第二十八天 单向链表
单向链表实现(1)
链表是在数据结构中经常见到的一种形式,实际上在Java中也可以通过引用传递的方式进行实现。
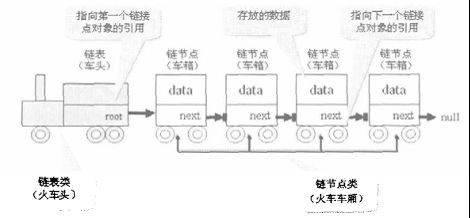
链表:所谓的链表就好像火车车厢一样,从火车头开始,每一节车厢之后都连着后一节车厢,如图:
每一节车厢就相当于一个节点,每一个节点除了要保存自己的内容外,还要保存下一个节点的引用,如图:
要想清楚的表示出一个节点之后还有另外一个节点,可以在一个节点的内部存放下一个节点的引用。
节点类:
class Node{
private String date;
private Node next;
public Node(String date){
this.date = date;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
每一个Node节点都有下一个Node对象的引用。
设置节点:
class LinkDemo01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node("火车头");
Node n1 = new Node("火车厢-A");
Node n2 = new Node("火车厢-B");
Node n3 = new Node("火车厢-C");
root.setNext(n1);
n1.setNext(n2);
n2.setNext(n3);
}
}
每一个节点都可以设置下一个节点,但是到第3个节点之后因为其不再有后续节点,所以不再单独设置关系。
节点的输出:判断一个节点之后是否还有后续节点,如果存在后续节点,则输出;如果不存在则不输出,所以输出可以使用方法的递归调用完成(递归调用就是自己调用自己),具体代码如下:
class LinkDemo02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node("火车头");
Node n1 = new Node("火车厢-A");
Node n2 = new Node("火车厢-B");
Node n3 = new Node("火车厢-C");
root.setNext(n1);
n1.setNext(n2);
n2.setNext(n3);
printNode(root);
}
public static void printNode(Node node){
System.out.print(node.getDate() + "\t");
if (node.getNext() != null) {
printNode(node.getNext());
}
}
}
1.1.1 单向链表实现(2)
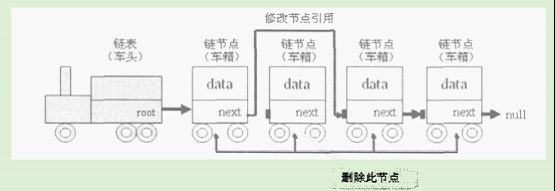
手工去处理各个节点的关系肯定会很麻烦,所以最好将节点的操作进行封装,这样用户使用起来就会比较方便。假设现在的节点操作有增加数据、查找数据、删除数据3种。如果要删除节点,则直接修改上一个节点的引用即可,如下图:
链表操作:
class Link{
class Node{
private String date;
private Node next;
public Node(String date){
this.date = date;
}
public void add(Node newNode){
if (this.next == null) {
this.next = newNode;
}else {
this.next.add(newNode);
}
}
public void print(){
System.out.println(this.date + "\t");
if (this.next != null) {
this.next.print();
}
}
public boolean search(String date){
if (date.equals(this.date)) {
return true;
}else {
if (this.next != null) {
return this.next.search(date);
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
public void delete(Node previous,String date){
if (date.equals(this.date)) {
previous.next = this.next;
}else {
if (this.next != null) {
this.next.delete(this,date);
}
}
}
}
private Node root;
public void addNode(String date){
Node newNode = new Node(date);
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = newNode;
}else {
this.root.add(newNode);
}
}
public void printNode(){
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.print();
}
}
public boolean contains(String name){
return this.root.search(name);
}
public void deleteNode(String date){
if (this.contains(date)) {
if (this.root.date.equals(date)) {
this.root = this.root.next;
}else {
this.root.next.delete(root, date);
}
}
}
}
class LinkDemo03{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Link l = new Link();
l.addNode("A");
l.addNode("B");
l.addNode("C");
l.addNode("D");
l.addNode("E");
System.out.println("==============删除之前============");
l.printNode();
l.deleteNode("C");
l.deleteNode("D");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("==============删除之后============");
l.printNode();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("查询节点:" + l.contains("A"));
}
}
运行结果:
==============删除之前============
A
B
C
D
E
==============删除之后============
A
B
E
查询节点:true
本文出自 “学习之家” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://5838311.blog.51cto.com/5828311/1017630