图像特效之三角几何应用
一:基本的三角函数知识

同样根据a, b的值可以计算出角度θ值,称之为反三角函数,角度θ=atan2(a, b)
图像处理中应用三角函数常常把中心点设置为A点,任意像素点B到A的距离可以根据三
角函数来计算得出,常见的计算模型如下:
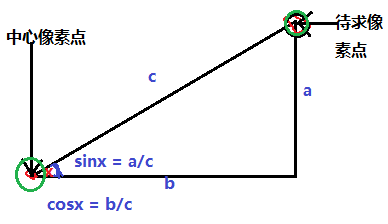
对待求像素点加以一定三角函数变化,可以实现很多意想不到的图形特效,中心像素点可以
通过以下计算获得
int centerX = width/2;
int centerY = height/2;
扫描到的像素点p(x, y)可以基于 中心像素点,角度θ,两点之间距离Radius可以通过如
下计算获得:
int trueX = col -centerX;
int trueY = row -centerY;
theta = Math.atan2((trueY),(trueX));
radius = Math.sqrt(trueX*trueX + trueY*trueY);
二:特效原理
实现的特效很简单,上述的三角几何中计算结果中,有两个可以改变其值再重新计算坐标
P(x,y)。一个是角度,另外一个是半径距离,分别对角度与距离加以一定权重值计算,得到
如下两种特效:
1. 哈哈镜效果,主要是改变半径值,计算方法如下:
double newRadius = Math.sqrt(radius) * factor;
newX = centerX + (newRadius * Math.cos(theta));
newY = centerY + (newRadius * Math.sin(theta));
其中factor为输入参数
2. 中心螺旋效果,主要是改变角度θ的值,计算方法如下:
newX = centerX + (radius * Math.cos(theta+degree * radius));
newY = centerY + (radius * Math.sin(theta+degree * radius));
其中degree为输入参数.
三:程序效果
哈哈镜效果:
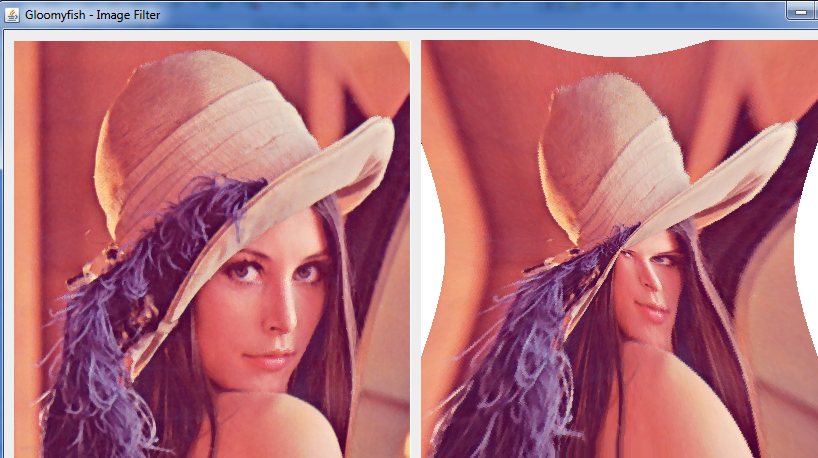
螺旋效果

两个滤镜程序的源代码如下:
1. Magic Mirror
package com.process.blur.study; import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; public class MagicMirrorFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp { private double factor = 15.0d; // default value public MagicMirrorFilter() { } public MagicMirrorFilter(double factor) { this.factor = factor; } public double getFactor() { return factor; } public void setFactor(double factor) { this.factor = factor; } @Override public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) { int width = src.getWidth(); int height = src.getHeight(); if ( dest == null ) dest = createCompatibleDestImage( src, null ); int[] inPixels = new int[width*height]; int[] outPixels = new int[width*height]; getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels ); int index = 0, outIndex = 0; int centerX = width/2; int centerY = height/2; double theta, radius; double newX, newY; int offsetX = 0, offsetY = 0; for(int row=0; row<height; row++) { int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0; for(int col=0; col<width; col++) { int trueX = col - centerX; int trueY = row - centerY; theta = Math.atan2((trueY),(trueX)); radius = Math.sqrt(trueX*trueX + trueY*trueY); double newRadius = Math.sqrt(radius) * factor; newX = centerX + (newRadius * Math.cos(theta)); newY = centerY + (newRadius * Math.sin(theta)); if (newX > 0 && newX < width) { offsetX = (int)newX; } else { newX = 0; } if (newY > 0 && newY < height) { offsetY = (int)newY; } else { newY = 0; } index = offsetY * width + offsetX; ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff; tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff; tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff; tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff; // use newX, newY and fill the pixel data now... outIndex = row * width + col; outPixels[outIndex] = (ta << 24) | (tr << 16) | (tg << 8) | tb; } } setRGB( dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels ); return dest; } } 2. Swirl
package com.process.blur.study; import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; public class SwirlFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp{ // recommended scope is [0.1 ~ 0.001] private double degree = 0.02d; // default value, public SwirlFilter() { } public double getDegree() { return degree; } public void setDegree(double degree) { this.degree = degree; } @Override public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) { int width = src.getWidth(); int height = src.getHeight(); if ( dest == null ) dest = createCompatibleDestImage( src, null ); int[] inPixels = new int[width*height]; int[] outPixels = new int[width*height]; getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels ); int index = 0, outIndex = 0; int centerX = width/2; int centerY = height/2; double theta, radius; double newX, newY; int offsetX = 0, offsetY = 0; for(int row=0; row<height; row++) { int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0; for(int col=0; col<width; col++) { int trueX = col - centerX; int trueY = row - centerY; theta = Math.atan2((trueY),(trueX)); radius = Math.sqrt(trueX*trueX + trueY*trueY); // the top trick is to add (degree * radius), generate the swirl effect... newX = centerX + (radius * Math.cos(theta + degree * radius)); newY = centerY + (radius * Math.sin(theta + degree * radius)); if (newX > 0 && newX < width) { offsetX = (int)newX; } else { offsetX = col; } if (newY > 0 && newY < height) { offsetY = (int)newY; } else { offsetY = row; } index = offsetY * width + offsetX; ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff; tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff; tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff; tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff; // use newX, newY and fill the pixel data now... outIndex = row * width + col; outPixels[outIndex] = (ta << 24) | (tr << 16) | (tg << 8) | tb; } } setRGB( dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels ); return dest; } }
转载文章请务必注明出处