在传输层上压缩WebService的请求和响应
在传输层上压缩WebService的请求和响应
场景
场景是这样的:客户端.NET 3.5应用程序,WCF实现WebService调用, 服务端Java,通过CXF提供WebService。 有一个方法提供了有一个字符串类型的参数,实际生产环境里会传100k以上的字符串。在并发量比较大的情况下,带宽占用很严重。所以寻找一种可以把传输的SOAP消息在客户端压缩,服务端解压缩的方法。
这里提供的方式在是客户端通过WCF的MessageEncoder机制对所有的SOAP请求消息压缩,SOAP响应消息解压缩,反过来在服务端通过一个Filter对所有的SOAP请求消息,对SOAP响应消息压缩。
请求的流程如下:
Client -> SOAP Request -> GzipMessageEncoder -> gzip binary -> GzipWebSericeFilter -> SOAP Request -> CXF
响应的流程如下:
CXF -> SOAP Response -> GzipWebServiceFilter -> gzip binary -> GzipMessageEncoder -> SOAP Response -> Client
其中.NET的WCF的GzipMessageEncoder是参照 WCF的Samples, 下载解压后路径WF_WCF_Samples\WCF\Extensibility\MessageEncoder\Compression
客户端
下面先来看一下客户端部分的代码:
GZipMessageEncoderFactory.cs 这文件主要是提供GZipMessageEncoder,在里面通过重写ReadMessage和WriteMessage方法来实现压缩和解压缩。 实际压缩和解压处理是使用GZipStream实现的。
下面是GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement.cs 这里的GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement类是为了在app.config里添加配置项。
然后我们就可以把这个GZipMessageEncodingElement配置到app.config里了
客户端最后的部分就是调用webservice, 这里的压缩和解压对于调用者和陪调用者是透明的。也就是同没有压缩和解压之前的使用方法一样。
服务端
服务端是一个Filter,和HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse的包装类。
入口:GzipWebServiceFilter.java
这里就是判断contentType,如果是gzip的就用GzipHttpServletRequestWrapper和GzipHttpServletResponseWrapper包装原始的Request和Response以实现压缩和解压缩。
GzipHttpServletRequestWrapper
GzipHttpServletResponseWrapper
这里做的主要事情就是在Resquest的getInputStream和Response的getOutputStream是返回一个拥有GZip功能的Stream,来代替原始的Stream。通过原始的Stream仍然是最终的输入和输出源。
然后在web.xml中把这个Filter作用于原来的WebService的Servlet
web.xml
webservice的配置和cxf原来的一样
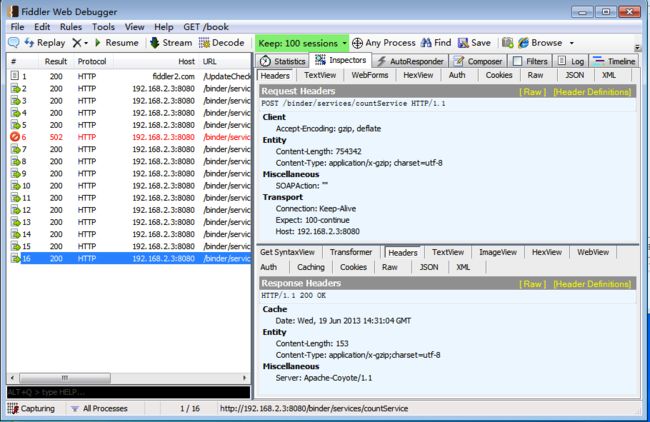
如果你想看一下实际的HTTP请求和响应是什么样子的可以用Fiddler Web Debugger来查看
本文的源代码在附件中。
本文的方案没有在最终的被用于生产环境,一个原因是比较复杂,另外一个是服务器在对大XML进行unmarshal的效率并不高。单本文的方案的好处就是不用对原有的webservice接口和实现进行修改。 最后在实际场景用我们使用 MTOM来解决问题的, 后面我还会写一篇文章来介绍这个方法。
场景
场景是这样的:客户端.NET 3.5应用程序,WCF实现WebService调用, 服务端Java,通过CXF提供WebService。 有一个方法提供了有一个字符串类型的参数,实际生产环境里会传100k以上的字符串。在并发量比较大的情况下,带宽占用很严重。所以寻找一种可以把传输的SOAP消息在客户端压缩,服务端解压缩的方法。
这里提供的方式在是客户端通过WCF的MessageEncoder机制对所有的SOAP请求消息压缩,SOAP响应消息解压缩,反过来在服务端通过一个Filter对所有的SOAP请求消息,对SOAP响应消息压缩。
请求的流程如下:
Client -> SOAP Request -> GzipMessageEncoder -> gzip binary -> GzipWebSericeFilter -> SOAP Request -> CXF
响应的流程如下:
CXF -> SOAP Response -> GzipWebServiceFilter -> gzip binary -> GzipMessageEncoder -> SOAP Response -> Client
其中.NET的WCF的GzipMessageEncoder是参照 WCF的Samples, 下载解压后路径WF_WCF_Samples\WCF\Extensibility\MessageEncoder\Compression
客户端
下面先来看一下客户端部分的代码:
GZipMessageEncoderFactory.cs 这文件主要是提供GZipMessageEncoder,在里面通过重写ReadMessage和WriteMessage方法来实现压缩和解压缩。 实际压缩和解压处理是使用GZipStream实现的。
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
//This class is used to create the custom encoder (GZipMessageEncoder)
internal class GZipMessageEncoderFactory : MessageEncoderFactory
{
readonly MessageEncoder _encoder;
//The GZip encoder wraps an inner encoder
//We require a factory to be passed in that will create this inner encoder
public GZipMessageEncoderFactory(MessageEncoderFactory messageEncoderFactory)
{
if (messageEncoderFactory == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("messageEncoderFactory", "A valid message encoder factory must be passed to the GZipEncoder");
_encoder = new GZipMessageEncoder(messageEncoderFactory.Encoder);
}
//The service framework uses this property to obtain an encoder from this encoder factory
public override MessageEncoder Encoder
{
get { return _encoder; }
}
public override MessageVersion MessageVersion
{
get { return _encoder.MessageVersion; }
}
//This is the actual GZip encoder
class GZipMessageEncoder : MessageEncoder
{
private const string GZipMediaType = "application/x-gzip";
private const string GZipContentType = GZipMediaType + "; charset=utf-8";
//This implementation wraps an inner encoder that actually converts a WCF Message
//into textual XML, binary XML or some other format. This implementation then compresses the results.
//The opposite happens when reading messages.
//This member stores this inner encoder.
readonly MessageEncoder _innerEncoder;
//We require an inner encoder to be supplied (see comment above)
internal GZipMessageEncoder(MessageEncoder messageEncoder)
{
if (messageEncoder == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("messageEncoder", "A valid message encoder must be passed to the GZipEncoder");
_innerEncoder = messageEncoder;
}
public override string ContentType
{
get { return GZipContentType; }
}
public override string MediaType
{
get { return GZipMediaType; }
}
//SOAP version to use - we delegate to the inner encoder for this
public override MessageVersion MessageVersion
{
get { return _innerEncoder.MessageVersion; }
}
public override bool IsContentTypeSupported(string contentType)
{
return contentType.StartsWith(GZipMediaType, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) || contentType.StartsWith("text/xml", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
}
//Helper method to compress an array of bytes
static ArraySegment<byte> CompressBuffer(ArraySegment<byte> buffer, BufferManager bufferManager, int messageOffset)
{
var memoryStream = new MemoryStream();
memoryStream.Write(buffer.Array, 0, messageOffset);
using (var gzStream = new GZipStream(memoryStream, CompressionMode.Compress, true))
{
gzStream.Write(buffer.Array, messageOffset, buffer.Count);
}
var compressedBytes = memoryStream.ToArray();
var bufferedBytes = bufferManager.TakeBuffer(compressedBytes.Length);
Array.Copy(compressedBytes, 0, bufferedBytes, 0, compressedBytes.Length);
bufferManager.ReturnBuffer(buffer.Array);
var byteArray = new ArraySegment<byte>(bufferedBytes, messageOffset, bufferedBytes.Length - messageOffset);
return byteArray;
}
//Helper method to decompress an array of bytes
static ArraySegment<byte> DecompressBuffer(ArraySegment<byte> buffer, BufferManager bufferManager)
{
var memoryStream = new MemoryStream(buffer.Array, buffer.Offset, buffer.Count - buffer.Offset);
var decompressedStream = new MemoryStream();
const int blockSize = 1024;
byte[] tempBuffer = bufferManager.TakeBuffer(blockSize);
using (var gzStream = new GZipStream(memoryStream, CompressionMode.Decompress))
{
while (true)
{
var bytesRead = gzStream.Read(tempBuffer, 0, blockSize);
if (bytesRead == 0)
break;
decompressedStream.Write(tempBuffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
bufferManager.ReturnBuffer(tempBuffer);
var decompressedBytes = decompressedStream.ToArray();
var bufferManagerBuffer = bufferManager.TakeBuffer(decompressedBytes.Length + buffer.Offset);
Array.Copy(buffer.Array, 0, bufferManagerBuffer, 0, buffer.Offset);
Array.Copy(decompressedBytes, 0, bufferManagerBuffer, buffer.Offset, decompressedBytes.Length);
var byteArray = new ArraySegment<byte>(bufferManagerBuffer, buffer.Offset, decompressedBytes.Length);
bufferManager.ReturnBuffer(buffer.Array);
return byteArray;
}
//One of the two main entry points into the encoder. Called by WCF to encode a Message into a buffered byte array.
public override ArraySegment<byte> WriteMessage(Message message, int maxMessageSize, BufferManager bufferManager, int messageOffset)
{
//Use the inner encoder to encode a Message into a buffered byte array
ArraySegment<byte> buffer = _innerEncoder.WriteMessage(message, maxMessageSize, bufferManager, messageOffset);
//Compress the resulting byte array
return CompressBuffer(buffer, bufferManager, messageOffset);
}
public override Message ReadMessage(Stream stream, int maxSizeOfHeaders, string contentType)
{
var gzStream = new GZipStream(stream, CompressionMode.Decompress, true);
return _innerEncoder.ReadMessage(gzStream, maxSizeOfHeaders);
}
public override Message ReadMessage(ArraySegment<byte> buffer, BufferManager bufferManager, string contentType)
{
//Decompress the buffer
ArraySegment<byte> decompressedBuffer = DecompressBuffer(buffer, bufferManager);
//Use the inner encoder to decode the decompressed buffer
Message returnMessage = _innerEncoder.ReadMessage(decompressedBuffer, bufferManager);
returnMessage.Properties.Encoder = this;
return returnMessage;
}
public override void WriteMessage(Message message, Stream stream)
{
using (var gzStream = new GZipStream(stream, CompressionMode.Compress, true))
{
_innerEncoder.WriteMessage(message, gzStream);
}
// innerEncoder.WriteMessage(message, gzStream) depends on that it can flush data by flushing
// the stream passed in, but the implementation of GZipStream.Flush will not flush underlying
// stream, so we need to flush here.
stream.Flush();
}
}
}
}
下面是GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement.cs 这里的GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement类是为了在app.config里添加配置项。
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
//This is the binding element that, when plugged into a custom binding, will enable the GZip encoder
public sealed class GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement
: MessageEncodingBindingElement //BindingElement
{
//We will use an inner binding element to store information required for the inner encoder
MessageEncodingBindingElement _innerBindingElement;
//By default, use the default text encoder as the inner encoder
public GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement()
: this(new TextMessageEncodingBindingElement()) { }
public GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement(MessageEncodingBindingElement messageEncoderBindingElement)
{
_innerBindingElement = messageEncoderBindingElement;
}
public MessageEncodingBindingElement InnerMessageEncodingBindingElement
{
get { return _innerBindingElement; }
set { _innerBindingElement = value; }
}
//Main entry point into the encoder binding element. Called by WCF to get the factory that will create the
//message encoder
public override MessageEncoderFactory CreateMessageEncoderFactory()
{
return new GZipMessageEncoderFactory(_innerBindingElement.CreateMessageEncoderFactory());
}
public override MessageVersion MessageVersion
{
get { return _innerBindingElement.MessageVersion; }
set { _innerBindingElement.MessageVersion = value; }
}
public override BindingElement Clone()
{
return new GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement(_innerBindingElement);
}
public override T GetProperty<T>(BindingContext context)
{
if (typeof(T) == typeof(XmlDictionaryReaderQuotas))
{
return _innerBindingElement.GetProperty<T>(context);
}
return base.GetProperty<T>(context);
}
public override IChannelFactory<TChannel> BuildChannelFactory<TChannel>(BindingContext context)
{
if (context == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
context.BindingParameters.Add(this);
return context.BuildInnerChannelFactory<TChannel>();
}
public override IChannelListener<TChannel> BuildChannelListener<TChannel>(BindingContext context)
{
if (context == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
context.BindingParameters.Add(this);
return context.BuildInnerChannelListener<TChannel>();
}
public override bool CanBuildChannelListener<TChannel>(BindingContext context)
{
if (context == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
context.BindingParameters.Add(this);
return context.CanBuildInnerChannelListener<TChannel>();
}
}
//This class is necessary to be able to plug in the GZip encoder binding element through
//a configuration file
public class GZipMessageEncodingElement : BindingElementExtensionElement
{
//Called by the WCF to discover the type of binding element this config section enables
public override Type BindingElementType
{
get { return typeof(GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement); }
}
//The only property we need to configure for our binding element is the type of
//inner encoder to use. Here, we support text and binary.
[ConfigurationProperty("innerMessageEncoding", DefaultValue = "textMessageEncoding")]
public string InnerMessageEncoding
{
get { return (string)base["innerMessageEncoding"]; }
set { base["innerMessageEncoding"] = value; }
}
//The only property we need to configure for our binding element is the type of
//inner encoder to use. Here, we support text and binary.
[ConfigurationProperty("messageVersion", DefaultValue = "Soap12")]
public string MessageVersion
{
get { return (string)base["messageVersion"]; }
set { base["messageVersion"] = value; }
}
//Called by the WCF to apply the configuration settings (the property above) to the binding element
public override void ApplyConfiguration(BindingElement bindingElement)
{
var binding = (GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement)bindingElement;
PropertyInformationCollection propertyInfo = ElementInformation.Properties;
var propertyInformation = propertyInfo["innerMessageEncoding"];
if (propertyInformation == null || propertyInformation.ValueOrigin == PropertyValueOrigin.Default) return;
var version = System.ServiceModel.Channels.MessageVersion.Soap12;
if ("Soap11" == MessageVersion)
{
version = System.ServiceModel.Channels.MessageVersion.Soap11;
}
switch (InnerMessageEncoding)
{
case "textMessageEncoding":
binding.InnerMessageEncodingBindingElement = new TextMessageEncodingBindingElement() { MessageVersion = version };
break;
case "binaryMessageEncoding":
binding.InnerMessageEncodingBindingElement = new BinaryMessageEncodingBindingElement();
break;
}
}
//Called by the WCF to create the binding element
protected override BindingElement CreateBindingElement()
{
var bindingElement = new GZipMessageEncodingBindingElement();
ApplyConfiguration(bindingElement);
return bindingElement;
}
}
}
然后我们就可以把这个GZipMessageEncodingElement配置到app.config里了
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<extensions>
<bindingElementExtensions>
<add name="gzipMessageEncoding" type="ConsoleApplication2.GZipMessageEncodingElement,ConsoleApplication2" />
</bindingElementExtensions>
</extensions>
<bindings>
<customBinding>
<binding name="countServiceSoapBinding">
<gzipMessageEncoding innerMessageEncoding="textMessageEncoding" messageVersion="Soap11"/>
<httpTransport manualAddressing="false"
authenticationScheme="Anonymous"
bypassProxyOnLocal="false"
hostNameComparisonMode="StrongWildcard"
proxyAuthenticationScheme="Anonymous"
realm=""
useDefaultWebProxy="true" />
</binding>
</customBinding>
</bindings>
<client>
<endpoint address="http://192.168.2.3:8080/binder/services/countService"
binding="customBinding" bindingConfiguration="countServiceSoapBinding"
contract="ServiceReference1.HolidayService" name="HolidayServiceImplPort" />
</client>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
客户端最后的部分就是调用webservice, 这里的压缩和解压对于调用者和陪调用者是透明的。也就是同没有压缩和解压之前的使用方法一样。
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
var service = new ServiceReference1.HolidayServiceClient();
var text =File.ReadAllText("c:\\words");
var len = service.countText(text);
Console.WriteLine("lenght = {0}", len);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
Console.WriteLine(e.StackTrace);
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}
服务端
服务端是一个Filter,和HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse的包装类。
入口:GzipWebServiceFilter.java
/**
* 把使用Gzip压缩的SOAP消息解压缩。
* @author matianyi
*
*/
public class GzipWebServiceFilter implements Filter {
public static final String CONTENT_TYPE = "application/x-gzip";
public static final String CONTENT_ENCODING = "utf-8";
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
if(req.getContentType() == null || !req.getContentType().startsWith(CONTENT_TYPE)){
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
chain.doFilter(new GzipHttpServletRequestWrapper(req), new GzipHttpServletResponseWrapper(resp));
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
这里就是判断contentType,如果是gzip的就用GzipHttpServletRequestWrapper和GzipHttpServletResponseWrapper包装原始的Request和Response以实现压缩和解压缩。
GzipHttpServletRequestWrapper
public class GzipHttpServletRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
public static final String CONTNET_TYPE_SOAP_1_2 = "application/soap+xml";
public static final String CONTNET_TYPE_SOAP_1_1 = "text/xml";
public GzipHttpServletRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request) {
super(request);
}
@Override
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new GzipServletInputStream(super.getInputStream());
}
@Override
public String getContentType() {
return CONTNET_TYPE_SOAP_1_2;
}
@Override
public String getHeader(String name) {
if ("content-type".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
return getContentType();
} else {
return super.getHeader(name);
}
}
}
class GzipServletInputStream extends ServletInputStream {
private GZIPInputStream delegate;
public GzipServletInputStream(ServletInputStream servletInputStream)
throws IOException {
super();
this.delegate = new GZIPInputStream(servletInputStream);
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return delegate.read();
}
}
GzipHttpServletResponseWrapper
public class GzipHttpServletResponseWrapper extends HttpServletResponseWrapper {
public GzipHttpServletResponseWrapper(HttpServletResponse response) {
super(response);
}
@Override
public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException {
return new GzipServletOutputStream(super.getOutputStream());
}
@Override
public void setCharacterEncoding(String charset) {
super.setCharacterEncoding(GzipWebServiceFilter.CONTENT_ENCODING);
}
@Override
public void setContentType(String type) {
super.setContentType(GzipWebServiceFilter.CONTENT_TYPE + "; charset=" + GzipWebServiceFilter.CONTENT_ENCODING);
}
}
class GzipServletOutputStream extends ServletOutputStream{
private GZIPOutputStream delegate;
public GzipServletOutputStream(ServletOutputStream servletOutputStream)
throws IOException {
super();
this.delegate = new GZIPOutputStream(servletOutputStream);
}
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
System.out.print((char)b);
delegate.write(b);
}
public void close() throws IOException {
delegate.close();
}
public void flush() throws IOException {
delegate.flush();
}
public void write(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
delegate.write(buf, off, len);
}
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException {
delegate.write(b);
}
}
这里做的主要事情就是在Resquest的getInputStream和Response的getOutputStream是返回一个拥有GZip功能的Stream,来代替原始的Stream。通过原始的Stream仍然是最终的输入和输出源。
然后在web.xml中把这个Filter作用于原来的WebService的Servlet
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<!-- The definition of the Root Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- Creates the Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>GzipWebServiceFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.cccis.ws.GzipWebServiceFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>GzipWebServiceFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/services/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<description>Apache CXF Endpoint</description>
<servlet-name>cxf</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>cxf</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/services/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
webservice的配置和cxf原来的一样
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-servlet.xml" />
<bean id="countServiceImpl" class="com.cccis.ws.HolidayServiceImpl" />
<jaxws:endpoint
id="countService"
implementor="#countServiceImpl"
serviceName="countService"
address="/countService" />
</beans>
如果你想看一下实际的HTTP请求和响应是什么样子的可以用Fiddler Web Debugger来查看

本文的源代码在附件中。
本文的方案没有在最终的被用于生产环境,一个原因是比较复杂,另外一个是服务器在对大XML进行unmarshal的效率并不高。单本文的方案的好处就是不用对原有的webservice接口和实现进行修改。 最后在实际场景用我们使用 MTOM来解决问题的, 后面我还会写一篇文章来介绍这个方法。