linux-IPC进程通信-管道

管道是Linux支持的最初Unix IPC形式之一。
管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动;
一个管道只能负责一个方向的数据传输。
需要双方通信时,需要建立起两个管道;
只能用于父子进程或者兄弟进程之间(具有亲缘关系的进程);
假如进程A与进程b通信,需要建立两个管道:
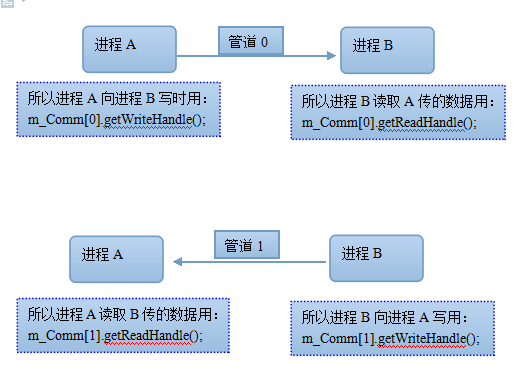
一个管道只能用于一个方向的通信,其另外的方向需要关闭.
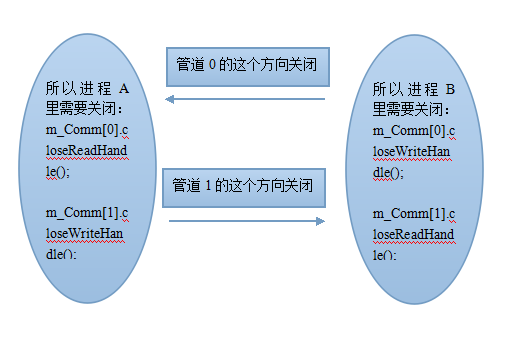
所以,假如A为父进程,B为子进程,那么父进程需关闭:
void CloseInParent(void)
{
m_Comm[0].closeReadHandle();
m_Comm[1].closeWriteHandle();
}
子进程需要关闭:
void CloselnSub(void)
{
m_Comm[0].closeWriteHandle();
m_Comm[1].closeReadHandle();
}
父进行进行读取需要的handle,即A需要的:
SOCKET getParentReadHandle(void) { return m_Comm[1].getReadHandle(); }
SOCKET getParentWriteHandle(void) { return m_Comm[0].getWriteHandle(); }
子进程进行读取需要的handle,即B需要的:
SOCKET getSubReadHandle(void) { return m_Comm[0].getReadHandle(); }
SOCKET getSubWriteHandle(void) { return m_Comm[1].getWriteHandle(); }
对Unix网络编程-进程通信书里管道例子进行编码,两个进程,子进程发文件名给父进程,父进程返回子进程文件内容:
头文件
#ifndef CPIPE_H
#define CPIPE_H
#include <cstddef>
#define SOCKET int
#define INVALID_SOCKET (SOCKET)(~0)
class YPipe
{
public:
YPipe(void);
~YPipe(void) { close(); }
bool open(bool boCanbeInherit = false);
void close(void) { closeReadHandle(); closeWriteHandle(); }
int read(void * lpBuff,size_t nLength);
int write(const void * lpBuff,size_t nLength);
SOCKET getReadHandle(void) const { return m_nPipe[READHANDLE_INDEX]; }
SOCKET getWriteHandle(void) const { return m_nPipe[WRITEHANDLE_INDEX]; }
void closeReadHandle(void) { closeImp(READHANDLE_INDEX); }
void closeWriteHandle(void) { closeImp(WRITEHANDLE_INDEX); }
protected:
enum
{
READHANDLE_INDEX = 0,
WRITEHANDLE_INDEX = 1,
};
void closeImp(int nIndex);
SOCKET m_nPipe[2];
};
class YPipePair
{
public:
YPipePair(void);
~YPipePair(void);
bool initEx(void);
void close(void)
{
m_Comm[0].close();
m_Comm[1].close();
}
void CloseInParent(void)
{
m_Comm[0].closeReadHandle();
m_Comm[1].closeWriteHandle();
}
void CloselnSub(void)
{
m_Comm[0].closeWriteHandle();
m_Comm[1].closeReadHandle();
}
SOCKET getParentReadHandle(void) { return m_Comm[1].getReadHandle(); }
SOCKET getParentWriteHandle(void) { return m_Comm[0].getWriteHandle(); }
SOCKET getSubReadHandle(void) { return m_Comm[0].getReadHandle(); }
SOCKET getSubWriteHandle(void) { return m_Comm[1].getWriteHandle(); }
protected:
enum
{
MASTER_2_SUBMGR = 0x00,
SUBMGR_2_MASTER = 0x01,
};
YPipe m_Comm[2];
};
#endif // CPIPE_H
//源文件
#include "cpipe.h"
#include <unistd.h>
YPipe::YPipe(void)
{
m_nPipe[0] = INVALID_SOCKET;
m_nPipe[1] = INVALID_SOCKET;
}
void YPipe::closeImp(int nIndex)
{
if (m_nPipe[nIndex] != INVALID_SOCKET)
::close(m_nPipe[nIndex]);
m_nPipe[nIndex] = INVALID_SOCKET;
}
bool YPipe::open(bool boCanbeInherit)
{
if (pipe(m_nPipe) == -1)
return false;
// m_nPipe[0] = CMX_Network_Function::checkAndChangeSocketID(m_nPipe[0]);
// m_nPipe[1] = CMX_Network_Function::checkAndChangeSocketID(m_nPipe[1]);
return true;
}
int YPipe::read(void * lpBuff,size_t nLength)
{
if (m_nPipe[READHANDLE_INDEX] == INVALID_SOCKET)
return -1;
return ::read(m_nPipe[READHANDLE_INDEX],lpBuff,nLength);
}
int YPipe::write(const void * lpBuff,size_t nLength)
{
if (m_nPipe[WRITEHANDLE_INDEX] == INVALID_SOCKET)
return -1;
return ::write(m_nPipe[WRITEHANDLE_INDEX],lpBuff,nLength);
}
YPipePair::YPipePair(void)
{
}
YPipePair::~YPipePair(void)
{
}
bool YPipePair::initEx(void)
{
YPipePair::close();
if (!m_Comm[SUBMGR_2_MASTER].open())
return false;
else if (!m_Comm[MASTER_2_SUBMGR].open())
return false;
}
main.cpp
#include "cpipe.h"
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <sys/stat.h>;
#include <fcntl.h>;
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <iostream>
void jobInSub(YPipePair &tp)
{
std::string strPath = "/home/cmy3/test.txt\n";
int a = write(tp.getSubWriteHandle(), strPath.c_str(), strPath.size());
char buf[1024];
int n = 0;
while ( ( n =read(tp.getSubReadHandle(),buf, 1024) )>0 ) //对方的写管道close的时候,才会返回0,所以对方记得要close
{
write(STDOUT_FILENO,buf, n);
}
}
void jobInParent(YPipePair &tp)
{
char buf[1024];
int n;
n =read(tp.getParentReadHandle(),buf, 1024) ;
buf[n]='\0';
int fileFd;
std::string strPath = "/home/cmy3/test.txt";
if( (fileFd = open(strPath.c_str(), O_RDONLY))<0 )
{
snprintf(buf+n,sizeof(buf)-n, ":cannot open,%s\n", strerror(errno));
n=strlen(buf);
write(tp.getParentWriteHandle(), buf, n);
}
else
{
while ( ( n =read(fileFd,buf, 1024) )>0 )
{
write(tp.getParentWriteHandle(),buf, n);
}
close(fileFd);
}
tp.close(); //记得要close
// ::close( tp.getParentWriteHandle() ); //记得要close
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
YPipePair tp;
tp.initEx();
int forkPid;
if( (forkPid = fork() )==0) //child
{
tp.CloselnSub();
jobInSub(tp); //send the filepath to parent ,and recv the file content
exit(0); //must exit , if not ,go ahead
}
tp.CloseInParent();
jobInParent(tp); //recv the filepath from sub, and send the file content
waitpid(0, NULL, 0);
std::cout<<"exitparent"<<std::endl;
exit(0);
return 0;
}