C++学习笔记(四)
前言
本篇是《C++ Primer》的学习笔记,以及自己尝试实现数据结构Vector的部分功能,借此练习动态数组操作,同时介绍一种使用VS 2013进行内存泄露检测的方法。
动态数组
1、申请动态数组
默认情况下,new 分配的对象,不管是单个分配的还是数组中的,都是默认初始化的。可以对数组中的元素进行值初始化,方法是在大小之后跟一对空括号。
int *pia = new int[10]; // 10个未初始化的int int *pib = new int[10](); // 10个值初始化为0的int string *psa = new string[10]; // 10个空string string *psb = new string[10](); // 同上
在C++ 11标准中,可以提供一个元素初始化器的花括号列表:
int *pic = new int[10]{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
// 10个string,前4个用给定的初始化器初始化,剩余进行值初始化
string *psc = new string[10]{"a","an","the",string(3,'x')};
注意初始化器数目不能大于元素数目,否则new 表达式失败,抛出异常。
动态分配一个空数组是合法的。
char arr[0]; // 错误:不能定义长度为0的数组 char *cp = new char[0]; // 正确,返回一个合法的非空指针,但不能解引用
2、释放动态数组
为了释放动态数组,我们必须在delete后面使用[],注意指针p是指向一个T对象数组的首元素,而不是一个类型为T的单一对象。
delete p; // 错误,p必须是指向一个动态分配的对象或者为空(null) delete[] p; // 正确,p必须是指向一个动态分配的数组或者为空(null)
即
T *a = new T(); delete a; T *b = new T[n]; delete[] b;
数组中的元素按逆序销毁,最后一个元素首先被销毁,然后是倒数第二个,依此类推。
为了避免内存泄露,在new 动态内存使用完毕后,必须将其归还给系统,即delete。
int i, *pi1 = &i, *pi2 = nullptr; double *pd = new double(33), *pd2 = pd; delete i; // 错误,i不是一个指针 delete pi1; // 未定义:pi1指向一个局部变量 delete pd; // 正确 delete pd2; // 未定义:pd2指向的内存已经被释放了 delete pi2; // 正确:释放一个空指针总是没有错误的
内存泄露与检测
内存泄露的关键就是记录分配的内存和释放内存的操作,看看能不能匹配。跟踪每一块内存的声明周期,例如:每当申请一块内存后,把指向它的指针加入到List中,当释放时,再把对应的指针从List中删除,到程序最后检查List就可以知道有没有内存泄露了。Window平台下的Visual Studio调试器和C运行时(CRT)就是用这个原理来检测内存泄露。
在VS中使用时,加上
#define _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC #include <crtdbg.h> #ifdef _DEBUG //重载new #define new new(_NORMAL_BLOCK, __FILE__, __LINE__) #endif
_CrtDumpMemoryLeaks(); 函数将显示当前内存泄露,也就是说程序运行到此行代码时的内存泄露,所有未销毁的对象都会报出内存泄露,因此要让这个函数尽量放到最后。
#define _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC
#include <crtdbg.h>
#ifdef _DEBUG //重载new
#define new new(_NORMAL_BLOCK, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#endif
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
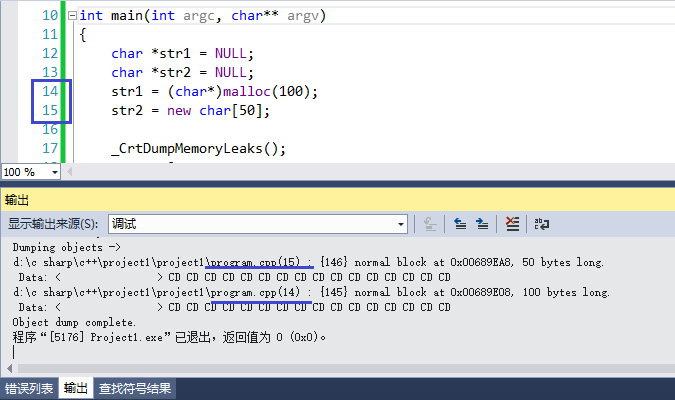
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
char *str1 = NULL;
char *str2 = NULL;
str1 = (char*)malloc(100);
str2 = new char[50];
_CrtDumpMemoryLeaks();
return 0;
}
运行上述代码,会在VS“输出(Output)”模块看到哪里出现内存泄露了,也就是申请动态内存后忘记释放。
数据结构Vector实现
练习动态数组操作,最好的题目就是重现数据结构vector,考察指针操作、内存泄露、泛型等重要知识点。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
#define log(message) cout<< message <<endl
#define nullptr NULL
#define DEFAULT_VALUE 0
/************************VS 2013检查内存泄露***************************/
#define _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC
#include <crtdbg.h>
#ifdef _DEBUG //重载new
#define new new(_NORMAL_BLOCK, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#endif
/************************VS 2013检查内存泄露***************************/
class VectorInt
{
private:
int *arr = nullptr;
int size = 10;
int count = 0;
int resize_times = 2;
public:
VectorInt();
VectorInt(int size);
VectorInt(const VectorInt& other);
~VectorInt() { delete[] arr; arr = nullptr; }
int Count() { return count; }
bool Empty() { return count == 0; }
int Get(int i);
void Add(int value);
};
VectorInt::VectorInt()
{
arr = new int[size];
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(int)*size); // The elements' initial value is 0.
}
VectorInt::VectorInt(int size)
{
if (size < 0)
{
log("The parameter 'size' is less than Zero.");
return;
}
this->size = size;
arr = new int[size]; // if size == 0 then arr = null.
}
VectorInt::VectorInt(const VectorInt& other)
{
while (size < other.count)
{
size = size * resize_times + 1;
}
delete[] arr;
arr = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < other.count; i++)
{
arr[i] = other.arr[i];
}
}
int VectorInt::Get(int i)
{
if (count <= 0 || arr == nullptr || size == 0)
{
log("The vector is Empty.");
return DEFAULT_VALUE;
}
if (i >= count || i < 0)
{
log("The parameter 'i' is out of range.");
return DEFAULT_VALUE;
}
return arr[i];
}
void VectorInt::Add(int value)
{
if (arr == nullptr)
{
log("The Vector is Error!");
return;
}
if (size <= count + 1)
{
size = size * resize_times + 1;
}
VectorInt TempVec(size);
memcpy(TempVec.arr, arr, sizeof(int)*count);
int *TempArr = arr;
arr = TempVec.arr;
TempVec.arr = TempArr;
arr[count] = value;
count++;
}
void TestMemoryLeak()
{
int *a = new int[10];
// memset按Byte处理,int共4 Byte,处理完x01010101,即16843009
memset(a, 1, sizeof(int)* 10);
cout << a[2] << endl;
delete[] a;
a = nullptr;
VectorInt vec;
cout << "vec.Count() == " << vec.Count() << endl;
cout << vec.Get(-1) << endl;
cout << vec.Get(2) << endl;
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
vec.Add(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < vec.Count(); i++)
{
cout << vec.Get(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl << endl;
cout << vec.Get(7) << endl;
cout << vec.Get(-1) << endl;
cout << vec.Get(1000) << endl;
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
vec.Add(-i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < vec.Count(); i++)
{
cout << vec.Get(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
TestMemoryLeak();
_CrtDumpMemoryLeaks();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Reference
C++内存泄露和检测