nginx:3、nginx反向代理,负载均衡,缓存及yum安装lnmp
前言
一、Nginx反向代理
二、Nginx负载均衡
三、Nginx页面缓存
四、LNMP
yum安装lnmp
五、Nginx读写分离
六、Nginx限速设置
七、Nginx生产中配置实例
八、
前言
在上篇博文中我们主要学习了nginx的安装,nginx配置、优化,nginx作为web服务器的操作讲解在这一篇博客中我们主要讲解, nginx的反向代理、负载均衡、缓存、URL重写以及读写分离详解。
一、Nginx之反向代理
1、正向代理与反向代理
(1).正向代理的概念
正向代理:是一个位于客户端和原始服务器(origin server)之间的服务器,为了从原始服务器取得内容,客户端向代理发送一个请求并指定目标(原始服务器),然后代理向原始服务器转交请求并将获得的内容返回给客户端。代理的是客户端,客户端必须要进行一些特别的设置才能使用正向代理。
(2).反向代理的概念
反向代理正好相反,代理的是服务器,并且客户端不需要进行任何特别的设置。客户端向反向代理的命名空间(name-space)中的内容发送普通请求,接着反向代理将判断向何处(原始服务器)转交请求,并将获得的内容返回给客户端,就像这些内容原本就是它自己的一样。
从安全性来讲:
正向代理允许客户端通过它访问任意网站并且隐藏客户端自身,因此你必须采取安全措施以确保仅为经过授权的客户端提供服务。反向代理对外都是透明的,访问者并不知道自己访问的是一个代理。
2.nginx 代理模块
这个模块可以转发请求到其他的服务器。HTTP/1.0无法使用keepalive(后端服务器将为每个请求创建并且删除连接)。nginx为浏览器发送HTTP/1.1并为后端服务器发送HTTP/1.0,这样浏览器就可以为浏览器处理keepalive。
如下例:
nginx作为反向代理服务器时工作特性:
接收客户端请求时,缓存在本地接收全部请求后再发往后端服务器;
接收后端服务器响应时,边接收边发送给客户端;而squid代理2个阶段都是边接收别发送
1.proxy_pass uri
用来定义协议内容:路径映射和uri
格式:
Syntax:proxy_pass URL;
Default: ―
Context:location, if in location, limit_except
Nginx通过proxy模块实现反向代理功能。在作为web反向代理服务器时,nginx负责接收客户请求,并能够根据URI、客户端参数或其它的处理逻辑将用户请求调度至上游服务器上(upstream server)。nginx在实现反向代理功能时的最重要指令为proxy_pass,它能够将location定义的某URI代理至指定的上游服务器(组)上。如下面的示例中,location的/uri将被替换为上游服务器上的/newuri。
location /bbs {
11 root /www/c.com/;
12 index index.html index.htm; #179为后端一台httpd服务器,本机180
13 proxy_pass #这里一定要带“/”
14 }
注意:这里http://192.168.100.179/ 这个“/”一定要带,不带的访问的是http://192.168.100.179/bbs/,而不是把“/bbs”映射成“/”
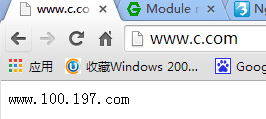
不过,这种处理机制中有两个例外:
一个是如果location的URI是通过模式匹配定义的,其URI将直接被传递至上游服务器,而不能为其指定转换的另一个URI。例如下面示例中的/forum将被代理为http://www.magedu.com/forum。
location ~ ^/bbs {
proxy_pass #此时这里后面不能带“/”否则会报错
}
第二个例外是,如果在loation中使用的URL重定向,那么nginx将使用重定向后的URI处理请求,而不再考虑上游服务器上定义的URI。如下面所示的例子中,传送给上游服务器的URI为
/index.php?page=<match>,而不是/index。
location / {
rewrite /(.*)$ /index.php?page=$1 break;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/index;
}
proxy模块的可用配置指令非常多,它们分别用于定义proxy模块工作时的诸多属性,如连接超时时长、代理时使用http协议版本等。下面对常用的指令做一个简单说明。
proxy_connect_timeout:nginx将一个请求发送至upstream server之前等待的最大时长;
proxy_cookie_domain:将upstream server通过Set-Cookie首部设定的domain属性修改为指定的值,其值可以为一个字符串、正则表达式的模式或一个引用的变量;
proxy_cookie_path: 将upstream server通过Set-Cookie首部设定的path属性修改为指定的值,其值可以为一个字符串、正则表达式的模式或一个引用的变量;
proxy_hide_header:设定发送给客户端的报文中需要隐藏的首部;
proxy_pass:指定将请求代理至upstream server的URL路径;
proxy_set_header:将发送至upsream server的报文的某首部进行重写;
proxy_redirect [default|off|redirect|replacement]:
当上游服务器返回的响应是重定向或刷新请求时,proxy_redirect会重写设定http首部的location或refresh;
proxy_send_timeout:在连接断开之前两次发送至upstream server的写操作的最大间隔时长;
proxy_read_timeout:在连接断开之前两次从接收upstream server接收读操作的最大间隔时长;
proxy_pass_header:发送给客户端的报文中不隐藏的首部;
porxy_pass_request_body:是否将http请求报文包体部分发往上游服务器
porxy_pass_request_header:是否将Http首部发往上游服务器
如下面的一个示例:
proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; #后端Http服务器记录日志时获取真是客户ip时在Nginx代理服务器上的设置,后端服务器也要做相应的设置 proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; #多次nginx转发时使用的? client_max_body_size 10m; client_body_buffer_size 128k; proxy_connect_timeout 30; proxy_send_timeout 15; proxy_read_timeout 15;
2.proxy_set_header
Syntax:proxy_set_header field(自定义变量名) value;
Default:proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header Connection close;
Context:http, server, location
3.proxy_http_version #指定版本可以使代理服务和后端服务是否使用长连接
Syntax: proxy_http_version 1.0 | 1.1;
Default:proxy_http_version 1.0;
Context:http, server, location
二、Nginx之负载均衡
upstream #定义服务器组,可以被proxy_pass,fastcgi_pass,uwsgi_pass调用
使用注意
1)只能用于http上下文
2)各server只能直接使用IP或域名,不需要协议
3)默认为加权轮询
使用方法:
1)先在主配置文件的http段定义upstream:
42 upstream webservers(自定义的组名字) {
43 server 192.168.100.179 weight=2;
44 server 192.168.100.175;
45 }
2)在server段中location段中调用:
20 location / {
21 #root /usr/share/nginx/html;
22 proxy_pass http://webservers/; #这里使用之前定义的组名,要加http://,组名后记得加"/"
23 index index.html index.htm;
24 }
格式:
server address [parametrs]
parametrs:
wight=#:设定权重
max_fails=#: 健康检查,最大失败尝试的次数,默认为1
fail_timeout=#:健康检查,失败尝试时长,默认为10s
down; 手动停止某节点,
backup: 标记为备用 当所有节点都故障时,此节点可以使用。 当使用ip_hash当所有服务器都当机时,不会自动启用该节点
大家想一下,如果不幸的是所有服务器都不能提供服务了怎么办,用户打开页面就会出现出错页面,那么会带来用户体验的降低,所以我们能不能像配置LVS是配置sorry_server呢,答案是可以的,但这里不是配置sorry_server而是配置backup。
upstream webservers {
server 192.168.100.179 weight=3 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=3 down;
server 192.168.100.175 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=3;
server 127.0.0.1:8080 backup;
least_conn;
}
server {
listen 80;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name alias another.alias;
server_name www.c.com c.com;
location / {
root /www/c.com/;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://webservers/;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
add_header X-Via $server_addr;
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
root /www/backup/;
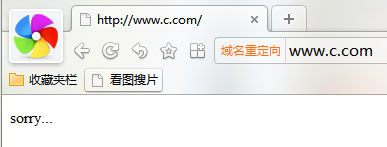
[root@BAIYU_180 nginx]# mkdir /www/backup
[root@BAIYU_180 nginx]# vi /www/backup/index.html
1 sorry...
将179,175的http服务都停止,此时访问www.c.com
还可以自定义健康检测():
health_check:自定义检测状态,只能用于location段,建议关闭访问日志
health_check [interval=time] [fails=number] [passes=number] [uri=uri] [math=name];
时间间隔默认5s 错误几次就将其标识为错误默认1次 通过几次就将其标识为正常,默认1此 访问的资源
math name {...} 用于http段中
调度算法:
Nginx的负载均衡模块调度算法
轮询(默认)。每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端某台服务器宕机,故障系统被自动剔除,使用户访问不受影响。Weight 指定轮询权值,Weight值越大,分配到的访问机率越高,主要用于后端每个服务器性能不均的情况下。
ip_hash。每个请求按访问IP的hash结果分配,这样来自同一个IP的访客固定访问一个后端服务器,有效解决了动态网页存在的session共享问题。
相当于lvs的sh算法,用来实现session绑定,与server address 一起使用
fair(第三方)。这是比上面两个更加智能的负载均衡算法。此种算法可以依据页面大小和加载时间长短智能地进行负载均衡,也就是根据后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。Nginx本身是不支持fair的,如果需要使用这种调度算法,必须下载Nginx的upstream_fair模块。
url_hash(第三方)。此方法按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,可以进一步提高后端缓存服务器的效率。Nginx本身是不支持url_hash的,如果需要使用这种调度算法,必须安装Nginx 的hash软件包。
least_conn 最少连接,相当于加权最少连接
一致性hash:
基于stick实现session绑定():
Syntax:sticky cookie name [expires=time] [domain=domain] [httponly] [secure] [path=path];
sticky route $variable ...;
sticky learn create=$variable lookup=$variable zone=name:size [timeout=time];
Default: ―
Context:upstream
This directive appeared in version 1.5.7.
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com;
server backend2.example.com;
sticky cookie srv_id expires=1h domain=.example.com path=/;
} 名称 过期时间 访问路径
keepalive #:定义长连接时间,用于后端服务器非http服务器时 只能用在upstream中
自定义响应首部:
add_header X-Via $server_addr; #在响应报文中添加子定义首部;向客户端说明代理服务器的ip
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status; #通知是否缓存命中
三、页面缓存
在反向代理场景中,nginx有一系列指令可用于定义其工作特性,如缓冲区大小等,给这些指令设定一个合理的值,可以有效提升其性能。
1)缓冲区设定
nginx在默认情况下在将其响应给客户端之前会尽可能地接收来upstream服务器的响应报文,它会将这些响应报文存暂存于本地并尽量一次性地响应给客户端。然而,在来自于客户端的请求或来自upsteam服务器的响应过多时,nginx会试图将之存储于本地磁盘中,这将大大降低nginx的性能。因此,在有着更多可用内存的场景中,应该将用于暂存这些报文的缓冲区调大至一个合理的值。
proxy_buffer_size size:设定用于暂存来自于upsteam服务器的第一个响应报文的缓冲区大小;
proxy_buffering on|off:启用缓冲upstream服务器的响应报文,否则,如果proxy_max_temp_file_size指令的值为0,来自upstream服务器的响应报文在接收到的那一刻将同步发送至客户端;一般情况下,启用proxy_buffering并将proxy_max_temp_file_size设定为0能够启用缓存响应报文的功能,并能够避免将其缓存至磁盘中;
proxy_buffers 8 4k|8k:用于缓冲来自upstream服务器的响应报文的缓冲区大小;
2)缓存
nginx做为反向代理时,能够将来自upstream的响应缓存至本地,并在后续的客户端请求同样内容时直接从本地构造响应报文。
proxy_cache zone|off:定义一个用于缓存的共享内存区域,其可被多个地方调用;缓存将遵从upstream服务器的响应报文首部中关于缓存的设定:
如 "Expires"、"Cache-Control: no-cache"、 "Cache-Control: max-age=XXX"、"private"和"no-store" 等,
但nginx在缓存时不会考虑响应报文的"Vary"首部。为了确保私有信息不被缓存,所有关于用户的私有信息可以upstream上通过"no-cache" or "max-age=0"来实现,也可在nginx设定proxy_cache_key必须包含用户特有数据如$cookie_xxx的方式实现,但最后这种方式在公共缓存上使用可能会有风险。因此,
在响应报文中含有以下首部或指定标志的报文将不会被缓存:
Set-Cookie
Cache-Control containing "no-cache", "no-store", "private", or a "max-age" with a non-numeric or 0 value
Expires with a time in the past
X-Accel-Expires: 0
proxy_cache_key:设定在存储及检索缓存时用于“键”的字符串,可以使用变量为其值,但使用不当时有可能会为同一个内容缓存多次;另外,将用户私有信息用于键可以避免将用户的私有信息返回给其它用户;
proxy_cache_lock:启用此项,可在缓存未命令中阻止多个相同的请求同时发往upstream,其生效范围为worker级别;
proxy_cache_lock_timeout:proxy_cache_lock功能的锁定时长;
proxy_cache_min_uses:某响应报文被缓存之前至少应该被请求的次数;
proxy_cache_path:定义一个用于保存缓存响应报文的目录,及一个保存缓存对象的键及响应元数据的共享内存区域(keys_zone=name:size),其可选参数有:
levels:每级子目录名称的长度,有效值为1或2,每级之间使用冒号分隔,最多为3级;
例如:levels=1:1:2 表示缓存目录是3层结构(最多只能有3层),1级目录名1个字符并且有16个,2级目录名1个字符并且有16个,3层目录名2个字符并且有256个
inactive:非活动缓存项从缓存中剔除之前的最大缓存时长;
max_size:缓存空间大小的上限,当需要缓存的对象超出此空间限定时,缓存管理器将基于LRU算法对其进行清理;
loader_files:缓存加载器(cache_loader)的每次工作过程最多为多少个文件加载元数据;
loader_sleep:缓存加载器的每次迭代工作之后的睡眠时长;
loader_threashold:缓存加载器的最大睡眠时长;
例如:
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/one levels=1 keys_zone=one:10m; proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/two levels=2:2 keys_zone=two:100m; proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/three levels=1:1:2 keys_zone=three:1000m;
proxy_cache_use_stale:在无法联系到upstream服务器时的哪种情形下(如error、timeout或http_500等)让nginx使用本地缓存的过期的缓存对象直接响应客户端请求;其格式为:
proxy_cache_use_stale error | timeout | invalid_header | updating | http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 | http_404 | off
proxy_cache_valid [ code ...] time:用于为不同的响应码设定不同时长的有效缓存时长,
例如:proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m;
proxy_cache_methods [GET HEAD POST]:为哪些请求方法启用缓存功能;
proxy_cache_bypass string:设定在哪种情形下,nginx将不从缓存中取数据;
例如:
proxy_cache_bypass $cookie_nocache $arg_nocache $arg_comment; proxy_cache_bypass $http_pragma $http_authorization;
4.proxy_cache_path
1)先在主配置文件的http段定义proxy_cache_path
proxy_cache_path /cache/nginx/ levels=1:1 keys_zone=mycache(名字):32m(大小); #只能在http段中定义
缓存路径(属主,属组要是nginx) 1级子目录的字符个数:2级子目录的字符个数
2)在server和location段中调用:
proxy_cache mycache(缓存文件名);
使用示例:
http {
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=STATIC:10m
inactive=24h max_size=1g;
server {
add_header X-Via $server_addr;
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
location / {
proxy_pass http://www.magedu.com;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache STATIC;
proxy_cache_valid 200 1d;
proxy_cache_valid 301 302 10m;
proxy_cache_vaild any 1m;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout invalid_header updating
http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
}
}
}
语法:proxy_cache_purge string ...; #缓存修剪方法,被请求的缓存将删除,
默认值:―
上下文:httpserver、location
语法:proxy_cache_revalidate on | off; #本地缓存过期后重新效验
默认值:proxy_cache_revalidate off;
上下文:http,server、location
此指令出现在版本 1.5.7 中。
Syntax:proxy_cache_use_stale error | timeout | invalid_header | updating | http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 | http_403 | http_404 | off ...; #哪种场景下使用已经过期的缓存来响应客户请求
Default:
proxy_cache_use_stale off;
Context:http, server, location
Syntax:proxy_cache_valid [code ...] time; #通过响应码来自定义缓存时长
Default:―
Context:http, server, location
四、动静分离
1)图片和其它文件分离
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.100.179;
}
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$ {
proxy_pass http://192.168.100.175;
}
2).php文件和其它文件分离
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.100.179;
}
location ~* \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass http://xxx;
}
五、LNMP
naginx服务器自己提供静态内容服务
对php的请求通过fastcgi模块代理至php-fpm模块
fastcgi:nginx与php
uwsgi:nginx与pathon
http:nginx与jsp
cgi:nginx与perl
1、安装
[root@BAIYU_180 ~]# yum install php-fpm php-mysql mysql-server mysql nginx
注意:这里不需要安装php,
2、整合nginx和php5
1)编辑/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf启用如下选项:
location ~ \.php$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
fastcgi模块的常用指令:
fastcgi_pass:指定fastcgi服务监听端口、地址、也支持使用 Uxin socket
fastcgi_bind 指定连接fpm服务时使用的地址
fastcgi_param: 定义传递给fpm的参数
fastcgi_index:php的主页面文件
结果是可以缓存的:
缓存空间使用proxy_cache_path也可以使用fastcgi_cache_path定义的,通过fastcgi_cache调用
2)编辑/etc/nginx/fastcgi_params,将其内容更改为如下内容:
fastcgi_param GATEWAY_INTERFACE CGI/1.1; fastcgi_param SERVER_SOFTWARE nginx; fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string; fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method; fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type; fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri; fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_URI $document_uri; fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root; fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol; fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr; fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port; fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr; fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port; fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name;
3)修改/etc/nginx/conf.d/virtual.conf主页面格式中添加php格式的主页,类似如下:
location / {
root html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
3、启动并测试
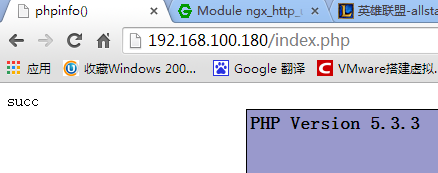
[root@BAIYU_180 php-fpm.d]# service php-fpm start 正在启动 php-fpm:[确定] [root@BAIYU_180 php-fpm.d]# netstat -nlptu Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 27487/nginx tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 27487/nginx tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1338/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1172/master tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 30106/php-fpm [root@BAIYU_180 php-fpm.d]# service nginx configtest nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful [root@BAIYU_180 php-fpm.d]# service nginx start 正在启动 nginx:[确定] [root@BAIYU_180 php-fpm.d]# service mysql start [root@BAIYU_180 nginx]# cd /usr/share/nginx/html/ [root@BAIYU_180 html]# ls 404.html 50x.html index.html nginx-logo.png poweredby.png [root@BAIYU_180 html]# vi index.php 1 <?php phpinfo(); ?>
.php资源使用,fastcgi_pass反向代理,fastcgi_cache定义缓存,用法和proxy_pass,proxy_cache一样
fastcgi_cache_path
fastcgi_cache
fastcgi_cache_vaild
fastcgi_connect_timeout:连接fastcgi服务器的超时时长
fastcgi_send_timeout: 向fastcgi服务器传输数据的超时时长
$fastcgi_script_name
location ~ \.php$ {
84 root /www/a.com/;
85 fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
86 fastcgi_index index.php;
87 fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
88 include fastcgi_params;
89 fastcgi_cache fcgi;
90 fastcgi_cache_valid 200 1h;
91 fastcgi_cache_valid 301 302 5m;
92 fastcgi_cache_valid any 1m;
93 }
六、nginx限速配置
nginx的限速功能通过limit_zone、limit_conn和limit_rate指令进行配置。首先需要在http上下文配置一个limit_zone,然后在需要的地方使用limit_conn和limit_rate 进行限速设置。下面是一个简单的例子。
http {
limit_zone first $binary_remote_addr 10m;
server {
location /downloads/ {
limit_conn first 1;
limit_rate 50k;
}
}
}
说明:
limit_zone:语法格式“limit_req_zone $variable zone=name:size rate=rate;”,实现针对每个IP定义一个存储session状态的容器。这个示例中定义了一个名叫first的10m大小的容器,这个名字会在后面的limit_conn中使用。
limit_conn first 1; 限制在first中记录状态的每个IP只能发起一个并发连接。
limit_rate 50k; 对每个连接限速50k. 注意,这里是对连接限速,而不是对IP限速。如果一个IP允许三个并发连接,那么这个IP就是限速为limit_rate×3,在设置的时候要根据自己的需要做设置调整,要不然会达不到自己希望的目的。
限制连接数的配置如下所示:
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=perip:10m;
limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=perserver:10m;
server {
...
limit_conn perip 10;
limit_conn perserver 100;
}
七、一个完整配置例(生产环境中使用)
user nobody nobody;
worker_processes 4;
worker_rlimit_nofile 51200;
error_log logs/error.log notice;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 51200;
}
http {
server_tokens off; #关闭软件版本信息
include mime.types;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host; #http请求报文中host首部;如果请求中没有host首部,则以处理此请求的主机的主机名代替
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; #记录多级代理的ip?
client_max_body_size 20m; #客户端单个大小最大为20m
client_body_buffer_size 256k; #内存中缓存的大小
proxy_connect_timeout 90; #连接后端服务器超时时间
proxy_send_timeout 90; #后端服务器发送响应报文超时时间
proxy_read_timeout 90; #读取...
proxy_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_buffers 4 64k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 128k;
default_type application/octet-stream;
charset utf-8;
client_body_temp_path /var/tmp/client_body_temp 1 2;
proxy_temp_path /var/tmp/proxy_temp 1 2;
fastcgi_temp_path /var/tmp/fastcgi_temp 1 2;
uwsgi_temp_path /var/tmp/uwsgi_temp 1 2;
scgi_temp_path /var/tmp/scgi_temp 1 2;
ignore_invalid_headers on;
server_names_hash_max_size 256;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
client_header_buffer_size 8k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
connection_pool_size 256;
request_pool_size 64k;
output_buffers 2 128k;
postpone_output 1460;
client_header_timeout 1m;
client_body_timeout 3m;
send_timeout 3m;
log_format main '$server_addr $remote_addr [$time_local] $msec+$connection '
'"$request" $status $connection $request_time $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
open_log_file_cache max=1000 inactive=20s min_uses=1 valid=1m;
access_log logs/access.log main;
log_not_found on;
sendfile on;
tcp_nodelay on;
tcp_nopush off;
reset_timedout_connection on;
keepalive_timeout 105;
keepalive_requests 100;
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_min_length 1024;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth no_last_modified no_etag;
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml application/json;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.(?!.*SV1)";
upstream tomcat8080 {
ip_hash;
server 172.16.100.103:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2;
server 172.16.100.104:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2;
server 172.16.100.105:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.magedu.com;
# config_apps_begin
root /data/webapps/htdocs;
access_log /var/logs/webapp.access.log main;
error_log /var/logs/webapp.error.log notice;
location / {
location ~* ^.*/favicon.ico$ {
root /data/webapps;
expires 180d;
break;
}
if ( !-f $request_filename ) {
proxy_pass http://tomcat8080;
break;
}
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 8088;
server_name nginx_status;
location / {
access_log off;
deny all;
return 503;
}
location /status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow 172.16.100.71;
deny all;
}
}
}
八、X-Forwarded-For
先来看一下X-Forwarded-For的定义:
X-Forwarded-For:简称XFF头,它代表客户端,也就是HTTP的请求端真实的IP,只有在通过了HTTP 代理或者负载均衡服务器时才会添加该项。它不是RFC中定义的标准请求头信息,
标准格式如下:
X-Forwarded-For: client1, proxy1, proxy2
从标准格式可以看出,X-Forwarded-For头信息可以有多个,中间用逗号分隔,
第一项为真实的客户端ip,剩下的就是曾经经过的代理或负载均衡的ip地址,经过几个就会出现几个。
当经过多个nginx代理时,其X-Forwarded-For头信息应该为客户端IP,Nginx1,Nginx2,、、、。
在默认情况下,Nginx并不会对X-Forwarded-For头做任何的处理,除非用户使用proxy_set_header 参数设置:
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for变量包含客户端请求头中的"X-Forwarded-For",与$remote_addr用逗号分开,如果没有"X-Forwarded-For" 请求头,则此时$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for等于$remote_addr。
$remote_addr变量的值是客户端的IP
当Nginx设置X-Forwarded-For等于$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for后会有两种情况发生
1、如果从Nginx1过来的请求没有设置X-Forwarded-For头(通常这种事情不会发生),而到了Nginx2设置将X-Forwarded-For设置为$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for的话,那么X-Forwarded-For的信息头应该为Nginx1的IP,因为相对于Nginx2负载均衡来说客户端即为Nginx1,这样的话,后端的web程序时死活也获得不了真实用户的IP的。
2、如果Nginx1设置了X-Forwarded-For,到了Nginx2我们这里又设置了一次,且值为$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for的话,那么X-Forwarded-For的内容变成 ”客户端IP,Nginx1负载均衡服务器IP“如果是这种情况的话,那后端的程序通过X-Forwarded-For获得客户端IP,则取逗号分隔的第一项即可。
如上两点所说,如果我们知道了Nginx1设置了X-Forwarded-For信息,且只有客户端真实的IP的话,那么我们的Nginx2负载均衡服务器可以不必理会该头,让它默认即可。
其实Nginx中还有一个$http_x_forwarded_for变量,这个变量中保存的内容就是请求中的X-Forwarded-For信息。如果后端获得X-Forwarded-For信息的程序兼容性不好的话(没有考虑到X-Forwarded-For含有多个IP的情况),最好就不要将X-Forwarded-For设置为$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for。应该设置为$http_x_forwarded_for或者干脆不设置!