Address space layout randomization
Address space layout randomization (ASLR) is a computer security method which involves randomly arranging the positions of key data areas, usually including the base of the executable and position of libraries, heap, and stack, in a process's address space.
Contents[hide]
|
[edit]Benefits
Address space randomization hinders some types of security attacks by making it more difficult for an attacker to predict target addresses. For example, attackers trying to execute return-to-libc attacks must locate the code to be executed, while other attackers trying to execute shellcode injected on the stack have to find the stack first. In both cases, the system obscures related memory-addresses from the attackers. These values have to be guessed, and a mistaken guess is not usually recoverable due to the application crashing.
[edit]Effectiveness
Address space layout randomization is based upon the low chance of an attacker guessing the locations of randomly-placed areas. Security is increased by increasing the search space. Thus, address space randomization is more effective when more entropy is present in the random offsets. Entropy is increased by either raising the amount of virtual memory area space over which the randomization occurs or reducing the period over which the randomization occurs. The period is typically implemented as small as possible, so most systems must increase VMA space randomization.
To defeat the randomization, attackers must successfully guess the positions of all areas they wish to attack. For data areas such as stack and heap, where custom code or useful data can be loaded, more than one state can be attacked by using NOP slides for code or repeated copies of data. This allows an attack to succeed if the area is randomized to one of a handful of values. In contrast, code areas such as library base and main executable need to be discovered exactly. Often these areas are mixed, for example stack frames are injected onto the stack and a library is returned into.
To begin, let us declare the following variables:
Where ![]() is the total amount of entropy:
is the total amount of entropy:
To calculate the probability of an attacker succeeding, we have to assume a number of attempts ![]() carried out without being interrupted by a signature-based IPS, law enforcement, or other factor; in the case of brute forcing, the daemon cannot be restarted. We also have to figure out how many bits are relevant and how many are being attacked in each attempt, leaving however many bits the attacker has to defeat.
carried out without being interrupted by a signature-based IPS, law enforcement, or other factor; in the case of brute forcing, the daemon cannot be restarted. We also have to figure out how many bits are relevant and how many are being attacked in each attempt, leaving however many bits the attacker has to defeat.
The following formulas represent the probability of success for a given set of ![]() attempts on
attempts on ![]() bits of entropy.
bits of entropy.
In many systems, ![]() can be in the thousands or millions; on modern 64-bit systems, these numbers typically reach the millions at least. For 32-bit systems at 2004 computer speeds which have 16 bits for address randomization, Shacham and co-workers state "… 16 bits of address randomization can be defeated by a brute force attack within minutes."[1] It should be noted that the authors' statement depends on the ability to attack the same application multiple times without any delay. Proper implementations of ASLR, like that included in grsecurity, provide several methods to make such brute force attacks infeasible. One method involves preventing an executable from executing for a configurable amount of time if it has crashed a certain number of times.
can be in the thousands or millions; on modern 64-bit systems, these numbers typically reach the millions at least. For 32-bit systems at 2004 computer speeds which have 16 bits for address randomization, Shacham and co-workers state "… 16 bits of address randomization can be defeated by a brute force attack within minutes."[1] It should be noted that the authors' statement depends on the ability to attack the same application multiple times without any delay. Proper implementations of ASLR, like that included in grsecurity, provide several methods to make such brute force attacks infeasible. One method involves preventing an executable from executing for a configurable amount of time if it has crashed a certain number of times.
Some systems implement Library Load Order Randomization, a form of ASLR which randomizes the order in which libraries are loaded. This supplies very little entropy. An approximation of the number of bits of entropy supplied per needed library appears below; this does not yet account for varied library sizes, so the actual entropy gained is really somewhat higher. Note that attackers usually need only one library; the math is more complex with multiple libraries, and shown below as well. Note that the case of an attacker using only one library is a simplification of the more complex formula for ![]() .
.
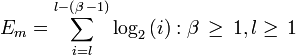
These values tend to be low even for large values of ![]() , most importantly since attackers typically can use only the C standard library and thus one can often assume that
, most importantly since attackers typically can use only the C standard library and thus one can often assume that ![]() . Interestingly, however, even for a small number of libraries there are a few bits of entropy gained here; it is thus potentially interesting to combine library load order randomization with VMA address randomization to gain a few extra bits of entropy. Note that these extra bits of entropy will not apply to other mmap() segments, only libraries.
. Interestingly, however, even for a small number of libraries there are a few bits of entropy gained here; it is thus potentially interesting to combine library load order randomization with VMA address randomization to gain a few extra bits of entropy. Note that these extra bits of entropy will not apply to other mmap() segments, only libraries.
[edit]Reducing entropy
Attackers may make use of several methods to reduce the entropy present in a randomized address space, ranging from simple information leaks to attacking multiple bits of entropy per attack (such as by heap spraying). There is little that can be done about this.
It is possible to leak information about memory layout using format string vulnerabilities. Format string functions such as printf use a variable argument listto do their job; format specifiers describe what the argument list looks like. Because of the way arguments are typically passed, each format specifier moves closer to the top of the stack frame. Eventually, the return pointer and stack frame pointer can be extracted, revealing the address of a vulnerable library and the address of a known stack frame; this can completely eliminate library and stack randomization as an obstacle to an attacker.
One can also decrease entropy in the stack or heap. The stack typically must be aligned to 16 bytes, and so this is the smallest possible randomization interval; while the heap must be page-aligned, typically 4096 bytes. When attempting an attack, it is possible to align duplicate attacks with these intervals; a NOP slide may be used with shellcode injection, and the string '/bin/sh' can be replaced with '////////bin/sh' for an arbitrary number of slashes when attempting to return to system. The number of bits removed is exactly ![]() for
for ![]() intervals attacked.
intervals attacked.
Such decreases are limited due to the amount of data in the stack or heap. The stack, for example, is typically limited to 8 MB[2] and grows to much less; this allows for at most 19 bits, although a more conservative estimate would be around 8–10 bits corresponding to 4–16 KB[2] of stack stuffing. The heap on the other hand is limited by the behavior of the memory allocator; in the case of glibc, allocations above 128 KB are created using mmap, limiting attackers to 5 bits of reduction. This is also a limiting factor when brute forcing; although the number of attacks to perform can be reduced, the size of the attacks is increased enough that the behavior could in some circumstances become apparent to intrusion detection systems.
[edit]History
The PaX project first coined the term "ASLR". It published the first design and implementation of ASLR in July 2001. This remains the most complete implementation, providing also kernel stack randomization from October 2002 onward. It also continues to provide the most entropy for each randomized layout compared to other implementations.[3]
[edit]Implementations
Several mainstream, general-purpose operating systems implement ASLR.
[edit]OpenBSD
Two years after ASLR was invented and published as part of PaX, a popular security patch for Linux, OpenBSD became the first mainstream operating system to support partial ASLR (and to activate it by default).[4] OpenBSD completed its ASLR support after Linux in 2008 when it added support for PIE binaries.[5]
[edit]Linux
Linux has enabled a weak form of ASLR by default since kernel version 2.6.12 (released June 2005).[6] The PaX and Exec Shield patchsets to the Linux kernel provide more complete implementations. Various Linux distributions including Adamantix, Alpine Linux, Hardened Gentoo, and Hardened Linux From Scratch come with PaX's implementation of ASLR by default.
The Exec Shield patch for Linux supplies 19 bits of stack entropy on a period of 16 bytes; and 8 bits of mmap base randomization on a period of 1 page of 4096 bytes. This places the stack base in an area 8 MB wide containing 524 288 possible positions; and the mmap base in an area 1 MB wide containing 256 possible positions.
Position-independent executable (PIE) implements a random base address for the main executable binary and has been in place since 2003. It provides the same address randomness to the main executable as being used for the shared libraries. The PIE feature is in use only for the network facing daemons – the PIE feature cannot be used together with the prelink feature for the same executable.
The prelink tool implements randomization at prelink time rather than runtime, because by design prelink aims to handle relocating libraries before the dynamic linker has to, which allows the relocation to occur once for many runs of the program. As a result, real address space randomization would defeat the purpose of prelinking.
[edit]Solaris
ASLR has been introduced in Solaris beginning with Solaris 11.1. ASLR in Solaris 11.1 can be set either by way of Zones or on a binary basis.[7]
[edit]Microsoft Windows
Microsoft's Windows Vista (released January 2007), Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 R2 have ASLR enabled by default, although only for those executables and dynamic link libraries specifically linked to be ASLR-enabled.[8] This did not include Internet Explorer 7 on Windows Vista prior to Service Pack 1; ASLR and Data Execution Prevention (DEP) are both disabled for application compatibility purposes.[9] Newer versions, including Internet Explorer 8 (released March 2009), enable these protections. A registry setting to forcibly enable or disable ASLR for all executables and libraries is found at "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\MoveImages".[10] ASLR can be disabled in Windows 7, by using the Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit provided by Microsoft, (the MoveImages registry setting has no effect in Windows 7[citation needed]).
The locations of the heap, stack, Process Environment Block, and Thread Environment Block are also randomized. A security whitepaper from Symantec noted that ASLR in 32-bit Windows Vista may not be as robust as expected, and Microsoft has acknowledged a weakness in its implementation.[11]
Host-based intrusion prevention systems such as WehnTrust[12] and Ozone[13] also offer ASLR for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 operating systems; however complete details of their implementation are not available.[14]
It was noted in February 2012[15] that ASLR on 32bit Windows systems prior to Windows 8 can have its effectiveness reduced in low memory situations.
[edit]Mac OS X
Apple introduced randomization of some library offsets in Mac OS X v10.5 (released October 2007).[16] Their implementation does not provide complete protection against attacks which ASLR is designed to defeat.[17][18][19][20] Mac OS X Lion 10.7 has improved ASLR implementation for all applications. Apple explains that "address space layout randomization (ASLR) has been improved for all applications. It is now available for 32-bit apps (as are heap memory protections), making 64-bit and 32-bit applications more resistant to attack."[21] Since OS X Mountain Lion 10.8 the kernel as well as kexts and zones are randomly relocated during system boot.[22]
[edit]iOS (iPhone, iPod touch, iPad)
Apple introduced ASLR in iOS 4.3.[23] Before Apple introduced ASLR in iOS 4.3, Stefan Esser made antid0te, a application to enable ASLR on the iPhone after theiPhone has jailbroken [24]
[edit]Android
Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich provides address space layout randomization (ASLR) to help protect system and third party applications from exploits due to memory-management issues. Position Independent Executable (PIE) support was added in Android 4.1.[25]
[edit]See also
- Buffer overflow
- Stack buffer overflow
- Stack-smashing protection
- NX bit