解决报表中的复杂过程计算
复杂计算在大多报表开发中都会遇到,开发人员多采用复杂sql、存储过程或者自定义数据集的方式为报表准备数据,其编写难度往往让报表开发人员望而却步,报表开发效率不高。如何改善该类报表的开发现状成了摆在很多程序员面前的难题。
本文通过一个实例说明如何使用集算器改善复杂报表的开发过程。
需求说明
某网络平台需要监测查看一定周期内的用户状况,需要为运营部门出具日报、周报、月报、年报等报表,每类报表中均包含本期与上期、上上期数据比较,故涉及数据量较大。这里以其日报为例(月报年报只是统计周期不同),报表格式如下:

报表分为两部分,上半部分为用户明细数据(本期、上期、上上期在线时长均不为空),由于用户较多报表中只显示按本期在线时长排序后的前十名和后十名;下半部分为本期数据与上期、上上期的比较结果(允许本期、上期、上上期在线时长为空)。
报表工具直接完成的难点在于:
1、 业务本身导致的数据集sql复杂,其中涉及大量嵌套、连接以及判断等。
2、 两部分数据不一致,可以采用两种做法,一是基于同一数据集在报表中写表达式过滤,二是基于两个数据集分别计算。前者的缺点在于数据记录较多的情况报表表达式过滤效率较低,且涉及格间计算使得报表奇慢;后者的缺点在于数据要重复读取,由于数据量大和sql复杂,同样导致效率底下。两种方法需实测后进行选择。
3、 前后十名的显示,报表本来因为记录条数过多而只显示其中的前后各十条看似减轻了报表展现压力。其实不然,由于无法通过sql直接取前后十条数据,故需通过报表工具完成,而其实现要通过大量的隐藏行辅助完成。不仅如此,报表的第一列中“前十名”“后十名”在不同行(组)内,报表中实际要取两遍数据(隐藏条件不同),对于报表运行本身无疑雪上加霜。
润乾报表实现
我们看看用报表工具实现,以润乾报表为例(其他报表工具类似)。这里采用两个数据集的方式完成(实测后确定)。
数据集SQL
数据集ds1:
select a.userid,a.first_logout_time,b.onlinetime current_time,c.onlinetimelast_time,d.onlinetime last_last_time from (select v.userid, v.first_logout_time from t_dw_zx_valid_accountv where v.standard_7d_time is notnull) a, (select userid, sum(onlinetime) onlinetime, max(account) from t_dw_zx_account_status_day where logtime >= ? and logtime < ?+1 group by userid having max(account) is not null) b, (select userid, sum(onlinetime) onlinetime, max(account) from t_dw_zx_account_status_day where logtime >= ?-1 and logtime < ? group by userid having max(account) is not null) c, (select userid, sum(onlinetime) onlinetime, max(account) from t_dw_zx_account_status_day where logtime >= ?-1 - 1 and logtime < ?-1 group by userid having max(account) is not null) d where a.userid = b.userid(+) and a.userid = c.userid(+) and a.userid = d.userid(+) and b.onlinetime is not null and c.onlinetime is not null and d.onlinetime is not null order by b.onlinetime desc
数据集ds2:
select count(case when d.userid is not null and c.userid is not null then1 else null end)valid_user_conti_act , count(case whend.userid is not null and c.userid is not null and b.userid is nullthen 1 else null end)valid_user_conti_act_lost , count(case whena.first_logout_time >= ?-1 anda.first_logout_time < ? then 1 else null end) valid_user_add1 , count(case whenb.userid is null and a.first_logout_time >= ?-1 and a.first_logout_time < ? then 1 else null end) valid_user_add_lost , count(case whend.userid is null and c.userid is not null and a.first_logout_time< ?-1 then 1 else null end)valid_user_back , count(case whend.userid is null and c.userid is not null and a.first_logout_time< ?-1 and b.userid is null then 1 else null end) valid_user_back_lost from (select v.userid, v.first_logout_time from t_dw_zx_valid_accountv where v.standard_7d_time is notnull) a, (select userid, sum(onlinetime) onlinetime, max(account) from t_dw_zx_account_status_day where logtime >= ? and logtime < ?+1 group by userid having max(account) is not null) b, (select userid, sum(onlinetime) onlinetime, max(account) from t_dw_zx_account_status_day where logtime >= ?-1 and logtime < ? group by userid having max(account) is not null) c, (select userid, sum(onlinetime) onlinetime, max(account) from t_dw_zx_account_status_day where logtime >= ?-1 - 1 and logtime < ?-1 group by userid having max(account) is not null) d where a.userid = b.userid(+) and a.userid = c.userid(+) and a.userid = d.userid(+)
报表模板及表达式

集算器实现
报表工具直接实现存在的诸多问题能否在集算器中得到改善呢?下面来看一下。
集算器脚本
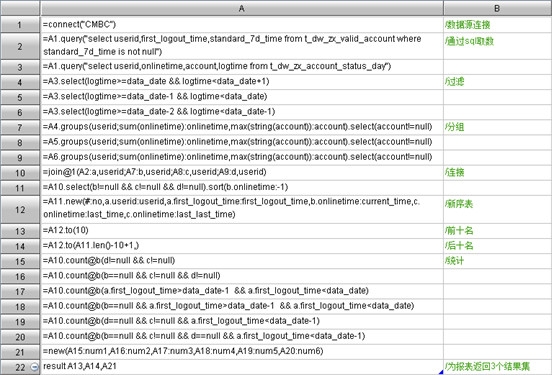
A4-A6:进行数据过滤;
A7-A9:按userid分组;
A10:将以上结果集进行关联;
A11:基于A10进行过滤后按在线时长排序;
A12:新序表,用于读取前后十名记录;
A13-A14:通过序号分别取前后十名记录;
A15-A20:计算汇总值;
A22:将前十名、后十名记录以及汇总值分别以不同结果集通过集算器JDBC返回给报表。
这里可以看到相对一整句复杂sql,集算器脚本可以分步编写,按照自然思维实现业务逻辑代码,较为清晰;而对于有序运算的有效支持使得取前后十名(A13、A14)非常容易;另外可为报表返回多个结果集解决了重复取数以及过于依赖隐藏行的问题。
报表调用
集算器只做数据计算,不负责展现,但集算器提供的JDBC可以为应用程序提供数据源支持,这里数据展现工作仍然由报表工具完成。
数据集设置

采用存储过程数据集接收集算器返回的三个结果集;类存储过程的调用方式,其中”cusInfo”为集算器脚本名称。
报表模板及表达式
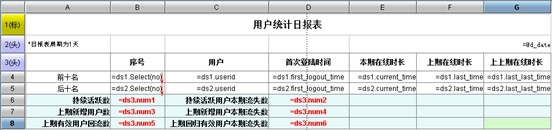
报表模板中只根据集算器的输出结果进行简单的展现即可,不再依赖任何隐藏行。
通过本例可以看到,报表复杂的的过程计算移植到集算器中后完全解决了上述提到的三个问题,报表只要做展现以及报表样式设计,减小了报表的开发难度和计算压力。