Android使用自己封装的Http和Thread、Handler实现异步任务
目录结构如下:
Http协议的封装:
使用http协议有request和response这两个主要的域,下边是Http协议封装的结构图
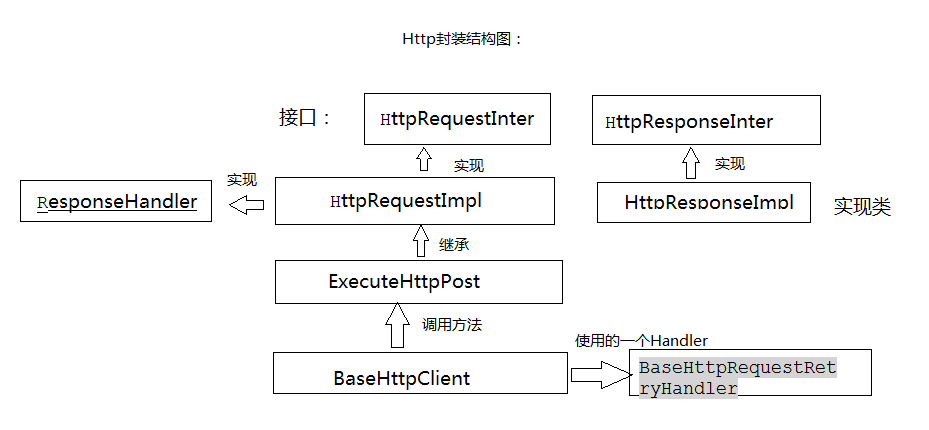
(1)HttpRequestInter.java:作为request域对象,应该可以获得客户端请求的地址和httpRequest对象,这样的话才可以获得客户端请求的参数等信息;另外public HttpResponseInter request() throws Exception; 使用这个方法,是当执行完request请求之后,返回一个response对象(这里用接口表示)
/** * 请求的接口 * @author xuliugen */
public interface HttpRequestInter {
//获得httpRequest
public HttpUriRequest getHttpRequest();
//获得http请求的url地址
public String getRequestURL();
//请求服务端:要返回一个response对象
public HttpResponseInter request() throws Exception;
}
(2)HttpResponseInter.java作为和(1)中相对应的response对象,应该具有的方法:获取返回的状态码、获取返回的流、获取返回返回的string数据等,下边的方法就是获取相应的数据
/** * 响应的接口 * @author xuliugen */
public interface HttpResponseInter {
//返回状态码
public int statusCode();
// 向客户端返回流数
public InputStream getResponseStream() throws IllegalStateException,IOException;
//向客户端返回字节数组
public byte[] getResponseStreamAsByte() throws IOException;
//向客户端返回JSON数据
public String getResponseStreamAsString() throws ParseException, IOException;
}
(3)这是HttpRequestImpl.java接口的实现类,我们可以看到我们不但实现了HttpRequestInter接口还实现了ResponseHandler 第二个就是用于当执行完request请求之后需要返回的数据,存放在一个response的Handler中。
public class HttpRequestImpl implements HttpRequestInter,ResponseHandler<HttpResponseInter> {
protected HttpUriRequest httpUriRequest;// 用于获取request的url地址
private AbstractHttpClient abstractHttpClient; // client对象
// 构造犯法
public HttpRequestImpl(AbstractHttpClient httpClient) {
this.abstractHttpClient = httpClient;
}
// get方法
public HttpUriRequest getHttpRequest() {
return httpUriRequest;
}
//获得request的url
public String getRequestURL() {
return httpUriRequest.getURI().toString();
}
//执行request请求,并返回�?个response对象接口
public HttpResponseInter request() throws Exception {
return abstractHttpClient.execute(httpUriRequest, this);//传入的ResponseHandler对象
}
/** * 继承ResponseHandler接口要实现的方法 * 执行完毕之后对response对象的处理接口 */
public HttpResponseInter handleResponse(HttpResponse response)throws ClientProtocolException, IOException {
//返回实现HttpResponseInter的类:返回给一个response接口
HttpResponseInter httpResponseInter = new HttpResponseImpl(response); //返回的时候需要response
return httpResponseInter;
}
}
(4)然后下边就是接口的实现类:HttpResponseImpl.java 可以在构造方法中看到一个HttpResponse response对象,这就是在执行完request之后的handler返回的response对象。
/** * 接口的实现类 * @author xuliugen */
public class HttpResponseImpl implements HttpResponseInter {
private HttpResponse response; // HttpResponse对象
private HttpEntity entity; // HttpEntity试题对象
public HttpResponseImpl(HttpResponse response) throws IOException {
this.response = response;
HttpEntity tempEntity = response.getEntity();// 获得服务器端返回的entity
if (null != tempEntity) {
entity = new BufferedHttpEntity(tempEntity);
}
}
// 返回response对象的状态码
public int statusCode() {
return response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
}
// 获得结果的stream
public InputStream getResponseStream() throws IllegalStateException,
IOException {
InputStream inputStream = entity.getContent();
return inputStream;
}
// 获得的结果转化为string
public String getResponseStreamAsString() throws ParseException,
IOException {
return EntityUtils.toString(entity);
}
// 获得的结果转化为字符数组
public byte[] getResponseStreamAsByte() throws IOException {
return EntityUtils.toByteArray(entity);
}
}
(5)ExecuteHttpPost.java这个类继承了HttpRequestImpl.java在里边主要写了两个构造方法,构造方法就是实际的进行post请求的方法,和参数的设置:
/** * 这里才是真正执行post请求的地�? * * 继承HttpRequestImpl 实现客户端向服务器端的请�? * * @author xuliugen * */
public class ExecuteHttpPost extends HttpRequestImpl {
public ExecuteHttpPost(AbstractHttpClient httpClient, String url) {
this(httpClient, url, null);
}
public ExecuteHttpPost(AbstractHttpClient httpClient, String url,HttpEntity entity) {
super(httpClient);//父类中的httpClient
this.httpUriRequest = new org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost(url);// 初始化httpUriRequest
if (null != entity) {// 设置参数
((HttpEntityEnclosingRequestBase) httpUriRequest).setEntity(entity);
}
}
}
(6)另外一个重要的类就是客户端的实现了:BaseHttpClient.java在这里边我们设置了一系列的方法,用于实现不同客户端的请求方法,以及如何将客户端请求的参数转化为post请求的参数类型、将返回的数据转化为相应的格式,方法的层叠调用,希望大家静下心慢慢看。
/** * HttpClient客户端的顶层类 */
public class BaseHttpClient {
private AbstractHttpClient httpClient;
public static final int DEFAULT_RETIES_COUNT = 5;
protected int retriesCount = DEFAULT_RETIES_COUNT;
// 设置最大连接数
public final static int MAX_TOTAL_CONNECTIONS = 100;
// 设置获取连接的最大等待时间
public final static int WAIT_TIMEOUT = 30000;
// 设置每个路由最大连接数
public final static int MAX_ROUTE_CONNECTIONS = 100;
// 设置连接超时时间
public final static int CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 10000;
// 设置读取超时时间
public final static int READ_TIMEOUT = 10000;
/** * 构造方法,调用初始化方法 */
public BaseHttpClient() {
initHttpClient();
}
/** * 初始化客户端参数 */
private void initHttpClient() {
//http的参数
HttpParams httpParams = new BasicHttpParams();
//设置最大连接数
ConnManagerParams.setMaxTotalConnections(httpParams,MAX_TOTAL_CONNECTIONS);
//设置获取连接的最大等待时间
ConnManagerParams.setTimeout(httpParams, WAIT_TIMEOUT);
//设置每个路由最大连接数
ConnPerRouteBean connPerRoute = new ConnPerRouteBean(MAX_ROUTE_CONNECTIONS);
ConnManagerParams.setMaxConnectionsPerRoute(httpParams, connPerRoute);
// 设置连接超时时间
HttpConnectionParams.setConnectionTimeout(httpParams, CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
// 设置读取超时时间
HttpConnectionParams.setSoTimeout(httpParams, READ_TIMEOUT);
HttpProtocolParams.setVersion(httpParams, HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1);
HttpProtocolParams.setContentCharset(httpParams, HTTP.UTF_8);
SchemeRegistry schemeRegistry = new SchemeRegistry();
schemeRegistry.register(new Scheme("http", PlainSocketFactory.getSocketFactory(), 80));//设置端口80
schemeRegistry.register(new Scheme("https", SSLSocketFactory.getSocketFactory(), 443));//设置端口443
//就是管理SchemeRegistry的
ClientConnectionManager clientConnectionManager = new ThreadSafeClientConnManager(httpParams, schemeRegistry);
httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(clientConnectionManager, httpParams);
//创建http重新连接的handler
httpClient.setHttpRequestRetryHandler(new BaseHttpRequestRetryHandler(retriesCount));
}
/** * 将参数转化为 List<BasicNameValuePair> 的集合 */
private List<BasicNameValuePair> parseParams(HashMap<String, Object> params) {
if (params == null || 0 == params.size()){
return null;
}
List<BasicNameValuePair> paramsList = new ArrayList<BasicNameValuePair>(params.size());
for (Entry<String, Object> entry : params.entrySet()) {
paramsList.add(new BasicNameValuePair(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue() + ""));
}
return paramsList;
}
/** * 向服务器端请求:当请求只有url 没有参数的时候 */
public String post(String url) throws Exception {
return post(url, null); //调用有参数的时候执行的post并将参数设置为null
}
/** * post请求之后返回T类型的结果 */
public <T> T post(String url, HashMap<String, Object> params, Class<T> clz) throws Exception {
String json = post(url, params);
return JSONUtil.fromJson(json, clz); //转化为具体的类型返回
}
/** * 当请求有参数的时候,其他函数间接调用该方法 */
public String post(String url, HashMap<String, Object> params) throws Exception {
//将传入的参数转化为参数实体:将params转化为enrity的对象:表单entity
UrlEncodedFormEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(parseParams(params));
return request(url, entity).getResponseStreamAsString();
}
/** * 将post执行的结果直接返回 */
public Result postAsResult(String url, HashMap<String, Object> params)throws Exception {
return post(url, params, Result.class);
}
/** * 将post执行的结果一Stream的形式返回 */
public InputStream postAsStream(String url, HashMap<String, Object> params) throws Exception {
//将传入的参数转化为参数实体
UrlEncodedFormEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(parseParams(params));
return request(url, entity).getResponseStream();
}
public HttpResponseInter request(String url, HttpEntity entity) throws Exception {
HttpRequestImpl httpRequestImpl = new ExecuteHttpPost(httpClient, url, entity);
return httpRequestImpl.request();
}
}
(7)最后一个就是我们在httpClient中使用的一个BaseHttpRequestRetryHandler.java用于实现网络重复请求的次数
/** * http重新尝试连接:主要用于完成尝试重新连接 * @author xuliugen */ public class BaseHttpRequestRetryHandler implements HttpRequestRetryHandler { private int max_retry_count;// 最大尝试连接的次数 public BaseHttpRequestRetryHandler(int maxretryCount) { this.max_retry_count = maxretryCount; } private static HashSet<Class<? extends IOException>> exceptionWhiteList = new HashSet<Class<? extends IOException>>(); private static HashSet<Class<? extends IOException>> exceptionBlackList = new HashSet<Class<? extends IOException>>(); static { exceptionWhiteList.add(NoHttpResponseException.class); exceptionWhiteList.add(UnknownHostException.class); exceptionWhiteList.add(SocketException.class); exceptionBlackList.add(SSLException.class); exceptionBlackList.add(InterruptedIOException.class); exceptionBlackList.add(SocketTimeoutException.class); } public boolean retryRequest(IOException exception, int executionCount,HttpContext context) { if (executionCount > max_retry_count){ return false; } if (exceptionBlackList.contains(exception.getClass())){ return false; } if (exceptionWhiteList.contains(exception.getClass())){ return true; } HttpRequest request = (HttpRequest) context.getAttribute(ExecutionContext.HTTP_REQUEST); boolean idempotent = (request instanceof HttpEntityEnclosingRequest); if (!idempotent) { // 濡傛灉璇锋眰琚涓烘槸骞傜瓑鐨勶紝閭d箞灏遍噸璇� return true; } Boolean b = (Boolean) context.getAttribute(ExecutionContext.HTTP_REQ_SENT); boolean sent = (b != null && b.booleanValue()); if (!sent) { return true; } return false; } } Service和AsyncTask的结合使用
大致流程如下:
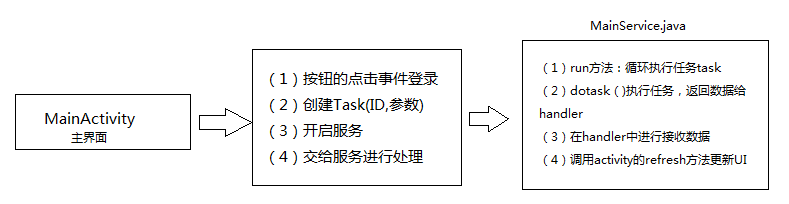
(1)我们将任务统一的交给Service进行处理,这样的话我们就需要一个Task实体
public class Task {
private int taskId;// 任务ID
private Map<String, Object> taskParams;// 参数
public static final int USER_LOGIN = 1; //自定义的一个任务ID
//构造方法和get、set方法省略
}
(2)下边就是统一管理Task的Service,在Service中我们不仅需要统一的管理Task即是异步任务,我们还需要负责管理更新界面的操作,因为更新界面的操作不能再住UI中进行,所以我们需要统一的管理activity,在Service中,我们执行异步任务的操作使用过Thread和Handler实现的。
public class MainService extends Service implements Runnable {
// 任务队列:用于存放任务的队列
private static Queue<Task> tasks = new LinkedList<Task>();
// 将需要更新的UI添加到集合中
private static ArrayList<Activity> appActivities = new ArrayList<Activity>();
private boolean isRun;// 是否运行线程
Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case Task.USER_LOGIN: {// 用户登录 :更新UI
//根据name找到activity:因为MAinActivity实现了MainActivityInter接口,所以可以强转为MainActivityInter类型
MainActivityInter activity = (MainActivityInter) getActivityByName("MainActivity");
activity.refresh(msg.obj.toString());
break;
}
default:
break;
}
};
};
/** * 添加任务到任务队列中 */
public static void newTask(Task t) {
tasks.add(t);
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
isRun = true;
Thread thread = new Thread(this);
thread.start();
super.onCreate();
}
/** * 让服务一直遍历执行 */
public void run() {
while (isRun) { // 去监听任务
Task task = null;
if (!tasks.isEmpty()) { // 判断队列中是否有值
task = tasks.poll();// 执行完任务后把改任务从任务队列中移除
if (null != task) {
doTask(task); // TO DO :执行任务
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
// 处理任务
private void doTask(Task task) {
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage();
msg.what = task.getTaskId();
switch (task.getTaskId()) {
case Task.USER_LOGIN: { // 用户登录
HashMap<String, Object> paramsHashMap = (HashMap<String, Object>) task.getTaskParams();
//访问网络,进行判断用户是否存在
String url = "http://172.23.252.89:8080/igouServ/userlogin.action";
BaseHttpClient httpClient = new BaseHttpClient();
try {
String result = httpClient.post(url, paramsHashMap);
msg.obj= result; //返回到handler进行处理
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
/** * 添加一个Activity对象到集合中 */
public static void addActivity(Activity activity) {
if (!appActivities.isEmpty()) {
for (Activity ac : appActivities) {
if (ac.getClass().getName().equals(ac.getClass().getName())) {
appActivities.remove(ac);
break;
}
}
}
appActivities.add(activity);
}
/** * 根据Activity的Name获取Activity对象 */
private Activity getActivityByName(String name) {
if (!appActivities.isEmpty()) {
for (Activity activity : appActivities) {
if (null != activity) {
if (activity.getClass().getName().indexOf(name) > 0) {
return activity;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
/** * 退出系统 */
public static void appExit(Context context) {
// Finish 所有的Activity
for (Activity activity : appActivities) {
if (!activity.isFinishing())
activity.finish();
}
// 结束 Service
Intent service = new Intent("com.xuliugen.frame.task.MainService");
context.stopService(service);
}
}
(3)为了可以让Service统一的管理activity的话,我们可以书写一个Interface接口MainActivityInter.java有两个方法,其中一个就是为了刷新界面,以便于我们在service中进行界面的操作
public interface MainActivityInter {
/** * 初始化操作 */
public void init();
/** * 刷新UI */
public void refresh(Object... params);
}测试步骤
(1)创建MainActivity.java 主要是为了模拟一次登录操作,在这里边我们需要开启服务,差UN该就爱弄一个任务,将任务加到Service管理的任务队列中去,然后其他的操作就交给MainService.java(Service)进行操作了。
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements MainActivityInter {
private Button btn_login;
private TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn_login = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn_login);
textView= (TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.textView1);
// 启动服务
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(this, MainService.class);
startService(serviceIntent);
btn_login.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
//构造参数传给Task进行处理
Map<String, Object> paramsHashMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(2);
paramsHashMap.put("userName", "xuliugen");
paramsHashMap.put("password", "123456");
Task task = new Task(Task.USER_LOGIN, paramsHashMap);
MainService.newTask(task);
}
});
// 将activity放入到activity队列集合中
MainService.addActivity(this);
}
/******************** 以下两个方法是MainActivityInter接口中的 ********************/
public void init() {
}
public void refresh(Object... params) {
//根据返回的参数进行更新UI
textView.setText(params[0].toString());
}
}
项目下载地址:https://github.com/xuliugen/HttpAndAsyncTaskFrame