Mem系列函数与Str系列函数总结(二) memcmp与strcmp/strncmp
二 比较函数
函数名称:memcmp
函数原型:int memcmp (const void *S1, const void *S2, size_t size)
函数功能:用于比较内存数据S1与S2的前size个字符,如若相同,返回0
函数返回:如果S1,S2相同返回0,不相同返回-1
参数说明: S1―待比较内存数据1
S2―待比较内存数据2
size―比较内存数据个数
用法:
void main()
{
int nResult = -2;
int nCount = 12;
char * CMP1 = NULL;
char * CMP2 = NULL;
char *S1 = "Frankie is best!";
char *S2 = "Frankie is no good!";
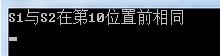
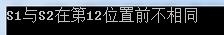
nResult = memcmp(S1,S2,nCount);
if(nResult == 0)
{
std::cout<<"S1与S2在第"<<nCount<<"位置前相同"<<std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout<<"S1与S2在第"<<nCount<<"位置前不相同"<<std::endl;
}
}
结果:
------------------------------------- 分界线------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
函数名称:memicmp
函数原型:int memicmp (const void *S1, const void *S2, size_t size)
函数功能:用于比较内存数据S1与S2的前size个字符,如若相同,返回0
特别注明:相对于memcmp而言,memicmp不区分字母大小写
函数返回:如果S1,S2相同返回0,不相同返回-1
用法:
void main()
{
int nResult = -2;
int nCount = 3;
char * S1 = "ABC";
char * S2 = "abc";
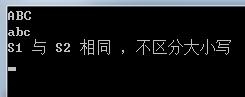
nResult = memicmp(S1,S2,nCount);
if(nResult == 0)
{
Out(S1);
Out(S2);
std::cout<<"S1 与 S2 相同 ,不区分大小写"<<std::endl;
}
}
结果:
------------------------------------- 分界线------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
函数名称:strcmp
函数原型:int strcmp(const char *S1,const char * S2);
函数功能:比较S1与S2字符串
函数返回:
当s1<s2时,返回为负数 注意不是-1
当s1==s2时,返回值= 0
当s1>s2时,返回正数 注意不是1
即:两个字符串自左向右逐个字符相比(按ASCII值大小相比较),直到出现不同的字符或遇'\0'为止。如:
"A"<"B" "a">"A" "computer">"compare"
特别注意:
strcmp(const char *s1,const char * s2)这里面只能比较字符串,不能比较数字等其他形式的参数。
参数说明:
S1:待比较字符串S1
S2:待比较字符串S2
用法:
void main()
{
int nResult = -2;
int nResult1 = -2;
int nResult2 = -2;
int nCount = 10;
char * CMP1 = NULL;
char * CMP2 = NULL;
char *S1 = "Frankie is best!";
char *S2 = "Frankie is no good!";
char *S3 = "A";
char *S4 = "B";
nResult = strcmp(S3,S4);
nResult1 = strcmp(S4,S3);
nResult2 = strcmp(S3,S3);
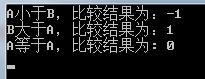
if(nResult == -1)
{
std::cout<<"A小于B,比较结果为:"<<nResult<<std::endl;
}
if(nResult1 == 1)
{
std::cout<<"B大于A,比较结果为:"<<nResult1<<std::endl;
}
if(nResult2 == 0)
{
std::cout<<"A等于A,比较结果为: "<<nResult2<<std::endl;
}
}
结果:
------------------------------------- 分界线------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
函数名称:strncmp
函数原型:int strncmp (const char *s1, const char *s2, size_t size)
函数功能:比较S1与S2字符串前size个字符的不同
函数返回:
此函数功能即比较字符串str1和str2的前maxlen个字符。如果前maxlen字节完全相等,返回值就=0;在前maxlen字节比较过程中,如果出现str1[n]与str2[n]不等,则返回(str1[n]-str2[n])。
用法:
void main()
{
int nResult = -2;
int nResult1 = -2;
int nResult2 = -2;
int nCount = 10;
char * CMP1 = NULL;
char * CMP2 = NULL;
char *S1 = "Frankie is best!";
char *S2 = "Frankie is no good!";
char *S3 = "ABCD";
char *S4 = "ABFC";
nResult = strncmp(S3,S4,3);
nResult1 = strncmp(S4,S3,3);
nResult2 = strncmp(S3,S3,3);
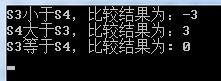
if(nResult != 0)
{
std::cout<<"S3小于S4,比较结果为:"<<nResult<<std::endl;
}
if(nResult1 != 0)
{
std::cout<<"S4大于S3,比较结果为:"<<nResult1<<std::endl;
}
if(nResult2 == 0)
{
std::cout<<"S3等于S4,比较结果为: "<<nResult2<<std::endl;
}
}
结果:
功能比较:
二者都可以用于字符串的比较,但是二者是有比较大的差异的:
因为strcmp是按照字节(byte-wise)比较的,并且比较的过程中会检查是否出现了"/0"结束符,一旦任意一个字符串指针前进过程中遇到结束符,将终止比较。
而memcmp函数是用于比较两个内存块的内容是否相等,在用于字符串比较时通常用于测试字符串是否相等,不常进行byte-wise的字符串比较。如果要比较的对象中包含一些由于边界对齐需求而填入结构对象中的空格、联合 (union)结束的额外空格、字符串所分配的空间未使用完的部分引起的“ ho les”的话,最好使用memcmp来完成。这些“holes”的内容是不确定的,在执行byte-wise比较时结果也是不明确的。
效率差异:
strcmp比较的字符串,而memcmp比较的是内存块,strcmp需要时刻检查是否遇到了字符串结束的 /0 字符,而memcmp则完全不用担心这个问题,所以memcmp的效率要高于strcmp