class targetClass) {
// This is somewhat tricky... we have to process introductions first,
// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
创建一个list 长度就和AdvisedSupport实例 里面存储的advisors集合长度一样
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);
boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, targetClass);
//获取一个AdvisorAdapterRegistry 实例 用于后面把advice包装成Interceptor用的
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
//开始遍历
for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
在beans.xml里面配置的advisor 是DefaultPointcutAdvisor类型 也就是PointcutAdvisor的子类 所以这里是符合的
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// Add it conditionally.
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
开始把advisor的集合 转换成MethodInterceptor的数组 这里就用到AdvisorAdapterRegistry 了
具体转换的过程 后面会写到
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
开始做pointcut的方法名称匹配 用的是正则表达式
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) {
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
判断成功 但是mm.isRuntime()是false 这个isRuntime的含义还有待研究 然后 把每个method对于的interceptors添加到一个总的集合
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
最后返回这个集合
return interceptorList;
}
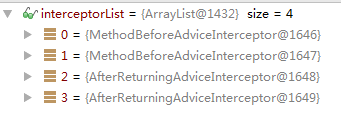
可以看到 返回的4个interceptor对象的集合
两个前置 两个后置 因为我在xml里是这样配置的
<bean id="studentProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="proxyInterfaces"> <value>com.test.aop.IStudent</value> </property> <property name="target"> <ref bean="targetStudent"/> </property> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>ReadingAdvisorBefore</value> <value>ReadingAdvisorBefore</value> <value>ReadingAdvisorAfter</value> <value>ReadingAdvisorAfter</value> </list> </property> </bean>
另外 这个过程中有一个advisor转换成Interceptor数组的过程 是这样的
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);
}
/**
* Adapter to enable {@link org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice}
* to be used in the Spring AOP framework.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
*/
class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
return (advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice);
}
public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
获取出advisor里面持有的advice对象
MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice) advisor.getAdvice();
然后用MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor这个类包装起来
return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice);
}
}
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
/**
* Create a new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor for the given advice.
* @param advice the MethodBeforeAdvice to wrap
*/
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor的构造方法很简单 就是把advice的引用传进来即可
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
这里就是后面调用前置后置通知的关键了 this.advice.before()调用了前置通知
mi.proceed(); 则重新回到proceed方法 开始执行下一个Interceptor 是递归的
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis() );
return mi.proceed();
}
}
好了至此就已经获取到 Interceptor chain 可以开始做调用了