rsync+inotify实现实时同步案例
随着应用系统规模的不断扩大,对数据的安全性和可靠性也提出的更好的要求,rsync在高端业务系统中也逐渐暴露出了很多不足,首先,rsync同步数据时,需要扫描所有文件后进行比对,进行差量传输。如果文件数量达到了百万甚至千万量级,扫描所有文件将是非常耗时的。而且正在发生变化的往往是其中很少的一部分,这是非常低效的方式。其次,rsync不能实时的去监测、同步数据,虽然它可以通过linux守护进程的方式进行触发同步,但是两次触发动作一定会有时间差,这样就导致了服务端和客户端数据可能出现不一致,无法在应用故障时完全的恢复数据。基于以上原因,rsync+inotify组合出现了!
1.1 inotify介绍
2.1 rsync+inotify同步逻辑图
3.1 环境部署
4.1 inotify-slave部署
4.1.1检查是否安装rsync
4.1.2 新建rsync用户及模块目录并更改其用户组
4.1.3 编写rsync daemon配置文件/etc/rsyncd.conf
4.1.4 配置虚拟用户的密码文件
4.1.5 启动rsync 服务
4.1.6 通过inotify-master测试推送
5.1 inotify-master部署
5.1.1 查看当前系统是否支持inotify
5.1.2 下载inotify源码包并编译安装
5.1.3 inotify之inotifywait命令常用参数详解
5.1.4 编写监控脚本并加载到后台执行
5.1.5 实时同步测试
1.1 inotify介绍
inotify是一种强大的、细粒度的、异步的文件系统事件控制机制。linux内核从2.6.13起,加入了inotify支持,通过inotify可以监控文件系统中添加、删除、修改、移动等各种事件,利用这个内核接口,第三方软件就可以监控文件系统下文件的各种变化情况,而inotify-tools正是实施监控的软件。
2.1 rsync+inotify同步逻辑图
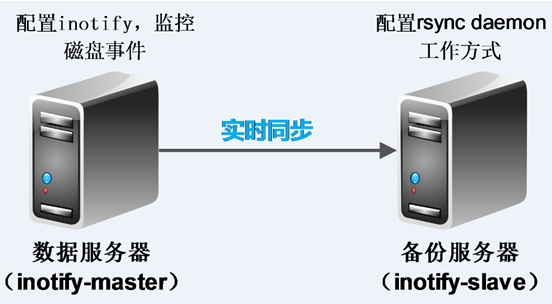
3.1 环境部署
主机名 |
主机IP地址 |
系统版本 |
系统内核版本 |
inotify-master |
192.168.1.128 |
CentOS release 6.4 (Final) |
2.6.32-358.el6.x86_64 |
inotify-slave |
192.168.1.160 |
CentOS release 6.4 (Final) |
2.6.32-358.el6.x86_64 |
4.1 inotify-slave部署
这里就是部署rsync服务,rsync daemon工作模式。
4.1.1检查是否安装rsync
1 2 |
[root@inotify-slave ~]# rpm -aq rsync rsync-3.0.6-9.el6.x86_64 |
4.1.2 新建rsync用户及模块目录并更改其用户组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
[root@inotify-slave mail]# useradd rsync -s /sbin/nologin -M #添加rsync用户 [root@inotify-slave mail]# grep rsync /etc/passwd rsync:x:2004:2004::/home/rsync:/sbin/nologin [root@inotify-slave mail]# mkdir /backup #创建rsync daemon工作模式的模块目录 [root@inotify-slave mail]# ll -d /backup/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 4月 22 14:13 /backup/ [root@inotify-slave mail]# chown rsync.rsync /backup/ #更改模块目录的用户组 [root@inotify-slave mail]# ll -d /backup/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 rsync rsync 4096 4月 22 14:13 /backup/ |
4.1.3 编写rsync daemon配置文件/etc/rsyncd.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
[root@inotify-slave /]# cat /etc/rsyncd.conf ##rsyncd.conf start## #工作中指定用户(需要指定用户) uid = rsync gid = rsync #相当于黑洞.出错定位 use chroot = no #有多少个客户端同时传文件 max connections = 200 #超时时间 timeout = 300 #进程号文件 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid #日志文件 lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock #日志文件 log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #模块开始 #这个模块对应的是推送目录 #模块名称随便起 [backup] #需要同步的目录 path = /backup/ #表示出现错误忽略错误 ignore errors #表示网络权限可写(本地控制真正可写) read only = false #这里设置IP或让不让同步 list = false #指定允许的网段 hosts allow = 192.168.1.0/24 #拒绝链接的地址,一下表示没有拒绝的链接。 hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32 #不要动的东西(默认情况) #虚拟用户 auth users = rsync_backup #虚拟用户的密码文件 secrets file = /etc/rsync.password #配置文件的结尾 #rsync_config_______________end |
4.1.4 配置虚拟用户的密码文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
[root@inotify-slave /]# echo "rsync_backup:leesir" >/etc/rsync.password [root@inotify-slave /]# cat /etc/rsync.password rsync_backup:leesir #注:rsync_backup为虚拟用户,leesir为这个虚拟用户的密码 [root@inotify-slave /]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password #为密码文件提权,增加安全性 [root@inotify-slave /]# ll /etc/rsync.password -rw-------. 1 root root 20 4月 22 14:20 /etc/rsync.password |
4.1.5 启动rsync 服务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
[root@inotify-slave /]# rsync --daemon #启动rsync服务 [root@inotify-slave /]# ps -ef |grep rsync root 14871 1 0 14:24 ? 00:00:00 rsync --daemon root 14873 14788 0 14:24 pts/0 00:00:00 grep rsync [root@inotify-slave /]# netstat -lnutp |grep rsync tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 14871/rsync tcp 0 0 :::873 :::* LISTEN 14871/rsync |
4.1.6 通过inotify-master测试推送
inotify-master配置密码文件,测试推送
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
[root@inotify-master ~]# echo "leesir" >/etc/rsync.password [root@inotify-master ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password leesir #注意:这里只要写密码即可,切记。 [root@inotify-master ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password [root@inotify-master ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password -rw------- 1 root root 7 4月 22 14:32 /etc/rsync.password [root@inotify-master ~]# echo "hello leesir">test.txt [root@inotify-master ~]# cat test.txt hello leesir [root@inotify-master ~]# rsync -avz test.txt [email protected]::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password sending incremental file list test.txt sent 82 bytes received 27 bytes 72.67 bytes/sec total size is 13 speedup is 0.12 |
inotify-slave检查:
1 2 3 4 5 |
[root@inotify-slave /]# ll /backup/ 总用量 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 13 4月 22 14:34 test.txt [root@inotify-slave /]# cat /backup/test.txt hello leesir |
5.1 inotify-master部署
注:
inotify是rsync客户端安装和执行的
企业场景压力测试200-300个同步限制,受网卡,磁盘,带宽等的制约。
5.1.1 查看当前系统是否支持inotify
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
[root@inotify-master ~]# ll /proc/sys/fs/inotify/ 总用量 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 4月 22 14:56 max_queued_events -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 4月 22 14:56 max_user_instances -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 4月 22 14:56 max_user_watches #显示这三个文件则证明支持。 |
拓展:
/proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_evnets
表示调用inotify_init时分配给inotify instance中可排队的event的数目的最大值,超出这个值的事件被丢弃,但会触发IN_Q_OVERFLOW事件。
/proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances
表示每一个real user ID可创建的inotify instatnces的数量上限。
/proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
表示每个inotify instatnces可监控的最大目录数量。如果监控的文件数目巨大,需要根据情况,适当增加此值的大小。
例如: echo 30000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
5.1.2 下载inotify源码包并编译安装
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
root@inotify-master tools]# wget http://github.com/downloads/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz #下载inotify源码包 .................................. root@inotify-master tools]# ll inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 358772 3月 14 2010 inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz [root@inotify-master tools]# tar zxf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz [root@inotify-master tools]# cd inotify-tools-3.14 [root@inotify-master inotify-tools-3.14]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/inotify-3.14 #配置inotify,并指定安装路径为/usr/local/inotify-3.14 ................................ [root@inotify-master inotify-tools-3.14]# make && make install ................................ |
5.1.3 inotify之inotifywait命令常用参数详解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
[root@inotify-master inotify-tools-3.14]# cd /usr/local/inotify-3.14/ [root@inotify-master inotify-3.14]# ./bin/inotifywait --help -r|--recursive Watch directories recursively. #递归查询目录 -q|--quiet Print less (only print events). #打印监控事件的信息 -m|--monitor Keep listening for events forever. Without this option, inotifywait will exit after one event is received. #始终保持事件监听状态 --excludei <pattern> Like --exclude but case insensitive. #排除文件或目录时,不区分大小写。 --timefmt <fmt> strftime-compatible format string for use with %T in --format string. #指定时间输出的格式 --format <fmt> Print using a specified printf-like format string; read the man page for more details. #打印使用指定的输出类似格式字符串 -e|--event <event1> [ -e|--event <event2> ... ] Listen for specific event(s). If omitted, all events are listened for. #通过此参数可以指定需要监控的事件,如下所示: Events: access file or directory contents were read #文件或目录被读取。 modify file or directory contents were written #文件或目录内容被修改。 attrib file or directory attributes changed #文件或目录属性被改变。 close file or directory closed, regardless of read/write mode #文件或目录封闭,无论读/写模式。 open file or directory opened #文件或目录被打开。 moved_to file or directory moved to watched directory #文件或目录被移动至另外一个目录。 move file or directory moved to or from watched directory #文件或目录被移动另一个目录或从另一个目录移动至当前目录。 create file or directory created within watched directory #文件或目录被创建在当前目录 delete file or directory deleted within watched directory #文件或目录被删除 unmount file system containing file or directory unmounted #文件系统被卸载 |
5.1.4 编写监控脚本并加载到后台执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
[root@inotify-master scripts]# cat inotify.sh #!/bin/bash #para host01=192.168.1.160 #inotify-slave的ip地址 src=/backup/ #本地监控的目录 dst=backup #inotify-slave的rsync服务的模块名 user=rsync_backup #inotify-slave的rsync服务的虚拟用户 rsync_passfile=/etc/rsync.password #本地调用rsync服务的密码文件 inotify_home=/usr/local/inotify-3.14 #inotify的安装目录 #judge if [ ! -e "$src" ] \ || [ ! -e "${rsync_passfile}" ] \ || [ ! -e "${inotify_home}/bin/inotifywait" ] \ || [ ! -e "/usr/bin/rsync" ]; then echo "Check File and Folder" exit 9 fi ${inotify_home}/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f' -e close_write,delete,create,attrib $src \ | while read file do # rsync -avzP --delete --timeout=100 --password-file=${rsync_passfile} $src $user@$host01::$dst >/dev/null 2>&1 cd $src && rsync -aruz -R --delete ./ --timeout=100 $user@$host01::$dst --password-file=${rsync_passfile} >/dev/null 2>&1 done exit 0 [root@inotify-master scripts]# sh inotify.sh & #将脚本加入后台执行 [1] 13438 [root@inotify-master scripts]# |
5.1.5 实时同步测试
inotify-master操作:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
[root@inotify-master scripts]# cd /backup/ [root@inotify-master backup]# ll 总用量 0 [root@inotify-master backup]# for a in `seq 200`;do touch $a;done #创建200个文件 [root@inotify-master backup]# ll --time-style=full-iso 总用量 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.141497569 +0800 1 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.172497529 +0800 10 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.235497529 +0800 100 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.236497529 +0800 101 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.237497529 +0800 102 ................................... |
inotify-slave检查
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
[root@inotify-slave backup]# ll --time-style=full-iso 总用量 0 -rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.393823754 +0800 1 -rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.393823754 +0800 10 -rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.393823754 +0800 100 -rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.393823754 +0800 101 -rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 2014-04-22 15:34:08.393823754 +0800 102 .......................... |